Abstract
Purpose
The study aims to examine the effect on intracranial pressure by calculating the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) using ultrasound in patients who underwent suspension direct laryngoscopy.
Methods
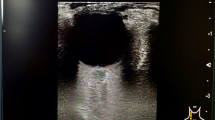
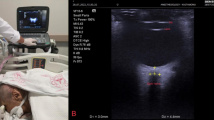
Thirty-three patients who underwent suspension direct laryngoscopy were included in this prospective observational study. ONSD measurement was performed using a high-frequency linear probe. The ONSD basal (T0) value was determined using ultrasound in the supine position before the induction. Ultrasonography was used to record ONSD in the Boyce Jackson position (T1) just before inserting the laryngeal blade, in the Boyce Jackson position just before removing the laryngeal blade (T2), and in the supine position (T3) just before extubation.
Results
A statistically significant rise (p < 0.001) was seen between the patients' baseline ONSD values and the values at T1, T2, and T3. The optic nerve sheat diameter level recorded prior to withdrawing the laryngeal blade (T2) was considerably greater than the ONSD level calculated instantly before insertion of the laryngeal blade (T1) (p < 0.001). The ONSD value prior to extubation (T3) following the removal of the laryngeal blade was considerably smaller than the ONSD value prior removing the laryngeal blade (T2) (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
This study found that when the laryngeal blade is mounted during the suspension direct laryngoscopy surgery, there is a significant increase in ultrasonographically measured ONSD and increased the ONSD even further during the time the mouth gag was remained in situ. This is the first research to indicate that measuring ONSD with ultrasonography during suspension direct laryngoscopy raises intracranial pressure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tong B, Fang R (2018) Analysis of pressure distribution during direct microlaryngoscopy. J Voice 32:122–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.04.012
Shribman AJ, Smith G, Achola KJ (1987) Cardiovascular and catecholamine responses to laryngoscopy with and without tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth 59:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/59.3.295
Hill AJ, Ro F, Underwood SM et al (1991) The haemodynamic effects of bronchoscopy Comparison of propofol and thiopentone with and without alfentanil pretreatment. Anaesthesia 46:266–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1991.tb11493
Redmann AJ, White GD, Makkad B, Howell R (2016) Asystole from direct laryngoscopy: a case report and literature review. Anesth Prog 63:197–200
Hendrix RA, Ferouz A, Bacon CK (1994) Admission planning and complications of direct laryngoscopy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 110:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989411000607
Robinson PM (1991) Prospective study of the complications of endoscopic laryngeal surgery. J Laryngol Otol 105:356–358. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100115981
Dip F, Nguyen D, Rosales A et al (2016) Impact of controlled intraabdominal pressure on the optic nerve sheath diameter during laparoscopic procedures. Surg Endosc 30:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4159-0
Kimberly HH, Shah S, Marill K, Noble V (2008) Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with direct measurement of intracranial pressure. Acad Emerg Med 15:201–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2007.00031.x
Kumar A, Seth A, Prakash S et al (2016) Attenuation of the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation with fentanyl, lignocaine nebulization, and a combination of both: a randomized controlled trial. Anesth Essays Res 10:661–666. https://doi.org/10.4103/0259-1162.191113
Lee DH, Park SJ (2011) Effects of 10% lidocaine spray on arterial pressure increase due to suspension laryngoscopy and cough during extubation. Korean J Anesthesiol 60:422–427. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2011.60.6.422
Helmke K, Hansen HC (1996) Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic: Evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension. II Patient study. Pediatr Radiol 26:706–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01383384
Sahu S, Panda N, Swain A et al (2021) Optic nerve sheath diameter: correlation with intra-ventricular intracranial measurements in predicting dysfunctional intracranial compliance. Cureus 13:e13008. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.13008
Hamaya Y, Dohi S (2000) Differences in cardiovascular response to airway stimulation at different sites and blockade of the responses by lidocaine. Anesthesiology 93:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200007000-00018
Liu D, Li Z, Zhang X et al (2017) Assessment of intracranial pressure with ultrasonographic retrobulbar optic nerve sheath diameter measurement. BMC Neurol 17:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-017-0964-5
Steinborn M, Fiegler J, Kraus V et al (2011) High resolution ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve and the optic nerve sheath: anatomic correlation and clinical importance. Ultraschall der Medizin 32:608–613. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1245822
Ozsari E, Demirhan A (2021) Effect of bronchoscopy on intracranial hypertension during different regimen of sedation by optic nerve sheath diameter. Neurol Asia 26:795–800. https://doi.org/10.54029/2021MTD
Tabari M, Alipour M, Ahmadi M (2013) Hemodynamic changes occurring with tracheal intubation by direct laryngoscopy compared with intubating laryngeal mask airway in adults: a randomized comparison trial. Egypt J Anaesth 29:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egja.2012.11.003
Barak M, Ziser A, Greenberg A et al (2003) Hemodynamic and catecholamine response to tracheal intubation: direct laryngoscopy compared with fiberoptic intubation. J Clin Anesth 15:132–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0952-8180(02)00514-7
Altiparmak B, Korkmaz Toker M, Uysal Aİ et al (2020) Evaluation of the effect of the mouth gag use on optic nerve sheath diameter of pediatric patients undergoing tonsillectomy or Adenotonsillectomy: an observational study. BMC Anesthesiol 20:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01079-7
Karali E, Demirhan A, Gunes A, Ural A (2020) Evaluation of the effect of Boyle-Davis mouth gag on intracranial pressure in patients undergoing adenotonsillectomy by using ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter measurement. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 131:109856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109856
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karali, E., Demirhan, A., Günes, A. et al. Assessment of intracranial pressure with ultrasonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter on patients undergoing suspension direct laryngoscopy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 1835–1840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07709-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07709-9