Abstract
Background
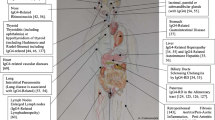
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a multi-organ immune-mediated disorder characterized by fibroinflammatory mass-forming lesions, mimicking malignancy or infection. While well-documented in salivary glands, orbit and thyroid in the head and neck, sinonasal IgG4-RD is rare.
Methods
Cases of sinonasal IgG4-RD were retrieved, and clinicopathological features reviewed.
Results
Seven cases of sinonasal IgG4-RD were identified over a 2-year period, including three males and four females, with an age range of 13–48 years (median: 32 years). Patients presented with cheek swelling, pain and visual disturbances. Serum IgG4 levels were mildly elevated. Storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis and plasma cell infiltration were seen in varying proportions. Destruction of bone and subepithelial mucoserous glands was present. ALK-1 negativity distinguished from inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor.
Conclusion
Sinonasal IgG4-RD expands the growing spectrum of IgG4-RD. A high degree of suspicion is required to include IgG4-RD in differential diagnosis of sinonasal masses, and perform detailed histological and immunohistochemical workup for accurate diagnosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A (2008) IgG4-related sclerosing disease. World J Gastroenterol 14:3948–3955
Ishida M, Hotta M, Kushima R, Shibayama M, Shimizu T, Okabe H (2009) Multiple IgG4-related sclerosing lesions in the maxillary sinus, parotid gland and nasal septum. Pathol Int 59:670–675
Kasashima S, Zen Y, Kawashima A et al (2008) Inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm: close relationship to IgG4-related periaortitis. Am J Surg Pathol 32:197–204
Takano K, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Himi T (2017) Recent advances in knowledge regarding the head and neck manifestations of IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx 44:7–17
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK et al (2012) Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 25:1181–1192
Ikeda R, Awataguchi T, Shoji F, Oshima T (2010) A case of paranasal sinus lesions in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142:458–459
Prabhu SM, Yadav V, Irodi A, Mani S, Varghese AM (2014) IgG4-related disease with sinonasal involvement: a case series. Indian J Radiol Imaging 24:117–120
Sasaki T, Takahashi K, Mineta M, Fujita T, Aburano T (2012) Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease mimicking invasive tumor in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Am J Neuroradiol 33:E19–E20
Song BH, Baiyee D, Liang J (2015) A rare and emerging entity: sinonasal IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Allergy Rhinol (Providence) 6:151–157
Pace C, Ward S (2010) A rare case of IgG4-related sclerosing disease of the maxillary sinus associated with bone destruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:2591–2593
Alt JA, Whitaker GT, Allan RW, Vaysberg M (2012) Locally destructive skull base lesion: IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Allergy Rhinol (Providence) 3:e41–e45
Lindau RH, Su YB, Kobayashi R, Smith RB (2013) Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease of the paranasal sinus. Head Neck 35:E321–E324
Cain RB, Colby TV, Balan V, Patel NP, Lal D (2014) Perplexing lesions of the sinonasal cavity and skull base: IgG4-related and similar inflammatory diseases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 151:496–502
Stone JH, Brito-Zeron P, Bosch X, Ramos-Casals M (2015) Diagnostic approach to the complexity of IgG4-related disease. Mayo Clinic Proc 90:927–939
Piao Y, Zhang Y, Yue C, Wang C, Zhang L (2018) Immunoglobulin G4-related chronic rhinosinusitis: a pitfall in the differential diagnosis of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Rosai- Dorfman disease, and fungal rhinosinusitis. Hum Pathol 73:82–88
Nishihara E, Hirokawa M, Ito M et al (2015) Graves’ disease patients with persistent hyperthyroidism and diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in the thyroid show no histopathological compatibility with IgG4-related disease. PLoS ONE 10:e0134143
Arora K, Rivera M, Ting DT, Deshpande V (2019) The histological diagnosis of IgG4-related disease on small biopsies: challenges and pitfalls. Histopathology 74:688–698
Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S et al (2020) The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 79:77–87
Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M et al (2015) Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis 74:190–195
Toyoda K, Oba H, Kutomi K, Furui S, Oohara A, Mori H et al (2012) MR Imaging of IgG4-Related Disease in the Head and Neck and Brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:2136–2139
Fujita A, Sakai O, Chapman MN, Sugimoto H (2012) IgG4-related disease of the head and neck: CT and MR imaging manifestations. Radiographics 32:1945–1958
Gontarz M, Wyszyńska-Pawelec G, Zapała J, Gałązka K, Tomaszewska R, Lazar A (2016) IgG4-related disease in the head and neck region: report of two cases and review of the literature. Pol J Pathol 67:370–375
Deshpande V (2015) IgG4 related disease of the head and neck. Head Neck Pathol 9:24–31
Kakkar A, Sakthivel P, Rajeshwari M, Kairo A, Sharma MC (2020) Recurrent sinonasal CD34-negative malignant solitary fibrous tumor diagnosed on STAT6 immunohistochemistry and NAB2-STAT6 fusion. Head Neck Pathol 14:250–256
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KK conceived and designed the study, compiled and interpreted the data, drafted the manuscript. AK conceived and designed the study, supervised the data collection and analysis, had final approval of the manuscript. SM, ASB provided radiological details. PC, HK, DM, HV, RK, PS were treating clinicians of the patients and provided clinical data. DJ, involved in acquisition and analysis of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
Approved by institute ethical committee.
Consent for publication
All authors approve the manuscript.
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
If requested, available.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, K., Kakkar, A., Manchanda, S. et al. Sinonasal IgG4-related disease: a rare and emerging entity broadening the differential diagnosis in the sinonasal universe. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 2883–2890 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06564-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06564-w