Abstract
Objective
A planning study was performed to evaluate dosimetric differences between intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for head and neck cancer (HNC) for sequential boost (Seq-boost) and simultaneous integrated boost techniques (SIB).
Methods
30 patients with HNC were included, 15 treated with SIB and 15 with Seq-Boost. For all patients both VMAT and IMRT plans were completed. The planning objective for PTV was 95% of dose covering minimum 95% of PTV; for spinal cord and brainstem Dmax was limited to 45 Gy and 54 Gy respectively. The parotids had a mean dose < 26 Gy limitation. The number of monitor units (MU) were scored for treatment delivery time efficiency.
Results
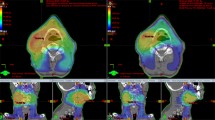
Both techniques achieved the set objectives regarding PTV coverage and organ sparing. SIB plans presented a statistically significant better homogeneity for VMAT (p = 0.0096), while Seq-boost showed a statistically significant better conformity for VMAT (p = 0.0049). For parotids only SIB plans showed a lower Dmean value obtained with VMAT, while Seq-boost plans showed statistically insignificant differences. For SIB plans the MU was reduced by 33.4% with VMAT, whereas in Seq-boost plans the reduction was by 19.1%.
Conclusion
VMAT shows dosimetric superiority to IMRT in some cases, however an adequate coverage of the target volumes and a suitable OAR sparing can be achieved with both techniques. Though IMRT is still the standard in HNC radiotherapy, VMAT can be safely implemented, offering at least similar target coverage and organ sparing, with significantly reduced MU.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chow LQM (2020) Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 382(1):60–72
Meccariello G, Maniaci A, Bianchi G, Cammaroto G, Iannella G, Catalano A, Sgarzani R, De Vito A, Capaccio P, Pelucchi S et al (2022) Neck dissection and trans oral robotic surgery for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 49(1):117–125
Nutting CM, Morden JP, Harrington KJ, Urbano TG, Bhide SA, Clark C, Miles EA, Miah AB, Newbold K, Tanay M et al (2011) Parotid-sparing intensity modulated versus conventional radiotherapy in head and neck cancer (PARSPORT): a phase 3 multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12(2):127–136
Baudelet M, Van den Steen L, Tomassen P, Bonte K, Deron P, Huvenne W, Rottey S, De Neve W, Sundahl N, Van Nuffelen G et al (2019) Very late xerostomia, dysphagia, and neck fibrosis after head and neck radiotherapy. Head Neck 41(10):3594–3603
Stromberger C, Cozzi L, Budach V, Fogliata A, Ghadjar P, Wlodarczyk W, Jamil B, Raguse JD, Böttcher A, Marnitz S (2016) Unilateral and bilateral neck SIB for head and neck cancer patients: intensity-modulated proton therapy, tomotherapy, and RapidArc. Strahlenther Onkol 192(4):232–239
Jiang L, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Liang F, Wu J, Wang R (2019) A comparison of clinical outcomes between simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) versus sequential boost (SEQ) intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(34):e16942
Buciuman N, Marcu LG (2021) Dosimetric justification for the use of volumetric modulated arc therapy in head and neck cancer—a systematic review of the literature. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 6(5):999–1007
Stieler F, Wolff D, Schmid H, Welzel G, Wenz F, Lohr F (2011) A comparison of several modulated radiotherapy techniques for head and neck cancer and dosimetric validation of VMAT. Radiother Oncol 101(3):388–393
Vanetti E, Clivio A, Nicolini G, Fogliata A, Ghosh-Laskar S, Agarwal JP, Upreti RR, Budrukkar A, Murthy V, Deshpande DD et al (2009) Volumetric modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the oropharynx, hypopharynx and larynx: A treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol 92(1):111–117
Broggi S, Perna L, Bonsignore F, Rinaldin G, Fiorino C, Chiara A, Frigerio C, Butti I, Sangalli G, Dell’Oca I et al (2014) Static and rotational intensity modulated techniques for head-neck cancer radiotherapy: a planning comparison. Phys Med 30(8):973–979
Beyzadeoglu M, Ozyigit G, Selek U (2015) Radiation therapy for head and neck cancers. Springer International Publishing Switzerland
Tejinder K, Kuldeep S (2012) Homogeneity Index: An objective tool for assessment of conformal radiation treatments. J Med Phys 37(4):207–213
Feuvret L, Noël G, Mazeron JJ, Bey P (2006) Conformity index: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(2):333–342
Wiehle R, Knippen S, Grosu AL, Bruggmoser G, Hodapp N (2011) VMAT and step-and-shoot IMRT in head and neck cancer: a comparative plan analysis. Strahlenther Onkol 187:820–825
Fung-Kee-Fung SD, Hackett R, Hales L, Warren G, Singh AK (2012) A prospective trial of volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy vs conventional intensity modulated radiation therapy in advanced head and neck cancer. World J Clin Oncol 3(4):57–62
Lee TF, Ting HM, Chao PJ, Fang FM (2012) Dual arc volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT) of nasopharyngeal carcinomas: a simultaneous integrated boost treatment plan comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapies and single arc VMAT. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 24(3):196–207
Lu SH, Cheng JCH, Kuo SH, Lee JJS, Chen LH, Wu JK (2012) Volumetric modulated arc therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a dosimetric comparison with TomoTherapy and step-and-shoot IMRT. Radiother Oncol 104(3):324–330
Clemente S, Wu B, Sanguineti G, Fusco V, Ricchetti F, Wong J, McNutt T (2011) SmartArc-based volumetric modulated arc therapy for oropharyngeal cancer: a dosimetric comparison with both intensity-modulated radiation therapy and helical tomotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80(4):1248–1255
Bertelsen A, Hansen CR, Johansen J, Brink C (2010) Single arc volumetric modulated arc therapy of head and neck cancer. Radiother Oncol 95(2):142–148
Mazzola R, Fiorentino A, Ricchetti F, Gregucci F, Corradini S, Alongi F (2018) An update on radiation therapy in head and neck cancers. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 18(4):359–364
Pow EH, Kwong DL, McMillan AS, Wong MC, Sham JS, Leung LH, Leung WK (2006) Xerostomia and quality of life after intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional radiotherapy for early-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma: initial report on a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(4):981–991
van der Veen J, Nuyts S (2017) Can intensity-modulated-radiotherapy reduce toxicity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma? Cancers 9:E135
Mendez LC, Moraes FY, Poon I, Marta GN (2016) The management of head and neck tumors with high technology radiation therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 16(1):99–110
Hoyne C, Dreosti M, Shakeshaft J, Baxi S (2017) Comparison of treatment techniques for reduction in the submandibular gland dose: a retrospective study. J Med Radiat Sci 64(2):125–130
Verbakel W, Cuijpers JP, Hoffmans D, Bieker M, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2009) Volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy vs. conventional IMRT in head-and-neck cancer: a comparative planning and dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(1):252–259
Studenski MT, Bar-Ad V, Siglin J, Cognetti D, Curry J, Tuluc M, Harrison AS (2013) Clinical experience transitioning from IMRT to VMAT for head and neck cancer. Med Dosim 38(2):171–175
Wilke C, Takiar V, Wang H, Moreno AC, Tung SS, Quinlan-Davidson SR, Garden AS, Rosenthal DI, Fuller CD, Gunn GB et al (2021) Defining the dose-volume criteria for laryngeal sparing in locally advanced oropharyngeal cancer utilizing split-field IMRT, whole-field IMRT and VMAT. J Appl Clin Med Phys 22(1):37–44
Petkar I, Rooney K, Roe JW, Patterson JM, Bernstein D, Tyler JM et al (2016) DARS: a phase III randomised multicentre study of dysphagia-optimised intensity- modulated radiotherapy (Do-IMRT) versus standard intensity-modulated radiotherapy (S-IMRT) in head and neck cancer. BMC Cancer 16(1):770
Rühle A, Grosu AL, Nicolay NH (2021) De-escalation strategies of (Chemo)radiation for head-and-neck squamous cell cancers-HPV and beyond. Cancers (Basel) 13(9):2204
Srivastava SP, Cheng CW, Das IJ (2016) The effect of slice thickness on target and organs at risk volumes, dosimetric coverage and radiobiological impact in IMRT planning. Clin Transl Oncol 18(5):469–479
Doornaert P, Verbakel WF, Bieker M, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2011) RapidArc planning and delivery in patients with locally advanced head-and-neck cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(2):429–435
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Anca Croitoru, Dr. Ioana Lupșe and Dr. Andrei Mavrodineanu who played a decisive role in plan realization and plan evaluation.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buciuman, N., Marcu, L.G. Is there a dosimetric advantage of volumetric modulated arc therapy over intensity modulated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer?. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 5311–5321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07452-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07452-1