Abstract
Purpose
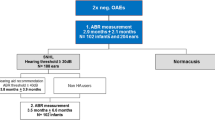
In this study, the efficacy and feasibility of melatonin in young children with and without comorbidities, undergoing auditory brainstem response audiometry (ABR) was evaluated. The aim of this study was primarily to evaluate the use of melatonin for ABR investigations in children with comorbidities. Second, the efficacy of melatonin was evaluated based on several factors like sleep-onset latency, sleep duration, frequency of awakenings as well as adverse events.
Methods
Click-induced ABR tests were performed at the outpatient clinic between January, 2018 and August, 2020. Investigations were considered successful when binaural testing was completed. A dose of melatonin depending on age, 5 mg for children younger than 6 years and 10 mg if older than 6 years, was administered after placement of electrodes.
Results
131 children were included in this study. 87% of all ABR investigations were performed successfully. Comorbidities such as neurodevelopmental disorders or developmental delays were present in 70% of all children. There was no significant difference in age (p = 0.36) or gender (p = 0.97) between the success and failed group. In addition, comorbidities were equally distributed between both groups. Mean sleep duration was 38 (SD 21) min and sleep-onset latency was 28 (SD 20) min No adverse events were documented.
Conclusion
Melatonin is effective for ABR examinations in infants and children with and without comorbidities. Furthermore, it allows for sequential testing in those at risk for progressive hearing loss. Clear instructions to caregivers and expertise of audiologists are a prerequisite for optimal outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007) Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 120(4):898–921
Avlonitou E, Balatsouras DG, Margaritis E, Giannakopoulos P, Douniadakis D, Tsakanikos M (2011) Use of chloral hydrate as a sedative for auditory brainstem response testing in a pediatric population. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75(6):760–763
Baculard F, Rieutord A, Eslami A, Cousin J, Van Den Abbeele T, Francois M (2007) Rectal pentobarbital sedation for children undergoing auditory brainstem response testing. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 124(2):61–65
Abulebda K, Patel VJ, Ahmed SS, Tori AJ, Lutfi R, Abu-Sultaneh S (2019) Comparison between chloral hydrate and propofol-ketamine as sedation regimens for pediatric auditory brainstem response testing. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 85(1):32–36
Schmidt CM, Knief A, Deuster D, Matulat P, am Zehnhoff-Dinnesen AG (2007) Melatonin is a useful alternative to sedation in children undergoing brainstem audiometry with an age dependent success rate–a field report of 250 investigations. Neuropediatrics 38(1):2–4
Guerlain J, Paul A, Rouillon I, Parodi M, Garabedian EN, Loundon N (2016) Efficiency of melatonin as compared to pentobarbital for audiometry brainstem response in children with associated disorders. Am J Audiol 25(3):206–210
Casteil L, Viquesnel A, Favier V, Guignard N, Blanchet C, Mondain M (2017) Study of the efficacy of melatonin for auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing in children. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 134(6):373–375
Hajjij A, Tahiri I, Anajar S, Essaadi M, Snoussi K (2020) Melatonin is useful alternative for sedation in children undergoing auditory brainstem responses testing. Eur J Pediatr 179(9):1431–1434
Busk Linnebjerg L, Wetke R (2013) Melatonin in children undergoing auditory brainstem response and auditory steady state response tests. Hearing Balance Commun 11(4):208–213. https://doi.org/10.3109/21695717.2013.855478
Claustrat B, Leston J (2015) Melatonin: physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie 61(2–3):77–84
Sander J, Shamdeen MG, Gottschling S, Gortner L, Graber S, Meyer S (2012) Melatonin does not influence sleep deprivation electroencephalogram recordings in children. Eur J Pediatr 171(4):675–679
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Reiter RJ (2011) Clinical uses of melatonin in pediatrics. Int J Pediatr 2011:892624
Dodge NN, Wilson GA (2001) Melatonin for treatment of sleep disorders in children with developmental disabilities. J Child Neurol 16(8):581–584
Schmidt CM, Bohlender JE, Deuster D, Knief A, Matulat P, Dinnesen AG (2004) The use of melatonin as an alternative to sedation in children undergoing brainstem audiometry. Laryngorhinootologie 83(8):523–528
Behrman DB, Bishop JL, Godsell J et al (2020) Efficacy of melatonin for auditory brainstem response testing in children: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 131:109861
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
All patients were managed in accordance with the routine clinical practice and ethical standards of the Antwerp University Hospital Antwerp.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struijk, C., van der Poel, N., Blommaerts, I. et al. The use of melatonin for auditory brainstem response audiometry in children with comorbidities. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 2303–2308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06923-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06923-1