Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to evaluate the effects of thymoquinone and propranolol on Hep-2 cells representing laryngeal Ca cell type in comparison with cisplatin. We also evaluated their combined effects.
Methods
Apoptotic effects were directly analyzed via mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase-3 assays. In addition, effects on apoptosis and cell cycle via Bcl-2, Bax, P53, and Cyclin D1 mRNA expressions and effects on angiogenesis via VEGFA mRNA expression were evaluated by RT-qPCR.
Results
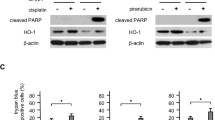
According to our results, it was determined that the anticancer effects of thymoquinone on Hep-2 cells were higher than propranolol. Our JC-1 and caspase-3 results showed an effect close to cisplatin, especially for 50 µM thymoquinone. Significant differences were also obtained in Bcl-2, Bax, P53, and cyclin D1 results for similar concentrations compared to the control. No effect of thymoquinone was seen for VEGFA. Propranolol alone had no significant effect on JC-1 and Caspase-3. Propranolol had an effect on Bcl-2, Bax mRNA expressions compared to the control, only at 250 µM concentration. Propranolol and its combinations increased VEGFA mRNA expression-like cisplatin.
Conclusion
Thymoquinone induced apoptosis and blocked the cell cycle in Hep-2 cells. The effects of propranolol, which was reported to have an antiangiogenesis effect in some studies, on apoptosis and cell cycle were limited except at high concentrations. For this cell line, why propranolol causes an increase in VEGFA expression should be evaluated extensively. Thymoquinone shows promise for cancer therapy, but studies need to be designed in vivo to evaluate the effects more reliably.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data in this article were obtained during the study process. The kits and devices used in the study are stated in the article.The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Lango MN (2009) Multimodal treatment for head and neck cancer. Surg Clin N Am 89(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2008.09.018. (viii)
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 63(1):11–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21166
Boeker R, Stromberger C, Heiland M, Beck-Broichsitter B, Hofmann VM, Neumann K, Ochsenreither S, Olze H, Dommerich S, Piwonski I, Coordes A (2021) Carcinoma of unknown primary and the 8th edition TNM classification for head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 131(9):E2534–E2542. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.29499
Silver CE, Beitler JJ, Shaha AR, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A (2009) Current trends in initial management of laryngeal cancer: the declining use of open surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(9):1333–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1028-2
Lefebvre JL, Andry G, Chevalier D, Luboinski B, Collette L, Traissac L, de Raucourt D, Langendijk JA, EORTC Head and Neck Cancer Group (2012) Laryngeal preservation with induction chemotherapy for hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: 10-year results of EORTC trial 24891. Ann Oncol 23(10):2708–2714. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds065
van Herpen CM, Mauer ME, Mesia R, Degardin M, Jelic S, Coens C, Betka J, Bernier J, Remenar E, Stewart JS, Preiss JH, van den Weyngaert D, Bottomley A, Vermorken JB, EORTC Head and Neck Group (2010) Short-term health-related quality of life and symptom control with docetaxel, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin (TPF), 5-fluorouracil (PF) for induction in unresectable locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer patients (EORTC 24971/TAX 323). Br J Cancer 103(8):1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605860
Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR, Mickiewicz E, Winquist E, Gorbounova V, Tjulandin S, Shin DM, Cullen K, Ervin TJ, Murphy BA, Raez LE, Cohen RB, Spaulding M, Tishler RB, Roth B, ViroglioRdel C, Venkatesan V, Romanov I, Agarwala S, Harter KW, Dugan M, Cmelak A, Markoe AM, Read PW, Steinbrenner L, Colevas AD, Norris CM Jr, Haddad RI, TAX 324 Study Group (2007) Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357(17):1705–1715. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa070956
Avcı G, BacakGüllü E (2013) Thymoquinone: a bioactive component of Nigella sativa. Kocatepe Vet J 6(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.5578/kvj.5251
Almajali B, Al-Jamal HAN, Taib WRW, Ismail I, Johan MF, Doolaanea AA, Ibrahim WN (2021) Thymoquinone, as a Novel Therapeutic Candidate of Cancers. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 14(4):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040369
Imran M, Rauf A, Khan IA, Shahbaz M, Qaisrani TB, Fatmawati S, Abu-Izneid T, Imran A, Rahman KU, Gondal TA (2018) Thymoquinone: A novel strategy to combat cancer: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 106:390–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.159
Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu C, Jennings NB, Armaiz-Pena G, Bankson JA, Ravoori M, Merritt WM, Lin YG, Mangala LS, Kim TJ, Coleman RL, Landen CN, Li Y, Felix E, Sanguino AM, Newman RA, Lloyd M, Gershenson DM, Kundra V, Lopez-Berestein G, Lutgendorf SK, Cole SW, Sood AK (2006) Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med 12(8):939–944. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1447
Annabi B, Lachambre MP, Plouffe K, Moumdjian R, Béliveau R (2009) Propranolol adrenergic blockade inhibits human brain endothelial cells tubulogenesis and matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion. Pharmacol Res 60(5):438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.05.005
Ozeki M, Nozawa A, Hori T, Kanda K, Kimura T, Kawamoto N, Fukao T (2016) Propranolol for infantile hemangioma: effect on plasma vascular endothelial growth factor. Pediatr Int 58(11):1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.12981
Kum JJ, Khan ZA (2015) Mechanisms of propranolol action in infantile hemangioma. Dermatoendocrinol 6(1):e979699. https://doi.org/10.4161/19381980.2014.979699
Kozanoglu I, Yandim MK, Cincin ZB, Ozdogu H, Cakmakoglu B, Baran Y (2013) New indication for therapeutic potential of an old well-known drug (propranolol) for multiple myeloma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139(2):327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1331-y
Tian L, Zhang J, Ren X, Liu X, Gao W, Zhang C, Sun Y, Liu M (2017) Overexpression of miR-26b decreases the cisplatin-resistance in laryngeal cancer by targeting ATF2. Oncotarget 8(45):79023–79033. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20784
Lei WB, Jia T, Su ZZ, Wen WP, Zhu XL (2008) Effect of chemotherapy with cisplatin and rapamycin against Hep-2 cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28(10):1838–1841 (PMID: 18971185)
Rooney S, Ryan MF (2005) Effects of alpha-hederin and thymoquinone, constituents of Nigella sativa, on human cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res 25(3B):2199–2204 (PMID: 16158964)
Zhou C, Chen X, Zeng W, Peng C, Huang G, Li X, Ouyang Z, Luo Y, Xu X, Xu B, Wang W, He R, Zhang X, Zhang L, Liu J, Knepper TC, He Y, McLeod HL (2016) Propranolol induced G0/G1/S phase arrest and apoptosis in melanoma cells via AKT/MAPK pathway. Oncotarget 7(42):68314–68327. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11599
Zhang H, Yu T, Wen L, Wang H, Fei D, Jin C (2013) Curcumin enhances the effectiveness of cisplatin by suppressing CD133+ cancer stem cells in laryngeal carcinoma treatment. Exp Ther Med 6(5):1317–1321. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2013.1297
Gao H, Dong H, Li G, Jin H (2018) Combined treatment with acetazolamide and cisplatin enhances chemosensitivity in laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells. Oncol Lett 15(6):9299–9306. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8529
Shao F, Lv M, Zheng Y, Jiang J, Wang Y, Lv L, Wang J (2015) The anti-tumour activity of rLj-RGD4, an RGD toxin protein from Lampetra japonica, on human laryngeal squamous carcinoma Hep-2 cells in nude mice. Biochimie 119:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2015.11.004
Tsuchida R, Das B, Yeger H, Koren G, Shibuya M, Thorner PS, Baruchel S, Malkin D (2008) Cisplatin treatment increases survival and expansion of a highly tumorigenic side-population fraction by upregulating VEGF/Flt1 autocrine signaling. Oncogene 27(28):3923–3934. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.38
Rooney S, Ryan MF (2005) Modes of action of alpha-hederin and thymoquinone, active constituents of Nigella sativa, against HEp-2 cancer cells. Anticancer Res 25(6B):4255–4259 (PMID: 16309225)
Liu X, Dong J, Cai W, Pan Y, Li R, Li B (2017) The effect of thymoquinone on apoptosis of SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cell by regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax. Int J Gynecol Cancer 27(8):1596–1601. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000001064
Khazaei M, Pazhouhi M (2017) Temozolomide-mediated apoptotic death is improved by thymoquinone in U87MG cell line. Cancer Invest 35(4):225–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2017.1289383
Soltani A, Pourgheysari B, Shirzad H, Sourani Z (2017) Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activities of thymoquinone in lymphoblastic leukemia cell line. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 33(4):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-016-0758-8
Barkat MA, Harshita AJ, Khan MA, Beg S, Ahmad FJ (2018) Insights into the targeting potential of thymoquinone for therapeutic intervention against triple-negative breast cancer. Curr Drug Targets 19(1):70–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450118666170612095959
Rotter A, de Oliveira ZNP (2017) Infantile hemangioma: pathogenesis and mechanisms of action of propranolol. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 15(12):1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.13365
Chang X, Li S, Xue XD, Chang F (2019) Propranolol regulates ERK1/2 signaling pathway and promotes chronic wound healing in diabetic rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(10):4498–4506. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201905_17962
Shepard MJ, Bugarini A, Edwards NA, Lu J, Zhang Q, Wu T, Zhuang Z, Chittiboina P (2018) Repurposing propranolol as an antitumor agent in von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.5.JNS172879
Lamy S, Lachambre MP, Lord-Dufour S, Béliveau R (2010) Propranolol suppresses angiogenesis in vitro: inhibition of proliferation, migration, and differentiation of endothelial cells. Vascul Pharmacol 53(5–6):200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2010.08.002
Rico M, Baglioni M, Bondarenko M, Laluce NC, Rozados V, André N, Carré M, Scharovsky OG, Menacho Márquez M (2017) Metformin and propranolol combination prevents cancer progression and metastasis in different breast cancer models. Oncotarget 8(2):2874–2889. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13760
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the Scientific Research Projects Unit of Alanya Alaaddin Keykubat University for the financial resources they have provided.
Funding
This study was supported by Alanya Alaaddin Keykubat University Scientific Research Projects Unit. Project ID: 2019-04-03-MAP01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The project idea was put forward by CŞ and EM. CŞ was found in all laboratory stages except cell culture. EM and DNS did cell culture stages and supported all other laboratory studies. BD supported the performance of caspase-3 and JC-1 assays. The writing phase of the study was done by ÇŞ, EM and DNS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics committee approval
This study does not have a design on biomaterials directly sourced from humans or animals. It has an in-vitro design, which excludes the conditions specified in the Helsinki Declaration. The study was performed with a commercially available cell line. Therefore, ethical committee approval is not required in our country.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Şahin, C., Maytalman, E., Nemutlu Samur, D. et al. The effect of thymoquinone and propranolol combination on epidermoid laryngeal carcinoma cell. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 2849–2858 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07825-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07825-0