Abstract
Purpose
To assess if 3D-4K exoscope is a valuable tool for temporal bone dissection and to evaluate its teaching potential.
Methods
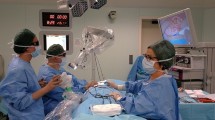
Six consecutive 3D-4K-exoscope-assisted cortical mastoidectomies were performed by a novice, an intermediate and an expert surgeon (two dissections each). All dissections were entirely recorded and later evaluated independently by three other experienced surgeons. The dissection end-product was evaluated according to the Melbourne Mastoidectomy Scale (MMS). Paired t test was used to assess whether novice and intermediate surgeons have a score improvement in the second dissection compared to the first one. Surgeons’ interactions, depth effect, and 3D impression were also assessed to perform a subjective analysis.
Results
Mean MMS scores for the novice, intermediate and expert surgeon were 11.3 ± 2.8, 13.8 ± 3.9 and 19 ± 1.3, respectively. Paired t test demonstrated a statically significant improvement between the first and the second dissection both for the novice and the intermediate surgeon (+ 4.7 and + 7 points; p = 0.0002). A high-quality magnification of the temporal bone was obtained, allowing the expert surgeon to identify all the anatomical structures without injuring them. The exoscope was capable of providing a high involvement in the dissections with very effective interactions between the expert surgeon and the trainees, that had access to the same surgical field view.
Conclusion
3D-4K-exoscope resulted adequate for a safe and effective mastoidectomy and showed a high potential for training and educational purposes. It can represent a valid option for surgical training of temporal bone dissection and a new interactive tool to understand the complex temporal bone anatomy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ricciardi L, Chaichana KL, Cardia A et al (2019) The exoscope in neurosurgery: an innovative “point of view”. A systematic review of the technical, surgical and educational aspects. World Neurosurg 124:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.202
Rubini A, Di Gioia S, Marchioni D (2020) 3D exoscopic surgery of lateral skull base. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(3):687–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05736-7
Smith S, Kozin ED, Kanumuri VV et al (2019) Initial experience with 3-dimensional exoscope-assisted transmastoid and lateral skull base surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 160(2):364–367. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599818816965
Garneau JC, Laitman BM, Cosetti MK et al (2019) The use of the exoscope in lateral skull base surgery: advantages and limitations. Otol Neurotol 40(2):236–240. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002095
Minoda R, Miwa T (2019) Non-microscopic middle ear cholesteatoma surgery: a case report of a novel head-up approach. Otol Neurotol 40(6):777–781. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002276
Colombo G, Ferreli F, Di Bari M et al (2021) Introducing the High-definition 3D exoscope in ear surgery: preliminary analysis of advantages and limits compared with operative microscope. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06510-w
George AP, De R (2010) Review of temporal bone dissection teaching: how it was, is and will be. J Laryngol Otol 124(2):119–125. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215109991617
Wong V, Unger B, Pisa J et al (2019) Construct validation of a printed bone substitute in otologic education. Otol Neurotol 40(7):e698–e703. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002285
Chae R, Sharon JD, Kournoutas I et al (2020) Replicating skull base anatomy with 3D technologies: a comparative study using 3D-scanned and 3D-printed models of the temporal bone. Otol Neurotol 41(3):e392–e403. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002524
Mowry SE, Jabbour N, Rose AS et al (2020) Multi-institutional comparison of temporal bone models: a Collaboration of the AAO-HNSF 3D-Printed Temporal Bone Working Group. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 164(5):1077–1084. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820960474
Kashikar TS, Kerwin TF, Moberly AC et al (2019) A review of simulation applications in temporal bone surgery. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 4(4):420–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/lio2.277
Talks BJ, Lamtara J, Wijewickrema S et al (2020) The Melbourne Mastoidectomy Scale: validation of an end-product dissection scale for cortical mastoidectomy. Clin Otolaryngol 45(5):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1111/coa.13569
De Virgilio A, Costantino A, Ebm C et al (2020) High definition three-dimensional exoscope (VITOM 3D) for microsurgery training: a preliminary experience. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277(9):2589–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06014-7
Colombo G, Di Bari M, Ferreli F (2022) Exoscope-assisted middle ear surgery. In: De Virgilio A, Spriano G (eds) Exoscope-Assisted surgery in otorhinolaryngology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-83168-0.00008-2
Herlan S, Marquardt JS, Hirt B, Tatagiba M, Ebner FH (2019) 3D exoscope system in neurosurgery-comparison of a standard operating microscope with a new 3D exoscope in the cadaver lab. Oper Neurosurg 17(5):518–524. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz081
Acknowledgements
We thank Bianca Festa for helping with the English language revision of the manuscript.
Funding
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombo, G., Di Bari, M., Canzano, F. et al. 3D-4K exoscope-assisted temporal bone dissection: a new frontier in surgical training. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 3875–3880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07137-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07137-1