Abstract
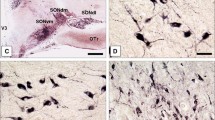
Protein expression of VGF (nonacronymic) is induced by nerve/brain-derived growth factor, neurotrophin 3, and insulin. VGF is synthesized by neurons in the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei of the hypothalamus. After enzymatic processing, smaller VGF-derived peptides are secreted into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood. These peptides play important roles by improving synaptic plasticity, neurogenesis, and energy homeostasis, which are impaired in schizophrenia. Based on previous observations of neuroendocrine and hypothalamic deficits in schizophrenia and to determine whether increased levels of the VGF fragment 23-62 in CSF, which have been described in a recent study, were related to changes in hypothalamic VGF expression, an immunohistochemical study was performed in 20 patients with schizophrenia and 19 matched control subjects. N- (D-20) and C-terminal (R-15) VGF antibodies yielded similar results and immunolabeled a vast majority of PVN and SON neurons. Additionally, D20-VGF immunohistochemistry revealed immunostained fibers in the pituitary stalk and neurohypophysis that ended at vessel walls, suggesting axonal transport and VGF secretion. The cell density of D20-VGF-immunoreactive neurons was reduced in the left PVN (P = 0.002) and SON (P = 0.008) of patients with schizophrenia. This study provides the first evidence for diminished hypothalamic VGF levels in schizophrenia, which might suggest increased protein secretion. Our finding was particularly significant in subjects without metabolic syndrome (patients with a body mass index ≤28.7 kg/m2). In conclusion, apart from beneficial effects on synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis, VGF may be linked to schizophrenia-related alterations in energy homeostasis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder J, Thakker-Varia S, Bangasser DA, Kuroiwa M, Plummer MR, Shors TJ, Black IB (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced gene expression reveals novel actions of vgf in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 23:10800–10808
APA (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th revised edition (dsm-iv-tr). American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Bartolomucci A, Pasinetti GM, Salton SR (2010) Granins as disease-biomarkers: translational potential for psychiatric and neurological disorders. Neuroscience 170:289–297
Bartolomucci A, Possenti R, Levi A, Pavone F, Moles A (2007) The role of the vgf gene and vgf-derived peptides in nutrition and metabolism. Genes Nutr 2:169–180
Bernstein HG, Keilhoff G, Steiner J, Dobrowolny H, Bogerts B (2010) The hypothalamus in schizophrenia research: No longer a wallflower existence. The Open Neuroendocrinol J 3:59–67
Bernstein HG, Stanarius A, Baumann B, Henning H, Krell D, Danos P, Falkai P, Bogerts B (1998) Nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in the human hypothalamus: reduced number of immunoreactive cells in the paraventricular nucleus of depressive patients and schizophrenics. Neuroscience 83:867–875
Brisch R, Bernstein HG, Dobrowolny H, Krell D, Stauch R, Trubner K, Steiner J, Ghabriel MN, Bielau H, Wolf R, Winter J, Kropf S, Gos T, Bogerts B (2011) A morphometric analysis of the septal nuclei in schizophrenia and affective disorders: reduced neuronal density in the lateral septal nucleus in bipolar disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 261:47–58
Cocco C, D’Amato F, Noli B, Ledda A, Brancia C, Bongioanni P, Ferri GL (2010) Distribution of vgf peptides in the human cortex and their selective changes in parkinson’s and alzheimer’s diseases. J Anat 217:683–693
Faludi G, Mirnics K (2011) Synaptic changes in the brain of subjects with schizophrenia. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:305–309
Ferri GL, Noli B, Brancia C, D’Amato F, Cocco C (2011) Vgf: An inducible gene product, precursor of a diverse array of neuro-endocrine peptides and tissue-specific disease biomarkers. J Chem Neuroanat
Futamura T, Toyooka K, Iritani S, Niizato K, Nakamura R, Tsuchiya K, Someya T, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Nawa H (2002) Abnormal expression of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in the forebrain and serum of schizophrenic patients. Mol Psychiatry 7:673–682
Green MJ, Matheson SL, Shepherd A, Weickert CS, Carr VJ (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in schizophrenia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 16:960–972
Guest PC, Schwarz E, Krishnamurthy D, Harris LW, Leweke FM, Rothermundt M, van Beveren NJ, Spain M, Barnes A, Steiner J, Rahmoune H, Bahn S (2011) Altered levels of circulating insulin and other neuroendocrine hormones associated with the onset of schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:1092–1096
Guest PC, Wang L, Harris LW, Burling K, Levin Y, Ernst A, Wayland MT, Umrania Y, Herberth M, Koethe D, van Beveren NJ, Rothermundt M, McAllister G, Leweke FM, Steiner J, Bahn S (2010) Increased levels of circulating insulin-related peptides in first onset, antipsychotic naive schizophrenia patients. Mol Psychiatry 15:118–119
Hahm S, Fekete C, Mizuno TM, Windsor J, Yan H, Boozer CN, Lee C, Elmquist JK, Lechan RM, Mobbs CV, Salton SR (2002) Vgf is required for obesity induced by diet, gold thioglucose treatment, and agouti and is differentially regulated in pro-opiomelanocortin- and neuropeptide y-containing arcuate neurons in response to fasting. J Neurosci 22:6929–6938
Hsu SM, Soban E (1982) Color modification of diaminobenzidine (dab) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 30:1079–1082
Huang JT, Leweke FM, Oxley D, Wang L, Harris N, Koethe D, Gerth CW, Nolden BM, Gross S, Schreiber D, Reed B, Bahn S (2006) Disease biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with first-onset psychosis. PLoS Med 3:e428
Jethwa PH, Ebling FJ (2008) Role of vgf-derived peptides in the control of food intake, body weight and reproduction. Neuroendocrinology 88:80–87
Keilhoff G, Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Roskoden T, Becker A (2010) Risperidone and haloperidol promote survival of stem cells in the rat hippocampus. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260:151–162
Levi A, Eldridge JD, Paterson BM (1985) Molecular cloning of a gene sequence regulated by nerve growth factor. Science 229:393–395
Levi A, Ferri GL, Watson E, Possenti R, Salton SR (2004) Processing, distribution, and function of vgf, a neuronal and endocrine peptide precursor. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24:517–533
Mai JK, Assheuer J, Paxinos G (2003) Atlas of the human brain. Academic Press, San Diego
Newcomer JW (2007) Antipsychotic medications: metabolic and cardiovascular risk. J Clin Psychiatry 68(4):8–13
Reif A, Fritzen S, Finger M, Strobel A, Lauer M, Schmitt A, Lesch KP (2006) Neural stem cell proliferation is decreased in schizophrenia, but not in depression. Mol Psychiatry 11:514–522
Ruetschi U, Zetterberg H, Podust VN, Gottfries J, Li S, Hviid Simonsen A, McGuire J, Karlsson M, Rymo L, Davies H, Minthon L, Blennow K (2005) Identification of csf biomarkers for frontotemporal dementia using seldi-tof. Exp Neurol 196:273–281
Ryan MC, Sharifi N, Condren R, Thakore JH (2004) Evidence of basal pituitary-adrenal overactivity in first episode, drug naive patients with schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:1065–1070
Sivukhina EV, Jirikowski GF, Bernstein HG, Lewis JG, Herbert Z (2006) Expression of corticosteroid-binding protein in the human hypothalamus, co-localization with oxytocin and vasopressin. Horm Metab Res 38:253–259
Snyder SE, Salton SR (1998) Expression of vgf mrna in the adult rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 394:91–105
Steiner J, Bernstein HG, Bielau H, Farkas N, Winter J, Dobrowolny H, Brisch R, Gos T, Mawrin C, Myint AM, Bogerts B (2008) S100b-immunopositive glia is elevated in paranoid as compared to residual schizophrenia: a morphometric study. J Psychiatr Res 42:868–876
Steiner J, Mawrin C, Ziegeler A, Bielau H, Ullrich O, Bernstein HG, Bogerts B (2006) Distribution of hla-dr-positive microglia in schizophrenia reflects impaired cerebral lateralization. Acta Neuropathol 112:305–316
Terwisscha van Scheltinga AF, Bakker SC, Kahn RS (2010) Fibroblast growth factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 36:1157–1166
Thakker-Varia S, Alder J (2009) Neuropeptides in depression: role of vgf. Behav Brain Res 197:262–278
Thakore JH (2004) Metabolic disturbance in first-episode schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 47:S76–S79
Tirupati S, Chua LE (2007) Body mass index as a screening test for metabolic syndrome in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders. Australas Psychiatry 15:470–473
Trani E, Ciotti T, Rinaldi AM, Canu N, Ferri GL, Levi A, Possenti R (1995) Tissue-specific processing of the neuroendocrine protein vgf. J Neurochem 65:2441–2449
van den Pol AN, Decavel C, Levi A, Paterson B (1989) Hypothalamic expression of a novel gene product, vgf: Immunocytochemical analysis. J Neurosci 9:4122–4137
Vargas HE, Gama CS, Andreazza AC, Medeiros D, Stertz L, Fries G, Palha J, Cereser KM, Berk M, Kapczinski F, Belmonte-de-Abreu PS (2008) Decreased serum neurotrophin 3 in chronically medicated schizophrenic males. Neurosci Lett 440:197–201
Watson E, Fargali S, Okamoto H, Sadahiro M, Gordon RE, Chakraborty T, Sleeman MW, Salton SR (2009) Analysis of knockout mice suggests a role for vgf in the control of fat storage and energy expenditure. BMC Physiol 9:19
Yazici MK, Anil Yagcioglu AE, Ertugrul A, Eni N, Karahan S, Karaagaoglu E, Tokgozoglu SL (2011) The prevalence and clinical correlates of metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia: findings from a cohort in turkey. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 261:69–78
Zhao Z, Lange DJ, Ho L, Bonini S, Shao B, Salton SR, Thomas S, Pasinetti GM (2008) Vgf is a novel biomarker associated with muscle weakness in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (als), with a potential role in disease pathogenesis. Int J Med Sci 5:92–99
Zubin J, Spring B (1977) Vulnerability–a new view of schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 86:103–126
Acknowledgments
Pembroke College (University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK) has invited JS for a Visiting Scholarship. This work was supported in part by the Stanley Medical Research Foundation to BB and JS (Grant No. 07R-1832). We are grateful to Henrik Dobrowolny for his skillful assistance in statistical analysis. Bianca Jerzykiewicz, Kathrin Paelchen, and Renate Stauch provided excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stefan Busse and Hans-Gert Bernstein contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busse, S., Bernstein, HG., Busse, M. et al. Reduced density of hypothalamic VGF-immunoreactive neurons in schizophrenia: a potential link to impaired growth factor signaling and energy homeostasis. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262, 365–374 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0282-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0282-7