Abstract
Purpose
The assessment of necrotizing external otitis requires a high index of suspicion by the attending physician. The purpose of the study is to determine the accuracy of parameters available at the Emergency Department for the diagnosis of this pathology.
Methods
Retrospective diagnostic accuracy study. Patients consulting at the Emergency Department for longstanding ear swelling, severe otalgia, and failure to respond to topical treatment were included. Otoscopy, physical examination, CT appearance, and analytical results were tested for the diagnosis of necrotizing external otitis, using nuclear imaging as gold standard. Sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios and ROC curves were calculated.
Results
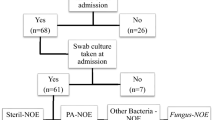
24 patients were included; 13 cases were necrotizing external otitis, and 11 cases were other external ear pathologies. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein levels were significantly associated with necrotizing external otitis (AUC 0.92 p < 0.001, and 0.8 p < 0.001). Positive likelihood ratios were 10.15 for values of erythrocyte sedimentation rate over 26 mm/h, and 8.25 for C-reactive protein levels over 10 mg/L. Negative likelihood ratios were 0.08 and 0.28, respectively. These results were significant. The rest of clinical and radiological parameters were less accurate.
Conclusions
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein are useful parameters in the evaluation of a case of longstanding otitis with clinical suspicion of necrotizing external otitis. If any of them is elevated, the probability of suffering this condition is significantly increased. If they are within normal ranges, an alternative diagnosis should be sought.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen D, Friedman P (1987) The diagnostic criteria of malignant external otitis. J Laryngol Otol 101(3):216–221
Rubin Grandis J, Branstetter BF 4th, Yu VL (2004) The changing face of malignant (necrotising) external otitis: clinical, radiological, and anatomic correlations. Lancet Infect Dis 4(1):34–39
Joshua BZ, Sulkes J, Raveh E, Bishara J, Nageris BI (2008) Predicting outcome of malignant external otitis. Otol Neurotol 29(3):339–343
Stern Shavit S, Soudry E, Hamzany Y, Nageris B (2016) Malignant external otitis: factors predicting patient outcomes. Am J Otolaryngol 37(5):425–430
Jacobsen LM, Antonelli PJ (2010) Errors in the diagnosis and management of necrotizing otitis externa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143(4):506–509
Mahdyoun P, Pulcini C, Gahide I et al (2013) Necrotizing otitis externa: a systematic review. Otol Neurotol 34(4):620–629
Sudhoff H, Rajagopal S, Mani N, Moumoulidis I, Axon PR, Moffat D (2008) Usefulness of CT scans in malignant external otitis: effective tool for the diagnosis, but of limited value in predicting outcome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265(1):53–56
Dabiri S, Karrabi N, Yazdani N et al (2020) Facial nerve paralysis in malignant otitis externa: comparison of the clinical and paraclinical findings. Acta Otolaryngol 140(12):1056–1060
van Kroonenburgh AMJL, van der Meer WL, Bothof RJP, van Tilburg M, van Tongeren J, Postma AA (2018) Advanced imaging techniques in skull base osteomyelitis due to malignant otitis externa. Curr Radiol Rep 6(1):3
Friedmann I (1990) Pathological lesions of the external auditory meatus: a review. J R Soc Med 83(1):34–37
Hn U, Prasad SC, Russo A, Grinblat G, Sanna M (2018) Cholesteatoma of the external auditory canal: review of staging and surgical strategy. Otol Neurotol 39(10):e1026–e1033
Mehrotra P, Elbadawey MR, Zammit-Maempel I (2011) Spectrum of radiological appearances of necrotising external otitis: a pictorial review. J Laryngol Otol 125(11):1109–1115
Chen YA, Chan KC, Chen CK, Wu CM (2011) Differential diagnosis and treatments of necrotizing otitis externa: a report of 19 cases. Auris Nasus Larynx 38(6):666–670
Chakraborty D, Bhattacharya A, Kamaleshwaran KK, Agrawal K, Gupta AK, Mittal BR (2012) Single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography of the skull in malignant otitis externa. Am J Otolaryngol 33(1):128–129
Stern Shavit S, Bernstine H, Sopov V, Nageris B, Hilly O (2019) FDG-PET/CT for diagnosis and follow-up of necrotizing (malignant) external otitis. Laryngoscope 129(4):961–966
Sturm JJ, Stern Shavit S, Lalwani AK (2020) What is the best test for diagnosis and monitoring treatment response in malignant otitis externa? Laryngoscope 130(11):2516–2517
Cooper T, Hildrew D, McAfee JS, McCall AA, Branstetter BF 4th, Hirsch BE (2018) Imaging in the diagnosis and management of necrotizing otitis externa: a survey of practice patterns. Otol Neurotol 39(5):597–601
Carter JV, Pan J, Rai SN, Galandiuk S (2016) ROC-ing along: evaluation and interpretation of receiver operating characteristic curves. Surgery 159(6):1638–1645
Attia J (2003) Moving beyond sensitivity and specificity: using likelihood ratios to help interpret diagnostic tests. Aust Prescr 26:111–113
Cohen D (1990) Borderline cases of malignant external otitis. Am J Otol 11(3):209–211
Shpitzer T, Stern Y, Cohen O, Levy R, Segal K, Feinmesser R (1993) Malignant external otitis in nondiabetic patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102:8702
Zimmerli W (2018) Osteomyelitis. Jameson J, & Fauci A.S., & Kasper D.L., & Hauser S.L., & Longo D.L., & Loscalzo J (Eds.), Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 20e. McGraw-Hill
Harris JC, Caesar DH, Davison C, Phibbs R, Than MP (2011) How useful are laboratory investigations in the emergency department evaluation of possible osteomyelitis? Emerg Med Australas 23(3):317–330
Maffulli N, Papalia R, Zampogna B, Torre G, Albo E, Denaro V (2016) The management of osteomyelitis in the adult. Surgeon 14(6):345–360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No funding was received for conducting this study. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vaca, M., Medina, M.M., Cordero, A.I. et al. Necrotizing external otitis: diagnostic clues in the emergency department. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 737–742 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08178-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08178-4