Abstract
Purpose
Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) is now frequently used to treat chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), but postoperative recurrence plagues many patients. We aimed to assess the value of the systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and the systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) for the prediction of postoperative recurrence in patients with CRSwNP.
Methods
A total of 143 patients with CRSwNP and 76 age- and sex-matched healthy subjects were enrolled. Patients were divided into the recurrence group and the non-recurrence group according to the recurrence of CRSwNP. Univariate and multivariate analyses showed independent risk factors for the recurrence. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was conducted to assess the predictive accuracy of the variables and determine the optimal cut-off values. Finally, a survival analysis was conducted.
Results
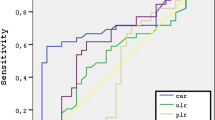
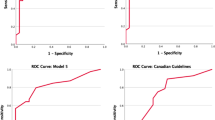
Univariate analysis revealed that age, sex, CRP, EOS, SIRI, SII, NLR, ELR, and Lund–Mackay CT scores were significant predictors of the recurrence of CRSwNP. Multivariate analysis confirmed that SIRI (OR = 1.310, p < 0.001) and Lund–Mackay CT scores (OR = 1.396, p < 0.001) were independent predictors. SIRI (AUC = 0.761, 95% CI: 0.685–0.836) had a certain value in predicting the recurrence of CRSwNP.
Conclusion
SIRI is a potential predictive marker of the postoperative recurrence of CRSwNP.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Shi JB, Fu QL, Zhang H et al (2015) Epidemiology of chronic rhinosinusitis: results from a cross-sectional survey in seven Chinese cities. Allergy 70:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12577
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C et al (2020) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 58:1–464. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin20.600
Mullol J, Azar A, Buchheit KM et al (2022) Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: quality of life in the biologics era. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 10:1434-1453.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2022.03.002
Kalińczak-Górna P, Radajewski K, Burduk P (2021) Relationship between the severity of inflammatory changes in chronic sinusitis and the level of vitamin d before and after the FESS procedure. J Clin Med 10:2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132836
Nair S, Dutta A, Rajagopalan R, Nambiar S (2011) Endoscopic sinus surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis: a comparative study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0119-8
Gollapudy S, Gashkoff DA, Poetker DM et al (2020) Surgical field visualization during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: comparison of propofol- versus desflurane-based anesthesia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 163:835–842. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820921863
DeConde AS, Mace JC, Levy JM et al (2017) Prevalence of polyp recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Laryngoscope 127:550–555. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26391
Arancibia C, Langdon C, Mullol J, Alobid I (2022) Twelve-year long-term postoperative outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinol J 60:261–269. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin21.148
Chong L, Piromchai P, Sharp S et al (2019) Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019:CD013513. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013513
Cho J-S, Kang J-H, Um J-Y et al (2014) Lipopolysaccharide induces pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMP production via TLR4 in nasal polyp-derived fibroblast and organ culture. PLoS ONE 9:e90683. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090683
Wang S, Zhang H, Xi Z et al (2017) Establishment of a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophilic nasal polyps. Exp Ther Med 14:5275–5282. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5208
Ware J, Corken A, Khetpal R (2013) Platelet function beyond hemostasis and thrombosis. Curr Opin Hematol. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0b013e32836344d3
Boztepe OF, Gün T, Demir M et al (2016) A novel predictive marker for the recurrence of nasal polyposis following endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:1439–1444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3753-z
Bayer K, Hamidovic S, Brkic FF et al (2023) Peripheral eosinophil count and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with revision sinus surgery. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Off J Eur Fed Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Soc EUFOS Affil Ger Soc Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Head Neck Surg 280:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07497-2
Qi Q, Zhuang L, Shen Y et al (2016) A novel systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) for predicting the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer after chemotherapy. Cancer 122:2158–2167. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30057
Hu B, Yang X-R, Xu Y et al (2014) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 20:6212–6222. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442
Jin Z, Wu Q, Chen S et al (2021) The associations of two novel inflammation indexes, SII and SIRI with the risks for cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality: a ten-year follow-up study in 85,154 individuals. J Inflamm Res 14:131–140. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S283835
Oka A, Ninomiya T, Fujiwara T et al (2020) Serum IgG4 as a biomarker reflecting pathophysiology and post-operative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int Off J Jpn Soc Allergol 69:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2019.12.004
Bachert C, Akdis CA (2016) Phenotypes and emerging endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 4:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2016.05.004
Lourijsen ES, Reitsma S, Vleming M et al (2022) Endoscopic sinus surgery with medical therapy versus medical therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 10:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00457-4
Moreno-Luna R, Martin-Jimenez DI, Callejon-Leblic MA et al (2022) Usefulness of bilateral mucoplasty plus reboot surgery in severe type-2 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinology 60:368–376. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin22.131
Ikeda K, Ito S, Hibiya R et al (2019) Postoperative management of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: impact of high-dose corticosteroid nasal spray. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 23:101–103. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1668515
Passali D, Bellussi LM, Damiani V et al (2020) Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis: the role of personalized and integrated medicine. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm 91:11–18. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i1-S.9243
Pawankar R (2003) Nasal polyposis: an update: editorial review. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 3:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00130832-200302000-00001
Bauer AM, Turner JH (2020) Personalized medicine in chronic rhinosinusitis: phenotypes, endotypes, and biomarkers. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 40:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2019.12.007
Kato A, Schleimer RP, Bleier BS (2022) Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 149:1491–1503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2022.02.016
Cao Y, Chen F, Sun Y et al (2019) LL-37 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin Exp Allergy J Br Soc Allergy Clin Immunol 49:990–999. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.13408
Poposki JA, Klingler AI, Stevens WW et al (2022) Elevation of activated neutrophils in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol 149:1666–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2021.11.023
Zhu ZZ, Wang WQ, Chen YJ, Lyu W (2021) Changes of histopathological and hematological characteristics in recurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 56:249–255. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200628-00532
Han R, Gu S, Zhang Y et al (2018) Estrogen promotes progression of hormone-dependent breast cancer through CCL2-CCR2 axis by upregulation of Twist via PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling. Sci Rep 8:9575. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27810-6
Liu M, Zhu H, Li J et al (2012) Group A Streptococcus secreted esterase hydrolyzes platelet-activating factor to impede neutrophil recruitment and facilitate innate immune evasion. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002624. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002624
Wang W, Xu Y, Wang L et al (2022) Single-cell profiling identifies mechanisms of inflammatory heterogeneity in chronic rhinosinusitis. Nat Immunol 23:1484–1494. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-022-01312-0
Takabayashi T, Kato A, Peters AT et al (2013) Increased expression of factor XIII-A in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol 132:584-592.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.02.003
Eisinger F, Patzelt J, Langer HF (2018) The platelet response to tissue injury. Front Med 5:317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00317
Sari O, Bashir AM (2022) Early change in platelet count and MPV levels of patients who received hemodialysis for the first time: Mogadishu somalia experience. Int J Clin Pract 2022:1503227. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1503227
Aktas G, Sit M, Tekce H et al (2013) Mean platelet volume in nasal polyps. West Indian Med J 62:515–518. https://doi.org/10.7727/wimj.2013.011
Kim S-J, Jenne CN (2016) Role of platelets in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) production and tissue injury. Semin Immunol 28:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2016.10.013
Klinger MHF, Jelkmann W (2002) Role of blood platelets in infection and inflammation. J Interferon Cytokine Res Off J Int Soc Interferon Cytokine Res 22:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1089/10799900260286623
Brescia G, Sfriso P, Marioni G (2019) Role of blood inflammatory cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 139:48–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2018.1538567
Brescia G, Pedruzzi B, Barion U et al (2016) Are neutrophil-, eosinophil-, and basophil-to-lymphocyte ratios useful markers for pinpointing patients at higher risk of recurrent sinonasal polyps? Am J Otolaryngol 37:339–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.02.002
Yu L, Jiang Y, Yan B et al (2022) Predictive value of clinical characteristics in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a cross-sectional study in the Chinese population. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 12:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22901
Dirajlal-Fargo S, Kulkarni M, Bowman E et al (2018) Serum albumin is associated with higher inflammation and carotid atherosclerosis in treated human immunodeficiency virus infection. Open Forum Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofy291
van Zanten AR, Dixon JM, Nipshagen MD et al (2005) Hospital-acquired sinusitis is a common cause of fever of unknown origin in orotracheally intubated critically ill patients. Crit Care 9:R583–R590. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3805
Helman SN, Barrow E, Edwards T et al (2020) The role of allergic rhinitis in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 40:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2019.12.010
Stevens WW, Schleimer RP (2016) AERD as an endotype of chronic rhinosinusitis. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 36:669–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2016.06.004
Acknowledgements
YQY and JZ are co-first authors. The authors thank Zongchi Liu, Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, for his participation in the study design and writing assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by the Jiangsu Science and Technology Plan Project (BE2019670) and Suzhou people's livelihood science and technology project (SYS2020115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YQY planned the study. YQY, JZ, and WXM collected and analyzed data. YQY wrote the article. MYZ, JZ, YHW, FWC, and MYL revised the manuscript and polished the language. All authors read and approved the final submitted paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Approval was obtained from the scientific committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (Protocol number: 2023/087). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhu, J., Zhang, M. et al. Systemic inflammation response index predicts the postoperative recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a retrospective study in the Chinese population. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 207–217 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08182-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08182-8