Abstract
Background
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a ubiquitous chronic disease with a growing incidence. We aimed to investigate the protective effect of naringenin against AR induced in rats.
Methods
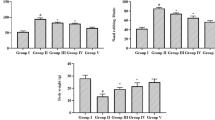
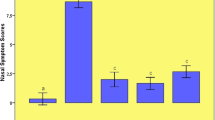
Thirty-two Sprague Dawley rats were divided into four groups of eight animals each. Group 1 represented the control group. The other 24 rats were sensitized with intraperitoneal 0.3 mg ovalbumin (OVA) and 30 mg aluminum hydroxide every other day for 14 days to induce AR. Ten microliters OVA was administered to both nostrils by inhalation for the following seven days to provoke AR. Group 2 represented the AR group and received no treatment. Group 3 was treated as the reference group and received 5 mg/kg desloratadine every day between days 15 and 21. Group 4 received 100 mg/kg naringenin orally between days 15 and 21. All animal’s sneezing and nasal itching scores were recorded on day 22. The rats were then sacrificed. Serum total IgE, IL4 and IL5 values were studied, and nasal structures were extracted ‘en bloc’ for histopathological examination.
Results
Significant clinical recovery was achieved in the group treated with naringenin. Serum total IgE, IL4 and IL5 values in the naringenin group were significantly lower than in the AR group, and significant histopathological improvement was observed compared to the AR group.
Conclusions
Naringenin produced significant clinical, biochemical and histopathological benefits in rats with induced AR. These effects suggest that naringenin is a promising agent for the treatment of AR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okubo K, Kurono Y, Fujieda S, Ogino S, Uchio E, Odajima H, Takenaka H (2014) Japanese guideline for allergic rhinitis 2014. AllergolInt 63(3):357–75
Nuhoglu C, Nuhoglu Y, Bankaoglu M, Ceran O (2010) A retrospective analysis of adenoidal size in children with allergic rhinitis and nonallergic idiopathic rhinitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 28(2–3):136
Kashiwabara M, Asano K, Mizuyoshi T, Kobayashi H (2016) Suppression of neuropeptide production by quercetin in allergic rhinitis model rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 16(1):132
Bousquet J, Schunemann H, Fonseca J, Samolinski B, Bachert C, Canonica GW, Casale T, Cruz A, Demoly P, Hellings P (2015) MACVIA-ARIA Sentinel NetworK for allergic rhinitis (MASK-rhinitis): the new generation guideline implementation. Allergy. 70(11):1372–92
Yasar M, Savranlar Y, Karaman H, Sagit M, Silici S, Ozcan I (2016) Effects of propolis in an experimental rat model of allergic rhinitis. Am J Otolaryngol 37(4):287–93
Erlund I (2004) Review of the flavonoids quercetin, hesperetin, and naringenin. Dietary sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, and epidemiology. Nutr Res 24(10):851–74
Hsiu S-L, Huang T-Y, Hou Y-C, Chin D-H, Chao P-DL (2002) Comparison of metabolic pharmacokinetics of naringin and naringenin in rabbits. Life Sci 70(13):1481–9
Ribeiro IA, Rocha J, Sepodes B, Mota-Filipe H, Ribeiro MH (2008) Effect of naringin enzymatic hydrolysis towards naringenin on the anti-inflammatory activity of both compounds. J MolCatal B Enzym 52:13–8
Tatar A, Parlak SN, Yayla M, Ugan RA, Polat E, Halici Z Eds (2015) Effects of allergic rhinitis and desloratadine on the submandibular gland in a rat allergy model. International Forum of Allergy and Rhinology, Wiley Online Library.
Sakat MS, Kilic K, Kandemir FM, Yildirim S, Sahin A, Kucukler S, Saglam YS (2018) The ameliorative effect of berberine and coenzyme Q10 in an ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis model. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(10):2495–505
Kilic K, Sakat MS, Yildirim S, Kandemir FM, Gozeler MS, Dortbudak MB, Kucukler S (2019) The amendatory effect of hesperidin and thymol in allergic rhinitis: an ovalbumin-induced rat model. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(2):407–15
Zhang Z, Kang H (2020) Protective effect of Asarumsieboldii essential oil on ovalbumin induced allergic rhinitis in rat. Biosci Rep 40(6):BSR20191370
Li J, Wang B, Luo Y, Zhang Q, Bian Y, Wang R (2020) Resveratrol-mediated SIRT1 activation attenuates ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in mice. MolImmunol 122:156–62
Greiner AN, Hellings PW, Rotiroti G, Scadding GK (2011) Allergic rhinitis. Lancet 378:2112–22
Ridolo E, Martignago I, Masieri S (2018) Mechanisms of allergic diseases in Otorhinolaryngology. J BiolRegulHomeost Agents 32(1 Suppl. 1):9
Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, Enomoto T, Okamoto Y, Kawauchi H, Suzaki H, Fujieda S, Masuyama K (2020) Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020. AllergolInt 69(3):331–45
Ren M, Tang Q, Chen F, Xing X, Huang Y, Tan X (2017) MahuangFuziXixin decoction attenuates Th1 and Th2 responses in the treatment of ovalbumin-induced allergic inflammation in a rat model of allergic rhinitis. J Immunol Res 2017:8254324
Jung HW, Jung J-K, Park Y-K (2011) Antiallergic effect of Ostericum koreanum root extract on ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse model and mast cells. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 29(4):338–48
Sagit M, Polat H, Gurgen SG, Berk E, Guler S, Yasar M (2017) Effectiveness of quercetin in an experimental rat model of allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(8):3087–95
Thakare VN, Osama M, Naik SR (2013) Therapeutic potential of curcumin in experimentally induced allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs. IntImmunopharmacol 17(1):18–25
Bozdemir K, Şahin E, Altintoprak N, Muluk NB, Cengiz BP, Acar M, Cingi C (2016) Is resveratrol therapeutic when used to treat allergic rhinitis in rats? Clin Invest Med 39(2):E63–E72
Rehman MU, Rahman Mir MU, Farooq A, Rashid SM, Ahmad B, Bilal Ahmad S, Ali R, Hussain I, Masoodi M, Muzamil S (2018) Naringenin (4, 5, 7-trihydroxyflavanone) suppresses the development of precancerous lesions via controlling hyperproliferation and inflammation in the colon of Wistar rats. Environ Toxicol 33(4):422–35
Da Pozzo E, Costa B, Cavallini C, Testai L, Martelli A, Calderone V, Martini C (2017) The citrus flavanonenaringenin protects myocardial cells against age-associated damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:9536148
Koçak İ, Sarac S, Aydogan E, Şentürk E, Akakın D, Koroglu K, Özer Ö (2017) Evaluation of the possible protective role of naringenin on gentamicin-induced ototoxicity: a preliminary study. Int J PediatrOtorhinolaryngol 100:247–53
Zhang L, Xu X, Jiang T, Wu K, Ding C, Liu Z, Zhang X, Yu T, Song C (2018) Citrus aurantiumnaringenin prevents osteosarcoma progression and recurrence in the patients who underwent osteosarcoma surgery by improving antioxidant capability. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:8713263
Manchope MF, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2017) Naringenin: an analgesic and anti-inflammatory citrus flavanone. Oncotarget 8(3):3766
Maatouk M, Elgueder D, Mustapha N, Chaaban H, Bzéouich IM, Loannou I, Kilani S, Ghoul M, Ghedira K, Chekir-Ghedira L (2016) Effect of heated naringenin on immunomodulatory properties and cellular antioxidant activity. Cell Stress Chaperones 21(6):1101–9
Fan R, Pan T, Zhu A-L, Zhang M-H (2017) Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic properties of naringenin via attenuation of NF-κB and activation of the heme oxygenase (HO)-1/related factor 2 pathway. Pharmacol Rep 69(5):1021–9
Shi Y, Dai J, Liu H, Li R-R, Sun P-L, Du Q, Pang L-l, Chen Z, Yin K-S (2009) Naringenin inhibits allergen-induced airway inflammation and airway responsiveness and inhibits NF-κB activity in a murine model of asthma. Can J PhysiolPharmacol 87(9):729–35
Shi Y, Tan Y, Mao S, Gu W (2014) Naringenin inhibits allergen-induced airway remodeling in a murine model of asthma. Mol Med Rep 9(4):1204–8
Iwamura C, Shinoda K, Yoshimura M, Watanabe Y, Obata A, Nakayama T (2010) Naringenin chalcone suppresses allergic asthma by inhibiting the type-2 function of CD4 T cells. AllergolInt 59(1):67–73
Moon P-D, Choi I-H, Kim H-M (2011) Naringenin suppresses the production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin through the blockade of RIP2 and caspase-1 signal cascade in mast cells. Eur J Pharmacol 671(1–3):128–32
Han NR, Moon PD, Ryu KJ, Kim NR, Kim HM, Jeong HJ (2018) Inhibitory effect of naringenin via IL-13 level regulation on thymic stromal lymphopoietin-induced inflammatory reactions. ClinExpPharmacolPhysiol 45(4):362–9
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in accordance with the PHS Policy on Human Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the Animal Welfare Act (7 U.S.C. et seq.); the animal use protocol was approved by the Animal Experiments ethical committee of Ataturk University. (No. E.1700320360-13:158;160).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şahin, A., Sakat, M.S., Kılıç, K. et al. The protective effect of Naringenin against ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 4839–4846 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06769-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06769-7