Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the Programmed Cell Death Ligand (PD-L1) expression at diagnosis and relapse in patients with head and neck carcinoma (HNSCC) treated with radio(chemo)therapy.
Methods
PD-L1 immunohistochemistry was performed in tumor cells (TC) and immune cells (IC) in 44 patients and scored as 0 = 0%, 1 = < 5%, 2 = 6–49% or 3 = ≥ 50% cells.
Results
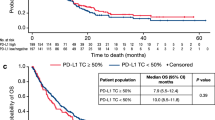
PD-L1 expression on TC before RT was scored as 0, 1, 2 and 3 in 28, 4, 8 and 4 patients, respectively. In 10 patients, IC did not show any PD-L1 expression; while in 8, 16, and 10 patients, PD-L1 expression was scored 1, 2 and 3, respectively. At relapse, 7/36 patients had a PD-L1 expression positivation in TC, while the opposite was observed in 6 patients. Overall, survival at 2 years was higher in patients with PD-L1 expression (90% versus 62.5%, p = 0.032).
Conclusion
PD-L1 expression may vary throughout the course of the disease. A re-evaluation of PD-L1 expression on biopsies at the time of recurrence should be recommended.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Costa AM, Young MR (2011) Immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: advances and deficiencies. Anticancer Drugs 22(7):674–681. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e328340fd18
Kiyota N, Hasegawa Y, Takahashi S et al (2017) A randomized, open-label, phase III clinical trial of nivolumab vs. therapy of investigator’s choice in recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a subanalysis of Asian patients versus the global population in checkmate 141. Oral Oncol 73:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.07.023.
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J et al (2016) Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 375(19):1856–1867. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1602252
Moskovitz JM, Moy J, Seiwert TY, Ferris RL (2017) Immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a review of current and emerging therapeutic options. Oncologist 22(6):680–693. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0318
Shahabi V, Postow MA, Tuck D, Wolchok JD (2015) Immune-priming of the tumor microenvironment by radiotherapy: rationale for combination with immunotherapy to improve anticancer efficacy. Am J Clin Oncol 38(1):90–97. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e3182868ec8
Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B et al (2014) Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J Clin Investig 124(2):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI67313
Dovedi SJ, Adlard AL, Lipowska-Bhalla G et al (2014) Acquired resistance to fractionated radiotherapy can be overcome by concurrent PD-L1 blockade. Can Res 74(19):5458–5468. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1258
Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I et al (2010) Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 28(19):3167–3175. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7609
Cho YA, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, Hong SP, Hong SD (2011) Relationship between the expressions of PD-L1 and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 47(12):1148–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.08.007
Lyford-Pike S, Peng S, Young GD et al (2013) Evidence for a role of the PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in immune resistance of HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Can Res 73(6):1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2384
Zandberg DP, Strome SE (2014) The role of the PD-L1:PD-1 pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol 50(7):627–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.04.003
Plavc G, Jesenko T, Orazem M, Strojan P (2020) Challenges in combining immunotherapy with radiotherapy in recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113197
Zargar M, McFarlane T, Chan KKW, Wong WWL (2017) Cost-Effectiveness of nivolumab in recurrent metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncologist. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0277
Ward MC, Shah C, Adelstein DJ, Geiger JL, Miller JA, Koyfman SA, Singer ME (2017) Cost-effectiveness of nivolumab for recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 74:49–55
Malm IJ, Bruno TC, Fu J et al (2015) Expression profile and in vitro blockade of programmed death-1 in human papillomavirus-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 37(8):1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.23706
Carbognin L, Pilotto S, Milella M et al (2015) Differential activity of nivolumab, pembrolizumab and MPDL3280A according to the tumor expression of programmed death-ligand-1 (PD-L1): sensitivity analysis of trials in melanoma, lung and genitourinary cancers. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0130142. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130142
Kim HR, Ha SJ, Hong MH et al (2016) PD-L1 expression on immune cells, but not on tumor cells, is a favorable prognostic factor for head and neck cancer patients. Sci Rep 6:36956. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36956
Powell SF, Gold KA, Gitau MM et al (2020) Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab with chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a phase IB study. J Clin Oncol: Off J Ame Soc Clin Oncol 38(21):2427–2437. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.03156
Outh-Gauer S, Le Tourneau C, Broudin C et al (2017) Current events in immunotherapy for upper aerodigestive tract cancer. Ann Pathol 37(1):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annpat.2016.12.013
Ferris RL (2015) Immunology and immunotherapy of head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol: Off J Ame Soc Clin Oncol 33(29):3293–3304. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.61.1509
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M et al (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7528):563–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14011
Feldman R, Gatalica Z, Knezetic J et al (2016) Molecular profiling of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1625-1638. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24290
Ukpo OC, Thorstad WL, Lewis JS Jr (2013) B7–H1 expression model for immune evasion in human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol 7(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-012-0406-z
Vassilakopoulou M, Avgeris M, Velcheti V et al (2016) Evaluation of PD-L1 expression and associated tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 22(3):704–713. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1543
Badoual C, Hans S, Merillon N et al (2013) PD-1-expressing tumor-infiltrating T cells are a favorable prognostic biomarker in HPV-associated head and neck cancer. Can Res 73(1):128–138. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2606
Karpathiou G, Casteillo F, Giroult JB et al (2017) Prognostic impact of immune microenvironment in laryngeal and pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: immune cell subtypes, immuno-suppressive pathways and clinicopathologic characteristics. Oncotarget 8(12):19310–19322. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14242
Lee Y, Auh SL, Wang Y et al (2009) Therapeutic effects of ablative radiation on local tumor require CD8+ T cells: changing strategies for cancer treatment. Blood 114(3):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-02-206870
Hecht M, Buttner-Herold M, Erlenbach-Wunsch K et al (2016) PD-L1 is upregulated by radiochemotherapy in rectal adenocarcinoma patients and associated with a favourable prognosis. Eur J Cancer 65:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2016.06.015
Lim SH, Hong M, Ahn S et al (2016) Changes in tumour expression of programmed death-ligand 1 after neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with squamous oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer 52:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.09.019
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR et al (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 366(26):2443–2454. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A et al (2015) Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 348(6230):124–128. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa1348
Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Polak P et al (2013) Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature 499(7457):214–218. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12213
Strome SE, Savva A, Brissett AE et al (2002) Squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsils: a molecular analysis of HPV associations. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 8(4):1093–1100
Seiwert TY, Burtness B, Mehra R et al (2016) Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol 17(7):956–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30066-3
Nagasaka M, Zaki M, Kim H et al (2016) PD1/PD-L1 inhibition as a potential radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a case report. J Immunother Cancer 4:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-016-0187-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AlD: Conceptualization; methodology; formal analysis and investigation; writing—original draft preparation; writing—review and editing. AU: Conceptualization; methodology; writing—review and editing; supervision. GL: Writing—review and editing; supervision. VC-C: Writing—review and editing; Supervision. OP: Writing—review and editing; supervision. FL: Conceptualization; methodology; writing—review and editing; supervision. US: Conceptualization; methodology; writing—review and editing; supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Yes.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delafoy, A., Uguen, A., Lemasson, G. et al. PD-L1 expression in recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 343–351 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06777-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06777-7