Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to evaluate the speech intelligibility benefit in noise provided by stapedotomy in the treatment of unilateral otosclerosis.
Methods
We enrolled adults suffering from unilateral conductive hearing loss and followed them up until 9 months after surgery. The patients underwent a free field speech hearing evaluation using the French Matrix test before and after stapedotomy. Speech material was sent to the front of the patients (S0) and noise was presented either at the front (N0), or at the operated ear (N-90) or at the non-operated ear (N + 90). The speech intelligibility benefit in noise was assessed by comparing Squelch effect (SE), Head shadow effect (HS) and Binaural redundancy (BR) before and after surgery. SE was measured as the difference in speech reception thresholds (SRT) between S0N + 90 situations before and after surgery, HS as the difference in SRT between S0N + 90 and S0N-90 situations, and BR as the difference in SRT between S0N0 situations before and after surgery. In addition, two quality of life’s questionnaires were completed by patients to evaluate their discomfort.
Results
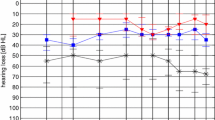
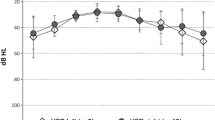
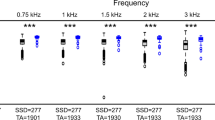
Among 25 patients, 19 were followed up during 9 months, 4 were excluded and 2 were lost for the following-up. Stapedotomy provided a restoration of SE of 3.7 dB SNR (p < 0.001) and a BR gain of 1.8 dB SNR (p < 0.001). HS did not show any statistical variation after surgery (p = 0.077). Finally, the questionnaires showed a residual hearing discomfort.
Conclusion
Stapedotomy provided a binaural benefit with the restoration of the SE and BR but which remained lower than in the normal-hearing population.
Trial Registration
The 07/02/2018 on Clinical.Trial.Gouv: NCT03587792.



Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Foster MF, Backous DD (2018) Clinical evaluation of the patient with otosclerosis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 51(2):319–326
Ealy M, Smith RJH (2011) Otosclerosis. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 70:122–129
Danesh AA, Shahnaz N, Hall JW (2018) The audiology of otosclerosis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 51(2):327–342
Batson L, Rizzolo D (2017) Otosclerosis: An update on diagnosis and treatment. JAAPA 30(2):17–22
Strömbäck K, Lundman L, Bjorsne A, Grendin J, Stjernquist-Desatnik A, Dahlin-Redfors Y (2017) Stapes surgery in Sweden: evaluation of a national-based register. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(6):2421–2427
Vincent R, Sperling NM, Oates J, Jindal M (2006) Surgical findings and long-term hearing results in 3,050 stapedotomies for primary otosclerosis: a prospective study with the otology-neurotology database. Otol Neurotol 27(8 Suppl 2):S25-47
de Souza JCR, Bento RF, Pereira LV, Ikari L, Souza SR, Della Torre AAG et al (2016) Evaluation of functional outcomes after stapes surgery in patients with clinical otosclerosis in a teaching institution. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 20(1):39–42
Avan P, Giraudet F, Büki B (2015) Importance of binaural hearing. Audiol Neurootol 20(Suppl 1):3–6
Sheffield SW, Romigh GD, Zurek PM, Bernstein JGW, Brungart DS (2019) A method for degrading sound localization while preserving binaural advantages for speech reception in noise. J Acoust Soc Am 145(2):1129
Arsenault MD, Punch JL (1999) Nonsense-syllable recognition in noise using monaural and binaural listening strategies. J Acoust Soc Am 105(3):1821–1830
Steven Colburn H, Shinn-Cunningham B, Kidd G, Durlach N (2006) The perceptual consequences of binaural hearing. Int J Audiol 45(Suppl 1):S34-44
Ahlstrom JB, Horwitz AR, Dubno JR (2009) Spatial benefit of bilateral hearing AIDS. Ear Hear 30(2):203–218
Schleich P, Nopp P, D’Haese P (2004) Head shadow, squelch, and summation effects in bilateral users of the MED-EL COMBI 40/40+ cochlear implant. Ear Hear 25(3):197–204
Rennies J, Kidd G (2018) Benefit of binaural listening as revealed by speech intelligibility and listening effort. J Acoust Soc Am 144(4):2147
Carlile S, Delaney S, Corderoy A (1999) The localisation of spectrally restricted sounds by human listeners. Hear Res 128(1–2):175–189
Luntz M, Egra-Dagan D, Attias J, Yehudai N, Most T, Shpak T (2014) From hearing with a cochlear implant and a contralateral hearing aid (CI/HA) to hearing with two cochlear implants (CI/CI): a within-subject design comparison. Otol Neurotol 35(10):1682–1690
Hey M, Hocke T, Hedderich J, Müller-Deile J (2014) Investigation of a matrix sentence test in noise: reproducibility and discrimination function in cochlear implant patients. Int J Audiol 53(12):895–902
Brand T, Kollmeier B (2002) Efficient adaptive procedures for threshold and concurrent slope estimates for psychophysics and speech intelligibility tests. J Acoust Soc Am 111(6):2801–2810
Kollmeier B, Warzybok A, Hochmuth S, Zokoll MA, Uslar V, Brand T et al (2015) The multilingual matrix test: principles, applications, and comparison across languages: a review. Int J Audiol 54(Suppl 2):3–16
Jansen S, Luts H, Wagener KC, Kollmeier B, Del Rio M, Dauman R et al (2012) Comparison of three types of French speech-in-noise tests: a multi-center study. Int J Audiol 51(3):164–173
Wagener KC, Brand T (2005) Sentence intelligibility in noise for listeners with normal hearing and hearing impairment: influence of measurement procedure and masking parameters. Int J Audiol 44(3):144–156
Gatehouse S, Noble W (2004) The speech, spatial and qualities of hearing scale (SSQ). Int J Audiol 43(2):85–99
Moulin A, Pauzie A, Richard C (2015) Validation of a French translation of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) and comparison with other language versions. Int J Audiol 54(12):889–898
Cox RM, Alexander GC (1995) The abbreviated profile of hearing aid benefit. Ear Hear 16(2):176–186
Löhler J, Gräbner F, Wollenberg B, Schlattmann P, Schönweiler R (2017) Sensitivity and specificity of the abbreviated profile of hearing aid benefit (APHAB). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(10):3593–3598
Wagener K, Josvassen JL, Ardenkjaer R (2003) Design, optimization and evaluation of a Danish sentence test in noise. Int J Audiol 42(1):10–17
Salcher R, Zimmermann D, Giere T, Lenarz T, Maier H (2017) Audiological results in SSD with an active transcutaneous bone conduction implant at a retrosigmoidal position. Otol Neurotol 38(5):642–647
Kraaijenga VJC, van Zon A, Smulders YE, Ramakers GGJ, Van Zanten GA, Stokroos RJ et al (2016) Development of a squelch effect in adult patients after simultaneous bilateral cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol 37(9):1300–1306
Cubick J, Buchholz JM, Best V, Lavandier M, Dau T (2018) Listening through hearing aids affects spatial perception and speech intelligibility in normal-hearing listeners. J Acoust Soc Am 144(5):2896
Bernstein JGW, Schuchman GI, Rivera AL (2017) Head shadow and binaural squelch for unilaterally deaf cochlear implantees. Otol Neurotol 38(7):e195-202
Akeroyd MA, Guy FH, Harrison DL, Suller SL (2014) A factor analysis of the SSQ (speech, spatial, and qualities of hearing scale). Int J Audiol 53(2):101–114
Hall JW, Derlacki EL (1986) Effect of conductive hearing loss and middle ear surgery on binaural hearing. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 95(5 Pt 1):525–530
Magliulo G, Gagliardi M, Muscatello M, Natale A (1990) Masking level difference before and after surgery in unilateral otosclerosis. Br J Audiol 24(2):117–121
Acknowledgements
We thank Alison Foote Ph.D. (Grenoble Alpes University Hospital, France) and Ihab Atallah MD, Ph.D. for English editing.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethics approval
ID CRB number 2017-A02900-53. The protocol was approved by a regional Ethics Committee (reference n° 17 12 01).
Consent to participate and for publication
All patients gave their oral and written consent kept in the department that conducted the study.
Availability of data and material
All the data are kept and are available in the department where the study was conducted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baguant, A., Schmerber, S., Baguant, K. et al. Binaural squelch effect in unilateral otosclerosis surgery: comparison of speech intelligibility in noise before-after surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 1301–1310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06797-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06797-3