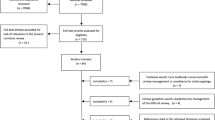
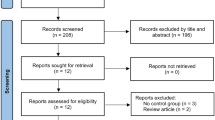
Abstract
Purpose
To provide a comprehensive review of the current strategies in the management of laryngeal hemangiomas, with an aim to introduce a management algorithm that aligns with the variable clinical presentations and anatomical complexities of these lesions.
Methods
We conducted an extensive literature search across major databases using specific and general terms, combined with Boolean operators, to ensure comprehensiveness. Articles from January 2004 to August 2023 were included, with findings categorized by management approach.
Results
Laryngeal hemangiomas exhibit a spectrum of manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic lesions to those causing severe airway obstruction. Optimal management demands an individualized approach tailored to the patient's unique presentation and anatomical considerations. Diverse treatment modalities, each with distinct indications, advantages, and limitations, are explored. Notable highlights encompass the prominent role of Beta-blockers, notably Propranolol, in addressing problematic infantile hemangiomas, the nuanced efficacy of laser therapies contingent upon hemangioma type and depth, and the critical relevance of tracheotomy in emergencies. Novel approaches like transoral robotic surgery and transoral ultrasonic surgery, demonstrate promise in specific scenarios. We propose a management algorithm based on the complexity and presentation of laryngeal hemangiomas, emphasizing individualized treatment strategies, thereby addressing the unique challenges and nuances of each case.
Conclusion
Laryngeal hemangioma management requires personalized approaches informed by diverse therapies, clinical expertise, and collaboration. The review introduces an algorithm spanning observation to advanced interventions, adapting to each case’s complexity. Ongoing research promises innovative treatments.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable, since this is a reveiw article containing no original data.
References
Kilcline C, Frieden IJ (2008) Infantile hemangiomas: how common are they? A systematic review of the medical literature. Pediatr Dermatol 25:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00626.x
Dickison P, Christou E, Wargon O (2011) A prospective study of infantile hemangiomas with a focus on incidence and risk factors. Pediatr Dermatol 28:663–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01568.x
de Lucas Laguna R, AEPap (2013) Angiomas y malformaciones vasculares,¿ qué debo saber. AEPap, editor Curso de actualización pediatría 49–56
Mulliken JB, Glowacki J (1982) Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: a classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg 69:412–420
Priya K (2023) A Cross-Sectional Study on Histopathology of Laryngeal Lesions in a Tertiary Care Center. Online Journal of Health and Allied Sciences 22:
Cox J, Bartlett E, Lee E (2014) Vascular malformations: a review. Semin Plast Surg 28:058–063. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1376263
Schwalb G, Cocca A, Attie M et al (2013) Malformaciones vasculares en pediatría. Hematología 17:55–59
Kunimoto K, Yamamoto Y, Jinnin M (2022) ISSVA classification of vascular anomalies and molecular biology. Int J Mol Sci 23:2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042358
Blei F (2017) ISSVA classification of vascular anomalies. In: Kim Y-W, Lee B-B, Yakes WF, Do Y-S (eds) Congenital vascular malformations: a comprehensive review of current management. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Heidelberg, pp 47–50
Dehart A, Richter G (2019) Hemangioma: recent advances. F1000Res 8:1926. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20152.1
Dinehart SM, Kincannon J, Geronemus R (2001) Hemangiomas: evaluation and treatment. Dermatol Surg 27:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00227.x
Enjolras O, Riche MC, Merland JJ, Escande JP (1990) Management of alarming hemangiomas in infancy: a review of 25 cases. Pediatrics 85:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.85.4.491
Huang C-M, Lee K-W, Huang C-J (2013) Radiation therapy for life-threatening huge laryngeal hemangioma involving pharynx and parapharyngeal space. Head Neck 35:E98–E101. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21919
Phillips J (1913) Angioma of the larynx, especially its relation to chronic laryngitis. Am J Dis Child. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.1913.04100260036002
Yoshpe N, Brodsky L, Ruben RJ (1983) Clinical-pathological correlates of congenital subglottic hemangiomas. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 92:4–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/00034894830920S401
Rahbar R, Nicollas R, Roger G et al (2004) The biology and management of subglottic hemangioma: past, present, future. Laryngoscope 114:1880–1891. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000147915.58862.27
Rutter MJ (2014) Congenital laryngeal anomalies. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 80:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2014.08.001
Orlow SJ, Isakoff MS, Blei F (1997) Increased risk of symptomatic hemangiomas of the airway in association with cutaneous hemangiomas in a “beard” distribution. J Pediatr 131:643–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3476(97)70079-9
Mesolella M, Allosso S, Mansueto G et al (2022) Strategies and controversies in the treatment with carbon dioxide laser of laryngeal hemangioma: a case series and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 101:326–331. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320952191
Sari F, Topdag M, Ozturk M et al (2014) Vocal cord hemangioma. J Craniofacial Surg 25:1565. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000753
Shim H, Kim MR (2021) Potassium-titanyl-phosphate (KTP) laser photocoagulation combined with resection using an ultrasonic scalpel for pharyngolaryngeal hemangioma via a transoral approach: case report and literature review. Am J Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.12659/AJCR.931042
Wu X, Mao W, He P, Wei C (2018) Curative effect of chemotherapy, KTP lasers, and CO 2 lasers combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of adult laryngeal hemangioma. Acta Otolaryngol 138:567–573. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2017.1419577
Wang C, Sun J, Guo L et al (2022) Low-dose sclerotherapy with lauromacrogol in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas: a retrospective analysis of 368 cases. Front Oncol 12:1014465. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1014465
Rotter A, de Oliveira ZNP (2017) Infantile hemangioma: pathogenesis and mechanisms of action of propranolol. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 15:1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.13365
Léauté-Labrèze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T et al (2008) Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 358:2649–2651
Painter SL, Hildebrand GD (2016) Review of topical beta blockers as treatment for infantile hemangiomas. Surv Ophthalmol 61:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2015.08.006
Zhang L, Mai H-M, Zheng J et al (2014) Propranolol inhibits angiogenesis via down-regulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in hemangioma derived stem cell. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:48–55
Ji Y, Li K, Xiao X et al (2012) Effects of propranolol on the proliferation and apoptosis of hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. J Pediatr Surg 47:2216–2223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.09.008
Tan ST, Wallis RA, He Y, Davis PF (2004) Mast cells and hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000105683.10752.A6
Ye Y, Zhong H, Dou L et al (2022) Propranolol inhibits the angiogenic capacity of hemangioma endothelia via blocking β-adrenoceptor in mast cell. Pediatr Res 92:424–429. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01683-4
Peridis S, Pilgrim G, Athanasopoulos I, Parpounas K (2011) A meta-analysis on the effectiveness of propranolol for the treatment of infantile airway haemangiomas. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.01.028
Vlastarakos PV, Papacharalampous GX, Chrysostomou M et al (2012) Propranolol is an effective treatment for airway haemangiomas: a critical analysis and meta-analysis of published interventional studies. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 32:213–221
D’Ambrosio PD, Cardoso PFG, da Silva PL et al (2022) Management of infantile subglottic hemangioma with T-tube placement and propranolol. J Bras Pneumol 48:e20210297
Hardison SA, Dodson KM, Rhodes JL (2014) Subglottic hemangioma treated with propranolol. Eplasty 14:ic2
Espahbodi M, Yan K, Chun RH, McCormick ME (2018) Management trends of infantile hemangioma: a national perspective. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 104:84–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.10.044
Wu L, Wu X, Xu X, Chen Z (2015) Propranolol treatment of subglottic hemangiomas: a review of the literature. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:19886–19890
Hoeger PH, Harper JI, Baselga E et al (2015) Treatment of infantile haemangiomas: recommendations of a European expert group. Eur J Pediatr 174:855–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-015-2570-0
Bitar MA, Moukarbel RV, Zalzal GH (2005) Management of congenital subglottic hemangioma: trends and success over the past 17 years. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2004.09.136
Javia LR, Zur KB, Jacobs IN (2011) Evolving treatments in the management of laryngotracheal hemangiomas: will propranolol supplant steroids and surgery? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:1450–1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.08.002
Alsaqoub SM, Almutairi SG, Bawazir SM et al (2019) Subglottic hemangioma can be missed: two case reports. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep 51:101308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsc.2019.101308
Moore J, Lee M, Garzon M et al (2001) Effective therapy of a vascular tumor of infancy with vincristine. J Pediatr Surg 36:1273–1276. https://doi.org/10.1053/jpsu.2001.25793
Durr ML, Meyer AK, Huoh KC et al (2012) Airway hemangiomas in PHACE syndrome. Laryngoscope 122:2323–2329. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23475
Denoyelle F, Garabédian E (2010) Propranolol may become first-line treatment in obstructive subglottic infantile hemangiomas. Otolaryngol-Head and Neck Surg 142:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.10.044
Ohlms LA, McGill TJI, Jones DT, Healy GB (1994) Interferon alfa-2A therapy for airway hemangiomas. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 103:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949410300101
Szymik-Kantorowicz S, Kobylarz K, Krysta M et al (2005) Interferon-α in the treatment of high-risk haemangiomas in infants. Eur J Pediatr Surg 15:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-830550
Zheng JW, Zhang L, Yuan W (2015) Treatment of alarming head and neck infantile hemangiomas with interferon-α2a: a clinical study in eleven consecutive patients. Drug Des Devel Ther. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S67682
Azadgoli B, Baker RY (2016) Laser applications in surgery. Ann Transl Med 4:452. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2016.11.51
Centric A, Hu A, Heman-Ackah YD et al (2014) Office-based pulsed-dye laser surgery for laryngeal lesions: a retrospective review. J Voice 28:262.e9-262.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.08.010
Reilly MJ, Cohen M, Hokugo A, Keller GS (2010) Molecular effects of fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing on photodamaged human skin. Arch Facial Plast Surg 12:321–325. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfacial.2010.38
Lucioni M, Marioni G, Della Libera D, Rizzotto G (2006) Adult laryngeal hemangioma CO2 laser excision. A single institution 3-year experience (Vittorio Veneto 2001–2003). Acta Otolaryngol 126:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480500452517
Clarós A, Fokouo JVF, Roqueta C, Clarós P (2015) Management of subglottic hemangiomas with carbon dioxide laser: our 25-year experience and comparison with the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79:2003–2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.05.007
Wang Y, Deng R, Qu J et al (2013) The application of the CO2 laser combined with pingyangmycin in the management of pharyngeal and laryngeal hemangioma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 27:489–491
Alshaya H, Alhejji A, Aldkhyyal A, Mesallam TA (2021) Management of adult laryngeal hemangioma with CO2 laser. Saudi Med J 42:1252–1253. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2021.42.11.20210319
Cholewa D, Waldschmidt J (1998) Laser treatment of hemangiomas of the larynx and trachea. Lasers Surg Med 23:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9101(1998)23:4%3c221::aid-lsm5%3e3.0.co;2-a
Fu C-H, Lee L-A, Fang T-J et al (2007) Endoscopic Nd:YAG laser therapy of infantile subglottic hemangioma. Pediatr Pulmonol 42:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.20530
Vlachakis I, Gardikis S, Michailoudi E, Charissis G (2003) Treatment of hemangiomas in children using a Nd:YAG laser in conjunction with ice cooling of the epidermis: techniques and results. BMC Pediatr 3:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-3-2
Saetti R, Silvestrini M, Cutrone C, Narne S (2008) Treatment of congenital subglottic hemangiomas: our experience compared with reports in the literature. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:848–851. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.134.8.848
Stier MF, Glick SA, Hirsch RJ (2008) Laser treatment of pediatric vascular lesions: port wine stains and hemangiomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 58:261–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.10.492
Yan Y, Olszewski AE, Hoffman MR et al (2010) Use of lasers in laryngeal surgery. J Voice 24:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2008.09.006
Pransky SM, Canto C (2004) Management of subglottic hemangioma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:509–512. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.moo.0000143980.41120.38
Wu X, Ma J, Zhang J, Wei C (2022) A comparison of potassium titanyl phosphate laser and pingyangmycin as treatment for adult laryngeal hemangioma. Ear Nose Throat J. https://doi.org/10.1177/01455613221086534
Madgy D, Ahsan SF, Kest D, Stein I (2001) The application of the potassium-titanyl-phosphate (KTP) laser in the management of subglottic hemangioma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.127.1.47
Kacker A, April M, Ward RF (2001) Use of potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser in management of subglottic hemangiomas. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 59:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5876(01)00451-7
Kawakami M, Hayashi I, Yoshimura K et al (2006) Adult giant hemangioma of the larynx: a case report. Auris Nasus Larynx 33:479–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2006.05.010
Winter H, Dräger E, Sterry W (2000) Sclerotherapy for treatment of hemangiomas. Dermatol Surg 26:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2000.98012.x
Lin P-F, Chen F-C, Chen J-Y, Jiang C-H (2020) Aesthetic outcome of intralesional injection of lauromacrogol as a single-agent treatment for uncomplicated infantile hemangiomas: a long-term follow-up study. J Dermatol 47:1119–1125. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.15473
Qu H, Lei X, Hu L et al (2021) Successful endoscopic sclerotherapy using lauromacrogol injection for laryngopharyngeal hemangioma. Ear Nose Throat J 100:662–666. https://doi.org/10.1177/01455613211043690
Kulkarni S, Dwivedi G, Singh A, Tiwari V (2023) Hemangioma—a rare cause of laryngeal growth in an adult and its management with sclerotherapy and laser surgery: a case report. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75:2485–2487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03765-7
Dutton SC, Plowman PN (1991) Paediatric haemangiomas: the role of radiotherapy. Br J Radiol 64:261–269
Wang W-H, Tsai K-Y (2015) Transoral robotic resection of an adult laryngeal haemangioma and review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol 129:614–618. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215115001036
Canadas KT, Baum ED, Lee S, Ostrower ST (2010) Case report: treatment failure using propanolol for treatment of focal subglottic hemangioma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:956–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.05.012
Mahadevan M, Barber C, Salkeld L et al (2007) Pediatric tracheotomy: 17 year review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:1829–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.08.007
de Almeida JR, Byrd JK, Wu R et al (2014) A systematic review of transoral robotic surgery and radiotherapy for early oropharynx cancer: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 124:2096–2102. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24712
Chia SH, Gross ND, Richmon JD (2013) Surgeon experience and complications with transoral robotic surgery (TORS). Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 149:885–892. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599813503446
Zohdi I, ElSharkawy L, ElBestar M (2021) Neoplasms of the larynx and laryngopharynx. Textbook of clinical otolaryngology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 449–463
Hung S-Y, Huang M-L, Huang H-H et al (2023) Transoral robotic surgery and transarterial embolization to treat adult laryngeal hemangioma. Ear Nose Throat J. https://doi.org/10.1177/01455613231198439
Valls-Mateus M, Román LS, Macho J et al (2017) Transoral ultrasonic surgery of pharyngolaryngeal giant hemangioma after ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx) embolization. Head Neck 39:1239–1242. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24745
Konior RJ, Holinger LD, Russell EJ (1988) Superselective embolization of laryngeal hemangioma. Laryngoscope. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198808000-00008
Zambudio AR, Calvo MJR, Lanzas JT et al (2003) Massive hemoptysis caused by tracheal hemangioma treated with interventional radiology. Ann Thorac Surg 75:1302–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04656-8
Tao X, Wu L, Li S et al (2023) Successful management of tracheal lobular capillary hemangioma with arterial embolization followed by electrosurgical snaring via flexible bronchoscopy in an 11-year-old boy: a case report and literature review. Front Med (Lausanne). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1088815
Prgomet D, Janjanin S, Bilić M et al (2009) A prospective observational study of 363 cases operated with three different harmonic scalpels. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:1965–1970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-0954-3
Wang X, Zhao X, Zhu W (2015) Resection of a laryngeal hemangioma in an adult using an ultrasonic scalpel: a case report. Oncol Lett 9:2477–2480. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3069
O’Neill JV, Snyder GG, Toomey JM (1976) Cryosurgery of supraglottic cavernous hemangioma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 102:55–57. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1976.00780060101016
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks Dr. Mohamed Amine Haireche for his valuable assistance in the editing of this review.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This scoping review has been conducted with a commitment to the highest ethical standards. We have adhered to guidelines for literature selection, data extraction, and synthesis to ensure the integrity and reliability of this review. Additionally, we respect the intellectual property rights of all authors and have appropriately cited and credited their work. No research involving human subjects or animals was conducted as part of this review. The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive overview of existing literature in a transparent and unbiased manner, with the goal of advancing knowledge in the field.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almothahbi, A., Bukhari, M., Almohizea, M. et al. Recent updates in laryngeal hemangioma management: a scoping review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 2211–2222 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08378-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08378-y