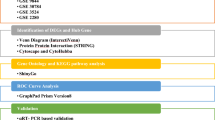
Abstract
Background
The prognostic and clinicopathological value of placental-Cadherin (CDH3) in multiple cancers is controversial. The diagnostic significance and functional mechanism of CDH3 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) have not been thoroughly investigated. This study aims to clarify the potential of CDH3 as biomarker for TSCC.
Methods
Here, meta-analysis, bioinformatics, along wet-lab techniques were employed to evaluate the diagnostic, as well as the prognostic value of CDH3 in diverse types of cancers, especially TSCC. Meta-analysis was used to determine the influence of CDH3 on prognostic and clinicopathological features in numerous cancers. Molecular biology function was used to investigate the role of CDH3 in TSCC cells. The relationship of CDH3 with tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) in TSCC was assessed using CIBERSORT. Moreover, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was done based on TCGA. Besides, the hub genes and associated cascades were uncovered based on gene co-expression with CDH3.
Results
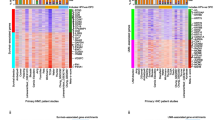
CDH3 upregulation correlated with worse overall survival and disease-free survival in various cancers. CDH3 was validated as an independent risk factor for HNSC and was linked to the onset of tumors, tumor stage, and infiltration depth. CDH3 silencing inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis of the CAL-27 cell line. CDH3 expression level correlated with infiltration by macrophages, T cells, T cell regulatory cells (Tregs), and plasma cells in TSCC. GSEA revealed that CDH3 influences multiple cancer-associated cascades. Besides, CBX3, CCHCR1, along NFYC were identified as the core hub genes for CDH3.
Conclusion
We identified CDH3 as a pan-cancer gene with potential prognostic and diagnostic significance in various cancers, particularly in TSCC, where it is tumorigenic.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin Y, Yang Y (2019) Bioinformatics-based discovery of PYGM and TNNC2 as potential biomarkers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci Rep 39(7):BSR0191612. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20191612
Perumal V, Corica T, Dharmarajan AM, Sun Z, Dhaliwal SS, Dass CR, Dass J (2019) Circulating tumour cells (CTC) Head and neck cancer and radiotherapy; future perspectives. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030367
Zhou H, Zhang J, Guo L, Nie J, Zhu C, Ma X (2018) The value of narrow band imaging in diagnosis of head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 8(1):515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19069-0
Jansen L, Buttmann-Schweiger N, Listl S, Ressing M, Holleczek B, Katalinic A, Luttmann S, Kraywinkel K, Brenner H, Group GCSW (2018) Differences in incidence and survival of oral cavity and pharyngeal cancers between Germany and the United States depend on the HPV-association of the cancer site. Oral Oncol 76:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.11.015
Zhu P, He L, Li Y, Huang W, Xi F, Lin L, Zhi Q, Zhang W, Tang YT, Geng C, Lu Z, Xu X (2014) OTG-snpcaller: an optimized pipeline based on TMAP and GATK for SNP calling from ion torrent data. PLoS ONE 9(5):e97507. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097507
Gardner SN, Frey KG, Redden CL, Thissen JB, Allen JE, Allred AF, Dyer MD, Mokashi VP, Slezak TR (2015) Targeted amplification for enhanced detection of biothreat agents by next-generation sequencing. BMC Res Notes 8:682. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1530-0
Hulpiau P, van Roy F (2009) Molecular evolution of the cadherin superfamily. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41(2):349–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2008.09.027
Sasaki M, Akiyama-Oda Y, Oda H (2017) Evolutionary origin of type IV classical cadherins in arthropods. BMC Evol Biol 17(1):142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-017-0991-2
Cappellesso R, Marioni G, Crescenzi M, Giacomelli L, Guzzardo V, Mussato A, Staffieri A, Martini A, Blandamura S, Fassina A (2015) The prognostic role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers E-cadherin and Slug in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 67(4):491–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12668
Franz L, Nicole L, Frigo AC, Ottaviano G, Gaudioso P, Saccardo T, Visconti F, Cappellesso R, Blandamura S, Fassina A, Marioni G (2021) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and neoangiogenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133339
Kourtidis A, Lu R, Pence LJ, Anastasiadis PZ (2017) A central role for cadherin signaling in cancer. Exp Cell Res 358(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.04.006
Nose A, Takeichi M (1986) A novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule: its expression patterns associated with implantation and organogenesis of mouse embryos. J Cell Biol 103(6 Pt 2):2649–2658. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.103.6.2649
Vieira AF, Paredes J (2015) P-cadherin and the journey to cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer 14:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0448-4
Paredes J, Albergaria A, Oliveira JT, Jeronimo C, Milanezi F, Schmitt FC (2005) P-cadherin overexpression is an indicator of clinical outcome in invasive breast carcinomas and is associated with CDH3 promoter hypomethylation. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 11(16):5869–5877. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0059
Shimoyama Y, Hirohashi S (1991) Expression of E- and P-cadherin in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res 51(8):2185–2192
Taniuchi K, Nakagawa H, Hosokawa M, Nakamura T, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Katagiri T, Nakamura Y (2005) Overexpressed P-cadherin/CDH3 promotes motility of pancreatic cancer cells by interacting with p120ctn and activating rho-family GTPases. Cancer Res 65(8):3092–3099. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008.5472.CAN-04-3646
Bauer R, Valletta D, Bauer K, Thasler WE, Hartmann A, Muller M, Reichert TE, Hellerbrand C (2014) Downregulation of P-cadherin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma induces tumorigenicity. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(9):6125–6132
Smythe WR, Williams JP, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM (1999) Cadherin and catenin expression in normal human bronchial epithelium and non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 24(3):157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5002(99)00032-x
Van Marck V, Stove C, Van Den Bossche K, Stove V, Paredes J, Vander Haeghen Y, Bracke M (2005) P-cadherin promotes cell-cell adhesion and counteracts invasion in human melanoma. Cancer Res 65(19):8774–8783. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4414
Hsiao TF, Wang CL, Wu YC, Feng HP, Chiu YC, Lin HY, Liu KJ, Chang GC, Chien KY, Yu JS, Yu CJ (2020) Integrative omics analysis reveals soluble cadherin-3 as a survival predictor and an early monitoring marker of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 26(13):3220–3229. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3972
Li L, Yu S, Wu Q, Dou N, Li Y, Gao Y (2019) KLF4-mediated CDH3 upregulation suppresses human hepatoma cell growth and migration via GSK-3beta signaling. Int J Biol Sci 15(5):953–961. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.30857
Azimi F, Scolyer RA, Rumcheva P, Moncrieff M, Murali R, McCarthy SW, Saw RP, Thompson JF (2012) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30(21):2678–2683. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.37.8539
Al Absi A, Wurzer H, Guerin C, Hoffmann C, Moreau F, Mao X, Brown-Clay J, Petrolli R, Casellas CP, Dieterle M, Thiery JP, Chouaib S, Berchem G, Janji B, Thomas C (2018) Actin cytoskeleton remodeling drives breast cancer cell escape from natural killer-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 78(19):5631–5643. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0441
Insua-Rodriguez J, Oskarsson T (2016) The extracellular matrix in breast cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 97:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.12.017
Lin S, Huang C, Gunda V, Sun J, Chellappan SP, Li Z, Izumi V, Fang B, Koomen J, Singh PK, Hao J, Yang S (2019) Fascin controls metastatic colonization and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation by remodeling mitochondrial actin filaments. Cell Rep 28(11):2824–2836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.011
Park JS, Burckhardt CJ, Lazcano R, Solis LM, Isogai T, Li L, Chen CS, Gao B, Minna JD, Bachoo R, DeBerardinis RJ, Danuser G (2020) Mechanical regulation of glycolysis via cytoskeleton architecture. Nature 578(7796):621–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-1998-1
Shen J, Cao B, Wang Y, Ma C, Zeng Z, Liu L, Li X, Tao D, Gong J, Xie D (2018) Hippo component YAP promotes focal adhesion and tumour aggressiveness via transcriptionally activating THBS1/FAK signalling in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 37(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0850-z
Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D (2019) Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell 49(3):347–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011
Sathyanarayana UG, Moore AY, Li L, Padar A, Majmudar K, Stastny V, Makarla P, Suzuki M, Minna JD, Feng Z, Gazdar AF (2007) Sun exposure related methylation in malignant and non-malignant skin lesions. Cancer Lett 245(1–2):112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2005.12.042
Sato N, Fukushima N, Maitra A, Matsubayashi H, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Goggins M (2003) Discovery of novel targets for aberrant methylation in pancreatic carcinoma using high-throughput microarrays. Cancer Res 63(13):3735–3742
Vered M, Lehtonen M, Hotakainen L, Pirila E, Teppo S, Nyberg P, Sormunen R, Zlotogorski-Hurvitz A, Salo T, Dayan D (2015) Caveolin-1 accumulation in the tongue cancer tumor microenvironment is significantly associated with poor prognosis: an in-vivo and in-vitro study. BMC Cancer 15:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1030-6
Collins RJ, Jiang WG, Hargest R, Mason MD, Sanders AJ (2015) EPLIN: a fundamental actin regulator in cancer metastasis? Cancer Metastasis Rev 34(4):753–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9595-8
Kong J, Shen S, Zhang Z, Wang W (2020) Identification of hub genes and pathways in cholangiocarcinoma by coexpression analysis. Cancer Biomark Sect A Dis Markers 27(4):505–517. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-190038
Meng W, Takeichi M (2009) Adherens junction: molecular architecture and regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(6):a002899. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a002899
Gnagnarella P, Raimondi S, Aristarco V, Johansson HA, Bellerba F, Corso F, Gandini S (2020) Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 1268:53–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46227-7_4
Matsui T, Shigeta T, Umeda M, Komori T (2015) Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) expression predicts metastasis in tongue cancer. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 120(4):436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2015.06.002
Yang X, Pang Y, Zhang J, Shi J, Zhang X, Zhang G, Yang S, Wang J, Hu K, Wang J, Jing H, Ke X, Fu L (2019) High expression levels of ACTN1 and ACTN3 indicate unfavorable prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. J Cancer 10(18):4286–4292. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.31766
Matsumura H, Mohri Y, Binh NT, Morinaga H, Fukuda M, Ito M, Kurata S, Hoeijmakers J, Nishimura EK (2016) Hair follicle aging is driven by transepidermal elimination of stem cells via COL17A1 proteolysis. Science 351(6273):aad4395. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad4395
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2620
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C, Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X, Perou CM (2010) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res BCR 12(5):R68. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr2635
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007
Shen Y, Xu J, Pan X, Zhang Y, Weng Y, Zhou D, He S (2020) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth via ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis 11(4):278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2485-1
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Yu, T. & Mao, L. Placental-Cadherin, a biomarker for local immune status and poor prognosis among patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 3597–3609 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07181-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07181-x