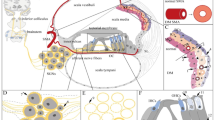
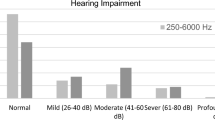
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, which, over time, lead to major chronic complications in various organs of the body. A growing body of research suggests that diabetes could also result in degenerative changes in the auditory system. To date, several attempts have been made to prevent and reduce diabetes-induced auditory complications. Such attempts have generally focused on disease modifying as well as other pharmacological treatments involving several herbal and non-herbal agents such as vitamins C and E, rutin, resveratrol, coffee, trigonelline, Dioscorea nipponica, red ginseng, Pterostilbene Bofutsushosan, Daisaikoto, tolrestat, ACE inhibitors (enalapril), Ca antagonists (nimodipine), Lipo-prostaglandin E1, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, and chlorogenic acid and also other strategies like acupuncture. However, there is no consensus about which are the most effective strategies for preventing and reducing auditory complications in diabetic patients with few side effects and maximum efficacy. This paper provides a comprehensive review of interventions for preventing and treating diabetes-induced auditory complications to help therapists.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olokoba AB, Obateru OA, Olokoba LB (2012) Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of current trends. Oman Med J 27(4):269–273
Gikas A, Sotiropoulos A, Pastromas V, Papazafiropoulou A, Apostolou O, Pappas S (2009) Seasonal variation in fasting glucose and A1C in patients with type 2 diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes 3(2):111–114
Asmat U, Abad Kh, Ismail Kh (2016) Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress––a concise. Saudi Pharm J 24(5):547–553
Fowler MJ (2008) Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 26(2):77–82
American Diabetes Association (2014) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37(1):81–90
Rance G, Chisari D, O’Hare F, Roberts L, Shaw J, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Szmulewicz D (2014) Auditory neuropathy in individuals with Type 1 diabetes. J Neurol 261(8):1531–1536
Rajamani S, Senniappan S, Radhakrishnan S (2018) Prevalence and factors influencing sensorineural hearing loss among type II diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Adv Med 5(3):732–737
Tsuda J, Sugahara K, Hori T, Kanagawa E, Takaki E, Fujimoto M et al (2016) A study of hearing function and histopathologic changes in the cochlea of the type 2 diabetes model Tsumura Suzuki obese diabetes mouse. Acta Otolaryngol 136(11):1097–1106
Helzner EP, Contrera KJ (2016) Type 2 diabetes and hearing impairment. Curr Diab Rep 16(1):3
Teng ZP, Tian R, Xing FL, Tang H, Xu JJ, Zhang BW, Qi JW (2017) An association of type 1 diabetes mellitus with auditory dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 127(7):1689–1697
Akinpelu OV, Mujica-Mota M, Daniel SJ (2014) Is type 2 diabetes mellitus associated with alterations in hearing? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 124(3):767–776
Dabrowski M, Mielnik-Niedzielska G, Nowakowski A (2013) Impact of different modifiable factors on hearing function in type 1 and type 2 diabetic subjects. A preliminary study. Ann Agric Environ Med 20(4):773–778
Diaz de León-Morales LV, Jáuregui-Renaud K, Garay-Sevilla ME, Hernández-Prado J, Malacara-Hernández JM (2005) Auditory impairment in patients with type diabetes mellitus. Arch Med Res 36(5):507–510
Khattar D, Khaliq F, Vaney N, Madhu SV (2016) Delayed auditory conduction in diabetes: is metformin-induced vitamin B12 deficiency responsible? Funct Neurol 31(2):95–100
Verma A, Bisht MS, Ahuja GK (1984) Involvement of central nervous system in diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47(4):414–416
Konrad-Martin D, Austin DF, Griest S, McMillan GP, McDermott D, Fausti S (2010) Diabetes-related changes in auditory brainstem responses. Laryngoscope 120(1):150–158
Biessels GJ, Cristino NA, Rutten GJ, Hamers FP, Erkelens DW, Gispen WH (1999) Neurophysiological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Course of development and effects of insulin treatment. Brain 122(4):757–768
Hong BN, Kang TH (2014) Distinction between auditory electrophysiological responses in type 1 and type 2 diabetic animal models. Neurosci Lett 5:309–314
Hong BN, Nam YH, Woo SH, Kang TH (2017) Chlorogenic acid rescues sensorineural auditory function in a diabetic animal model. Neurosci Lett 640:64–69
Hong BN, Yi TH, Park R, Kim SY, Kang TH (2008) Coffee improves auditory neuropathy in diabetic mice. Neurosci Lett 441(3):302–306
Fowler CG, Chiasson KB, Colman RJ, Kemnitz JW, Beasley TM, Weindruch RH (2015) Hyperinsulinemia/diabetes, hearing, and aging in the University of Wisconsin calorie restriction monkeys. Hear Res 328:78–86
Shehata G, Eltayeb A (2010) Cognitive function and event-related potentials in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Child Neurol 25(4):469–474
Cooray G, Nilsson E, Wahlin A, Laukka EJ, Brismar K, Brismar T (2011) Effects of intensified metabolic control on CNS function in type 2 diabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36(1):77–86
Mochizuki Y, Oishi M, Hayakawa Y, Matsuzaki M, Takasu T (1998) Improvement of P300 latency by treatment in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Electroencephalogr 29(4):194–196
Chen HC, Chung CH, Lu CH, Chien WC (2019) Metformin decreases the risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in patients with diabetes mellitus: a 14-year follow-up study. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res 16(4):324–327
Muñoz-Carlin Mde L, Rodríguez-Moctezuma JR, Gómez Latorre JG, Montes-Castillo ML, Juárez-Adauta S (2010) Effects of glycine on auditory evoked potentials among diabetic patients with auditory pathway neuropathy. Rev Med Chil 138(10):1246–1252
Ma F, Gomez-Marin O, Lee DJ, Balkany T (1998) Diabetes and hearing impairment in Mexican American adults: a population based study. J Laryngol Otol 112:835–839
Virtaniemi J, Kuusisto J, Karjalainen L, Karjalainen S, Laakso M (1995) Improvement of metabolic control does not normalize auditory brainstem latencies in subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Otolaryngol 16(3):172–176
Asma A, Azmi MN, Mazita A, Marina MB, Salina H, Norlaila M (2011) A single blinded randomized controlled study of the effect of conventional oral hypoglycemic agents versus intensive short-term insulin therapy on pure tone audiometry in type ii diabetes mellitus. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63(2):114–118
Bainbridge KE, Cowie CC, Gonzalez F 2nd, Hoffman HJ, Dinces E, Stamler J, Cruickshanks KJ (2016) Risk factors for hearing impairment among adults with diabetes: the hispanic community health study/study of latinos (HCHS/SOL). J Clin Transl Endocrinol 6:15–22
Castañeda R, Rodriguez I, Nam YH, Hong BN, Kang TH (2017) Trigonelline promotes auditory function through nerve growth factor signaling on diabetic animal models. Phytomedicine 36:128–136
Erkan SO, Tuhanioğlu B, Gürgen SG, Özdaş T, Taştekin B, Pelit A, Görgülü O (2019) The effect of resveratrol on the histologic characteristics of the cochlea in diabetic rats. Laryngoscope 129(1):E1–E6
Gonzalez-Gonzalez S, Cazevieille C, Caumes B (2020) Resveratrol treatment reduces neuromotor impairment and hearing loss in a mouse model of diabetic neuropathy and nerve injury. J Diabetes Clin Res 2(2):59–67
Suzuki S, Hinokio Y, Ohtomo M, Hirai M, Hirai A, Chiba M et al (1998) The effects of coenzyme Q10 treatment on maternally inherited diabetes mellitus and deafness, and mitochondrial DNA 3243 (A to G) mutation. Diabetologia 41(5):584–588
Hong BN, Yi TH, Kim SY, Kang TH (2009) High-dosage pyridoxine-induced auditory neuropathy and protection with coffee in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 32(4):597–603
Hong BN, Ji MG, Kang TH (2013) The efficacy of red ginseng in type 1 and type 2 diabetes in animals. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:593181
Nam YH, Moon HW, Lee YR, Kim EY, Rodriguez I, Jeong SY, Castañeda R, Park JH, Choung SY, Hong BN, Kang TH (2019) Panax ginseng (Korea Red Ginseng) repairs diabetic sensorineural damage through promotion of the nerve growth factor pathway in diabetic zebrafish. J Ginseng Res 43(2):272–281
Lee YR, Hong BN, Her YR, Castañeda R, Moon HW, Kang TH (2015) Amelioration of auditory response by DA9801 in diabetic mouse. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 230747
Kim DH, Hong BN, Le HT, Hong HN, Lim CW, Park KH, Kim TW, Kang TH (2012) Small molecular weight PEGylation of diosgenin in an in vivo animal study for diabetic auditory impairment treatment. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22(14):4609–4612
Özdaş S, Taştekin B, Gürgen SG, Özdaş T, Pelit A, Erkan SO et al (2020) Pterostilbene protects cochlea from ototoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by inhibiting the apoptosis. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.16.908798
Hori T, Sugahara K, Tsuda J, Hirose Y, Hashimoto M, Takemoto Y et al (2019) Oral administration of an herbal medicine to prevent progressive hearing loss in a mouse model of diabetes. Auris Nasus Larynx 46(5):703–708
Merkhan M, Abdullah K (2019) The role of vitamin C and E in improving hearing loss in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Coll Med Mosul 41(1):184–189
Doostkam A, Mirkhani H, Iravani K, Karbalay-Doust S, Zarei K (2020) Effect of rutin on diabetic auditory neuropathy in an experimental rat model. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.02068
Yildiz O, Ozata M, Ozkardeş A, Corakçi A, Gündoğan N, Gündoğan MA (1996) carnitine treatment improves brain stem auditory evoked potentials in diabetic rats. NeuroReport 7(18):2957–2959
Notvest RR, Inserra JJ (1987) Tolrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor, prevents nerve dysfunction in conscious diabetic rats. Diabetes 36(4):500–504
Biessels GJ, Laak M, Kamal A, Gispen WH (2005) Effects of the Ca2+ antagonist nimodipine on functional deficits in the peripheral and central nervous system of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Brain Res 1035:86–93
Manschot SM, Gispen WH, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ (2003) Nerve conduction velocity and evoked potential latencies in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: effects of treatment with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 19(6):469–477
Ahn JH, Kim TY, Kim YJ, Han MW, Yoon TH, Chung JW (2006) Lipo-prostaglandin E1 in combination with steroid therapy is effective for treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in Korean patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 23(12):1339–1343
Li X, Wang R, Sun LJ, Jiang ZG, Fu ZQ, Guo Y, et al (2010) Study of intratympanic methylprednisolone injections in diabetics with a sudden sensorineural hearing loss. 90(44):3103–6
Yang W, Li X, Zhong J, Mei X, Liu H, Yang L (2020) et Intratympanic versus intravenous corticosteroid treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients: proposed study protocol for a prospective, randomized superiority trial. Trials 21(1):135
Kakehata S, Sasaki A, Oji K, Futai K, Ota S, Makinae K, Shinkawa H (2006) Comparison of intratympanic and intravenous dexamethasone treatment on sudden sensorineural hearing loss with diabetes. Otol Neurotol 27(5):604–608
Li J, Zhang X, Guo H, Zhang Y, Sun N, Wang L (2016) Acupuncture for tinnitus, hearing loss in patients with type 2 diabetes using the twirling; reinforcing-reducing. Int J Tradit Chin Med 38(8):713–716
Agrawal Y, Carey JP, Della Santina CC, Schubert MC, Minor LB (2009) Disorders of balance and vestibular function in US adults: data from the national health and nutrition examination survey, 2001–2004. Arch Intern Med 169(10):938–944
Kamali B, Hajiabolhassan F, Fatahi J, Nasli Esfahani E, Sarrafzadeh J, Faghihzadeh S (2013) Effects of diabetes mellitus type Ι with or without neuropathy on vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Acta Med Iran 51:107–112
Román-Pintos LM, Villegas-Rivera G, Rodríguez-Carrizalez AD, Miranda-Díaz AG, Cardona-Muñoz EG (2016) Diabetic polyneuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. J Diabetes Res 2016:3425617
Unal M, Vayisglu Y (2015) Auditory neuropathy/dyssynchrony: a retrospective analysis of 15 cases. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 19(2):151–155
Skyler JS (2004) Effects of glycemic control on diabetes complications and on the prevention of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 22(4):162–166
Scicchitano P, Cameli M, Maiello M, Modesti PA, Muiesan ML, Novo S, Palmiero P, Saba PS, Pedrinelli R, Ciccone MM (2014) Nutraceuticals and dyslipidaemia: beyond the common therapeutics. J Funct Foods 6:11–32
Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Pinto M, Di Teo C, Fornarelli F, Gesualdo M, Mezzina A, Sabatelli E, Scicchitano P, Quaranta N (2012) Endothelial function and cardiovascular risk in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Atherosclerosis 225(2):511–516
Hao J, Hua L, Fu X, Zhang X, Zou Q, Li Y (2018) Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of human peripheral blood reveals susceptibility loci of diabetes-related hearing loss. J Hum Genet 63(12):1241–1250
Funding
This research received no specific Grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajiabolhassan, F., Tavanai, E. Diabetes-induced auditory complications: are they preventable? a comprehensive review of interventions. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 3653–3665 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06630-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06630-x