Abstract
Purpose
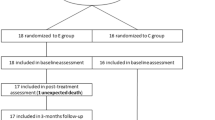
The aim of the study is to demonstrate the effectiveness of spraying odor particles using sinus rinse kits for olfactory rehabilitation in patients with total laryngectomy.
Methods
Olfactory rehabilitation was performed by applying four different odorant particles orthonasally using a sinus rinse kit pump for 30 min each day for a duration of 6 months. Olfactory function was evaluated by performing olfactory tests before the rehabilitation and at sixth month after the rehabilitation process.
Results
The average CCCRC score prior to olfactory rehabilitation was 2.28 ± 0.79 (between 1.50 and 3.75), while it was 4.46 ± 0.5 (between 3.50 and 5.25) out of a maximum score of 7 after 6 months of olfactory rehabilitation (p value < 0.0001)
Conclusion
Our results suggest that the use of sinus rinse kits is very simple, inexpensive, easy-to-use, and effective in providing passive olfaction to patients requiring olfactory rehabilitation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanna E, Sherman A, Cash D, Adams D, Vural E, Fan CY et al (2004) Quality of life for patients following total laryngectomy vs chemoradiation for laryngeal preservation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:875–879. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.130.7.875
Johnson JT, Casper J, Lesswing NJ (1979) Toward the total rehabilitation of the alaryngeal patient. Laryngoscope 89:1813–1819. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-197911000-00014
Ackerstaff AH, Hilgers FJ, Aaronson NK, Balm AJ (1994) Communication, functional disorders and lifestyle changes after total laryngectomy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 19:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.1994.tb01234
Arthur C. Guyton, John E. Hall. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 10. Edition. 2000;678–81
Richard L Doty. Handbook of Olfaction and Gustation: Second Edition, Revised and Expanded, 2003;630–38
Veyseller B, Ozucer B, Aksoy F, Yildirim YS, Gürbüz D, Balikçi HH et al (2012) Reduced olfactory bulb volume and diminished olfactory function in total laryngectomy patients: a prospective longitudinal study. Am J Rhinol Allergy 26:191–193. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2012.26.3768
Veyseller B, Aksoy F, Yildirim YS, Bayraktar FG, Gurbuz D, Savas Y et al. Reduced olfactory bulb volume in total laryngectomy patients: a magnetic resonance imaging study.Rhinology 2011;49:112–6 https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhino10.001
Hilgers FJM, Van Dam FSAM, Keyzers S, Koster MN, van As CJ, MullerMJ. Rehabilitation of olfaction after laryngectomy by means of a nasal airflow-inducing manoeuvre—the “polite yawning” technique. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;126:726–32 https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.126.6.726
Hilgers FJM, Jansen HA, Van As CJ, Polak MF, Muller MJ, van dam Frits SAM. Long-term results of olfaction rehabilitation using the nasal airflow-inducing “polite yawning” manoeuvre after total laryngectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002;128:648–54 https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.128.6.648
Goktas O, Fleiner F, Paschen C, Lammert I, Schrom T (2008) Rehabilitation of the olfactory sense after laryngectomy: long-term use of the larynx bypass. Ear Nose Throat J 87:528–530. https://doi.org/10.1177/014556130808700913
Moor JW, Rafferty A, Sood S (2010) Can laryngectomees smell? Considerations regarding olfactory rehabilitation following total laryngectomy. J Laryngol Otol 124:361–365. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215109992489
Goektas O, Fleiner F, Frieler K, Scherer H, Paschen C (2008) The scent-diffusing ventilator for rehabilitation of olfactory function after laryngectomy. Am J Rhinol 22:487–490. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajr.2008.22.3213
Cain WS, Gent JF, Goodspeed RB, Leonard G (1988) Evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in the connecticut chemosensory clinical research center. Laryngoscope 98:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198801000-00017
Kern RC (2000) Chronic sinusitis and anosmia: pathologic changes in the olfactory mucosa. Laryngoscope 110:1071–1077. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200007000-00001
Konstantinidis I, Tsakiropoulou E, Constantinidis J (2016) Long term effects of olfactory training in patients with post-infectious olfactory loss. Rhinology 54:170–175. https://doi.org/10.4193/rhin15.264
Pellegrino R, Han P, Reither N, Hummel T (2019) Effectiveness of olfactory training on different severities of posttraumatic loss of smell. Laryngoscope 129:1737–1743. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27832
Callahan CD, Hinkebein JH (2002) Assessment of anosmia after traumatic brain injury: performance characteristics of the University of Pennsylvania smell identification test. J Head Trauma Rehabil 17:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001199-200206000-00006
Hawkes C (2003) Olfaction in neurodegenerative disorder. Mov Disord 18:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10379
Klimek L, Moll B, Amedee RG, Mann WJ (1997) Olfactory function after microscopic endonasal surgery in patients with nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol 11:251–255. https://doi.org/10.2500/105065897781446621
Moore-Gillon V (1985) The nose after laryngectomy. J R Soc Med 78:435–439. https://doi.org/10.1177/014107688507800603
Ritter FN (1964) Fate of olfaction after laryngectomy. Arch Otolaryngol 79:169–171. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1964.00750030175013
Fuji M, Fukazawa K, Hatta C, Yasuno H, Sakagami M (2002) Olfactory acuity after total laryngectomy. Chem Senses 27:117–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/27.2.117
Van Dam FS, Hilgers FJ, Emsbroek G, Touw FI, van As CJ, de Jong N (1999) Deterioration of olfaction and gustation as a consequence of total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 109:1150–1155. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199907000-00027
Henkin RI, Hoye RC, Ketcham AS, Gould WJ (1968) Hyposmia following laryngectomy. Lancet 2:479–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90647-8
Schwartz DN, Mozell MM, Youngentob SL (1987) Improvement of olfaction in laryngectomised patients with the larynx bypass. Laryngoscope 97:1280–1286. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198711000-00006
Goktas O, Lammert I, Bert J (2005) Rehabilitation of the olfactory sense after laryngectomy the larynx bypass [in German]. Laryngorhinootologie 84:829–832. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-870117
Gilchrist AG (1973) Rehabilitation after laryngectomy. Acta Otolaryngol 75:511–518. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016487309139782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare, as this report is not industry-sponsored, and we did not receive any financial support.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kesimli, M.C., Kaya, D., Aydemir, L. et al. A simple method for olfactory rehabilitation following total laryngectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 4917–4921 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06711-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06711-x