Abstract
Purpose
The purpose is to investigate possible vestibulopathy in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), inner ear tests, including cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials (cVEMPs and oVEMPs) via various stimulation modes, were adopted.
Methods
Fifty BPPV patients were enrolled in this study. All patients underwent pure tone audiometry, cVEMPs, oVEMPs, and caloric tests. The recurrence status, abnormal rates of inner ear tests, and the characteristic parameters of VEMPs, such as wave latencies and amplitudes, were analyzed.
Results
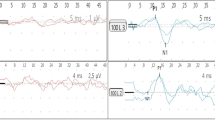
In affected ears, the abnormal rates of acoustic cVEMPs, vibratory oVEMPs, galvanic cVEMPs, and galvanic oVEMPs were 62%, 28%, 36%, and 14%, respectively. The abnormalities of acoustic cVEMPs were significantly larger than those of vibratory oVEMPs, and acoustic/vibratory VEMPs had significantly higher abnormal rates than the corresponding galvanic VEMPs.
Conclusion
BPPV patients may have both otolithic and neural dysfunctions. Otolithic organ damage occurs more frequently than retrootolithic neural degeneration, and the saccular macula might have a greater extent of damage than the utricular macula.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data and materials support the published claims and comply with field standards.
Code availability
All software applications or custom code support the published claims and comply with field standards.
References
von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F, Feldmann M, Ziese T, Lempert T, Neuhauser H (2007) Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:710–715. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.100420
Schuknecht HF (1969) Cupulolithiasis. Arch Otolaryngol 90:765–778. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1969.00770030767020
Walther LE, Wenzel A, Buder J, Bloching MB, Kniep R, Blödow A (2014) Detection of human utricular otoconia degeneration in vital specimen and implications for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:3133–3138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2784-6
Kao WT, Parnes LS, Chole RA (2017) Otoconia and otolithic membrane fragments within the posterior semicircular canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 127:709–714. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26115
Korres S, Gkoritsa E, Giannakakou-Razelou D, Yiotakis I, Riga M, Nikolpoulos TP (2011) Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in patients with BPPV. Med Sci Monit 17:CR42-47. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.881328
Welling DB, Parnes LS, O’Brien B, Bakaletz LO, Brackmann DE, Hinojosa R (1997) Particulate matter in the posterior semicircular canal. Laryngoscope 107:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199701000-00018
Colebatch JG, Halmagyi GM (1992) Vestibular evoked potentials in human neck muscles before and after unilateral vestibular deafferentation. Neurology 42:1635–1636. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.42.8.1635
Rosengren SM, McAngus Todd NP, Colebatch JG (2005) Vestibular-evoked extraocular potentials produced by stimulation with bone-conducted sound. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1938–1948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2005.03.019
Colebatch JG, Halmagyi GM, Skuse NF (1994) Myogenic potentials generated by a click-evoked vestibulocollic reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.57.2.190
Iwasaki S, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, Burgess AM, Kim J, Colebatch JG, Curthoys IS (2007) Head taps evoke a crossed vestibulo-ocular reflex. Neurology 68:1227–1229. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000259064.80564.21
Iwasaki S, Takai Y, Ozeki H, Ito K, Karino S, Murofushi T (2005) Extent of lesions in idiopathic sudden hearing loss with vertigo: study using click and galvanic vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:857–862. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.131.10.857
Murofushi T, Takegoshi H, Ohki M, Ozeki H (2002) Galvanic-evoked myogenic responses in patients with an absence of click-evoked vestibulo-collic reflexes. Clin Neurophysiol 113:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(01)00738-6
Chang CM, Young YH, Jaw FS, Wang CT, Cheng PW (2017) Degeneration of the vestibular nerve in unilateral Meniere’s disease evaluated by galvanic vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials. Clin Neurophysiol 128:1617–1624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.004
Yetiser S, Ince D, Gul M (2014) An analysis of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 123:686–695. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489414532778
Sreenivasan A, Sivaraman G, Parida PK, Alexander A, Saxena SK, Suria G (2015) The clinical utility of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in patients of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Clin Diagn Res 9:MC01-3. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/9953.6058
Longo G, Onofri M, Pellicciari T, Quaranta N (2012) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: is vestibular evoked myogenic potential testing useful? Acta Otolaryngol 132:39–43. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2011.619570
Singh NK, Barman A (2015) Efficacy of ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potential in identifying posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ear Hear 36:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1097/AUD.0000000000000097
Nakahara H, Yoshimura E, Tsuda Y, Murofushi T (2013) Damaged utricular function clarified by oVEMP in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 133:144–149. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2012.720030
Bhattacharyya N, Gubbels SP, Schwartz SR, Edlow JA, El-Kashlan H, Fife T, Holmberg JM, Mahoney K, Hollingsworth DB, Roberts R, Seidman MD, Prasaad Steiner RW, Tsai Do B, Voelker CC, Waguespack RW, Corrigan MD (2017) Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update) Executive Summary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 156:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816689660
Ross MD, Peacor D, Johnsson LG, Allard LF (1976) Observations on normal and degenerating human otoconia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 85:310–326. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348947608500302
Wang SJ, Weng WJ, Jaw FS, Young YH (2010) Ocular and cervical vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials: a study to determine whether air- or bone-conducted stimuli are optimal. Ear Hear 31:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181bdbac0
Welgampola MS, Carey JP (2010) Waiting for the evidence: VEMP testing and the ability to differentiate utricular versus saccular function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:281–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.05.024
Singh NK, Apeksha K (2016) Efficacy of cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in evaluation of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:2523–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3867-3
Chen G, Dai X, Ren X, Lin N, Zhang M, Du Z, Zhang E (2020) Ocular vs. cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol 11:596454. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.596454
Gacek RR (2003) Pathology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo revisited. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 112:574–582. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940311200702
Brandt T, Huppert D, Hecht J, Karch C, Strupp M (2006) Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo: a long-term follow-up (6–17 years) of 125 patients. Acta Otolaryngol 126:160–163. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480500280140
Funding
This work was supported by Far Eastern Memorial Hospital (Grant number FEMH-2016-C-029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and the design of the work: CM Chang and PW Cheng. The acquisition of data and drafting of the manuscript: CM Chang, WC Lo, YH Young, LJ Liao, PH Wu, PC Cheng, and PW Cheng. The analysis and interpretation of data: CM Chang and PW Cheng. Supervisor: PW Cheng. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Research Ethics Review Committee of Far Eastern Memorial Hospital approved this study (No. 104136-E).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, CM., Lo, WC., Young, YH. et al. Evaluation of retrootolithic function using galvanic vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 3415–3423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07094-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07094-9