Abstract
Objective
The present meta-analysis aims to compare the efficacy of intratympanic steroid (ITS) injection and hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy as salvage treatments for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL).
Data sources
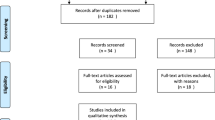
Comprehensive searches were performed in PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library from the date of the database inception to June 2020. All studies reporting the use of salvage ITS and HBO treatments in refractory SSNHL patients were included. Subsequently, the full texts of the eligible studies were evaluated.
Methods
The quality and bias of the studies were assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale and Cochrane’s risk of bias tools for nonrandomized and randomized studies, respectively. The data were analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software (Version 3; Biostat, Englewood, NJ).
Results
Three hundred and fourteen subjects in 3 observational studies and 1 randomized controlled trial met our inclusion criteria. The pooled results demonstrated that there were no significant differences in the mean posttreatment hearing gain between the ITS and HBO groups. The changes in word discrimination and hearing gain at 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 and 8000 Hz were also comparable between the two salvage treatment groups.
Conclusions
The pooled results demonstrated that there were no significant differences in hearing improvements between salvage ITS injection and salvage HBO therapy after failed primary systemic steroid treatment in patients with SSNHL. However, spontaneous recovery could bias the treatment outcomes, and these results should be interpreted with caution. Clinicians may choose these salvage treatments according to personal experience and treatment availability. In cases in which specialized HBO facilities are difficult to access, salvage ITS injection can be provided with comparable responses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM et al (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 146(3_suppl):S1–S35
Byl FM Jr (1984) Sudden hearing loss: eight years’ experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope 94(5 Pt 1):647–661
Seggas I, Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A, Tzonou A, Sismanis A (2011) Intratympanic steroid therapy for sudden hearing loss: a review of the literature. Otol Neurotol 32(1):29–35
Arastou S, Tajedini A, Borghei P (2013) Combined intratympanic and systemic steroid therapy for poor-prognosis sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 25(70):23–28
Battaglia A, Burchette R, Cueva R (2008) Combination therapy (intratympanic dexamethasone + high-dose prednisone taper) for the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 29(4):453–460
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR et al (2019) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update) executive summary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 161(2):195–210
Lazarini PR, Camargo AC (2006) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: etiopathogenic aspects. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 72(4):554–561
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD (2010) Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 120(5):1011–1021
Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A, Sismanis A, Tzonou A, Seggas I (2013) Intratympanic and systemic steroids for sudden hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 34(4):771–776
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N (1980) The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol 106(12):772–776
Li H, Feng G, Wang H, Feng Y (2015) Intratympanic steroid therapy as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of conventional therapy: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Clin Ther 37(1):178–187
Imsuwansri T, Poonsap P, Snidvongs K (2012) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure from oral and intratympanic corticosteroid. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 5(Suppl 1):S99-s102
Hosokawa S, Sugiyama KI, Takahashi G et al (2017) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as adjuvant treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic steroids. Audiol Neurootol 22(1):9–14
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928
Wells GA, Shea B, O’connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M et al. The Newcastle-ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm [cited 01 Sep 2020]
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Cvorovic L, Jovanovic MB, Milutinovic Z, Arsovic N, Djeric D (2013) Randomized prospective trial of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and intratympanic steroid injection as salvage treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 34(6):1021–1026
Gülüstan F, Yazıcı ZM, Alakhras WM et al (2018) Intratympanic steroid injection and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of refractory sudden hearing loss. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 84:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.10.013
Sun H, Qiu X, Hu J, Ma Z (2018) Comparison of intratympanic dexamethasone therapy and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the salvage treatment of refractory high-frequency sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol 39(5):531–535
Yang CH, Wu RW, Hwang CF (2013) Comparison of intratympanic steroid injection, hyperbaric oxygen and combination therapy in refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 34(8):1411–1416
El Sabbagh NG, Sewitch MJ, Bezdjian A, Daniel SJ (2017) Intratympanic dexamethasone in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 127(8):1897–1908
Ng JH, Ho RC, Cheong CS, Ng A, Yuen HW, Ngo RY (2015) Intratympanic steroids as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss? A meta-analysis Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(10):2777–2782
Agarwal L, Pothier DD (2009) Vasodilators and vasoactive substances for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:D003422
O’Malley MR, Haynes DS (2008) Sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 41(3):633–649 (x–xi)
Zhao D, Tong B, Wang Q, Hellstrom S, Duan M (2016) A comparison of effects of systemic and intratympanic steroid therapies for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis. J Otol 11(1):18–23
Goto F, Fujita T, Kitani Y, Kanno M, Kamei T, Ishii H (1979) Hyperbaric oxygen and stellate ganglion blocks for idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 88(5–6):335–342
Lamm K, Lamm C, Arnold W (1998) Effect of isobaric oxygen versus hyperbaric oxygen on the normal and noise-damaged hypoxic and ischemic guinea pig inner ear. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 54:59–85
Plafki C, Peters P, Almeling M, Welslau W, Busch R (2000) Complications and side effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Aviat Space Environ Med 71(2):119–124
Muzzi E, Zennaro B, Visentin R, Soldano F, Sacilotto C (2010) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: review of rationale and preliminary report. J Laryngol Otol 124(2):e2
Kitoh R, Nishio S-Y, Usami S-I (2020) Treatment algorithm for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss based on epidemiologic surveys of a large Japanese cohort. Acta Otolaryngol 140(1):32–39
Almosnino G, Holm JR, Schwartz SR, Zeitler DM (2018) The role of hyperbaric oxygen as salvage therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 127(10):672–676
Bayoumy AB, van der Veen EL, Alexander de Ru J (2018) Assessment of spontaneous recovery rates in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144:655–656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T-CK: conduct and analysis. W-CC: design and interpretation of data. C-HY: interpretation of data. M-ST: interpretation of data. Y-TT: interpretation of data. Y-CL: design, analysis and interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, TC., Chao, WC., Yang, CH. et al. Intratympanic steroid injection versus hyperbaric oxygen therapy in refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279, 83–90 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06616-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-06616-9