Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effectiveness of in-office blue laser therapy on dyspnea in patients with type 3 Reinke’s edema.
Methods
The medical records and video-recordings of patients with Reinke’s edema type 3 who had undergone office-based blue laser therapy between March 2022 and January 2023 were reviewed. The primary outcome measures assessed before and after surgery were dyspnea severity, risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and disease regression. The severity of dyspnea was measured using the Dyspnea Severity Index (DSI), the risk of OSA was assessed using the STOP-BANG questionnaire, and disease regression was assessed by reviewing the laryngeal examination before and after surgery. The Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10) was used as a secondary outcome measure.
Result
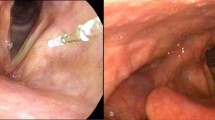
A total of 10 patients were included. The mean age of the study population was 58.9 ± 4.2 years. The male-to-female ratio was 2:3. In total, 20 vocal fold lesions were treated among which 18 were reviewed. Eight lesions regressed completely and 10 partially. There was a statistically significant drop in the mean score of DSI after surgery (16.1 ± 10.2 pre-operatively vs 2.3 ± 2.3 post-operatively, p-value < 0.001). The mean STOP-BANG score decreased from 4.8 ± 1.47 to 3.1 ± 1.28 (p-value = 0.001). There was also a significant improvement in VHI-10 score (22.7 ± 7.0 vs 4.4 ± 5.6, p-value < 0.001).
Conclusion
Office-based blue laser therapy offers a safe and effective treatment for shortness of breath in patients with type 3 Reinke’s edema.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request.
References
Zeitels SM, Hillman RE, Bunting GW, Vaughn T (1997) Reinke’s edema: phonatory mechanisms and management strategies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 106(7 Pt 1):533–543. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949710600701
Dewan K, Chhetri DK, Hoffman H (2022) Reinke’s edema management and voice outcomes. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 7(4):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1002/lio2.840
Woo P (2008) Laryngeal examinations and visualizations. In: The Singer's voice, pp. 55–57. Plural Publishing, Inc, San Diego
Hamdan AL, Khalifee E, Abi Akl PR, Ghanem A, El Hage A (2020) Pathogenic role of Reinke’s edema in snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. J Voice 34(3):456–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2018.12.001
Courey MS, Garrett CG, Ossoff RH (1997) Medial microflap for excision of benign vocal fold lesions. Laryngoscope 107(3):340–344. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199703000-00012
Sataloff RT, Spiegel JR, Heuer RJ, Baroody MM, Emerich KA, Hawkshaw MJ, Rosen DC (1997) Laryngeal mini-microflap: a new technique and reassessment of the microflap saga. J Voice 9(2):198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0892-1997(05)80253-x
Wang CT, Lai MS, Liao LJ, Lo WC, Cheng PW (2013) Transnasal endoscopic steroid injection: a practical and effective alternative treatment for benign vocal fold disorders. Laryngoscope 123(6):1464–1468. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23715
Woo P (2018) Hyaluronidase injection in the vocal folds for vocal hemorrhage, reinke edema, and hyaluronic acid overinjection: a novel application in the larynx. J Voice 32(4):492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.07.004
Hamdan AL, Ghanem A, Abi Akl PR, El Hage A (2022) Unsedated office-based thulium laser therapy in patients with Reinke’s edema. J Voice 36(1):134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.03.017
Pitman MJ, Lebowitz-Cooper A, Iacob C, Tan M (2012) Effect of the 532nm pulsed KTP laser in the treatment of Reinke’s edema. Laryngoscope 122(12):2786–2792. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23576
Koufman JA, Rees CJ, Frazier WD, Kilpatrick LA, Wright SC, Halum SL, Postma GN (2007) Office-based laryngeal laser surgery: a review of 443 cases using three wavelengths. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(1):146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2007.02.041
Ghanem A, Hamdan AL (2022) Unsedated office-based blue laser therapy in female patients with Reinke’s edema: a retrospective review of 8 cases. J Voice S0892–1997(22):00266–00271
Hamdan AL, Abi Zeid Daou C, Ghanem A, Ar Feghali P, Hosri J, Sataloff RT (2023) Office-based laser therapy in Reinke’s edema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Voice S0892–1997(22):00392–00397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.12.003
Yonekawa H (1988) A clinical study of Reinke’s edema. Auris Nasus Larynx 15(1):57–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0385-8146(88)80010-5
Hess MM, Fleischer S, Ernstberger M (2018) New 445 nm blue laser for laryngeal surgery combines photoangiolytic and cutting properties. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(6):1557–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-4974-8
Miller BJ, Abdelhamid A, Karagama Y (2021) Applications of office-based 445 nm blue laser transnasal flexible laser surgery: a case series and review of practice. Ear Nose Throat J 100(1):105S-112S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320960544
Gartner-Schmidt JL, Shembel AC, Zullo TG, Rosen CA (2014) Development and validation of the dyspnea index (DI): a severity index for upper airway-related dyspnea. J Voice 28(6):775–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.12.017
Chung F, Abdullah HR, Liao P (2016) STOP-bang questionnaire: a practical approach to screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 149(3):631–638. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.15-0903
Rosen CA, Lee AS, Osborne J, Zullo T, Murry T (2004) Development and validation of the voice handicap index-10. Laryngoscope 114(9):1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200409000-00009
Koszewski IJ, Hoffman MR, Young WG, Lai YT, Dailey SH (2015) Office-based photoangiolytic laser treatment of Reinke’s edema: safety and voice outcomes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(6):1075–1081
Novakovic D, MacKay S (2015) Adult obstructive sleep apnoea and the larynx. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 23(6):464–469. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0000000000000209
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by PARF, JH, CAZD and AG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by A-LH and Patrick ARF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study has been approved by American University of Beirut Institutional Review Board, Approval Number: BIO-2022-0280.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdan, AL., Abou Raji Feghali, P., Hosri, J. et al. Office-based blue laser therapy for dyspnea in patients with type 3 Reinke’s edema. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 3323–3328 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07964-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07964-4