Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to evaluate the pain, neuromusculoskeletal complications, and quality of life (QoL) in patients who had undergone partial parotidectomy (PP) for benign parotid tumors.
Patients and methods
All patients were evaluated before (T0) and at 1 week (T1) and 1 month (T2) after surgery. The patients were assessed for cervical range of motion (ROM), neck pain (NRS), neuropathic pain (DN4), neck disability (NDI), facial disability (FDI), and the presence of facial neuropathy, and QoL.
Results
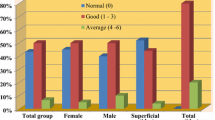
Twenty patients were included. A slight decrease was noted in cervical ROM, mild neck pain and disability were seen in T1. The DN4 score markedly increased at T1 (4.25) compared to T0 (0.1). Then it declined to 1.95 at T2. While there was no neuropathy in any of the patients at T0, it was present in 3 patients at T1. However, all improved at T2. QoL was negatively affected at T1 but showed improvement at T2. There was a significant correlation between NRS and NDI, FDI.
Conclusion
Neuromusculoskeletal problems and impaired QoL may develop in patients who have undergone PP. It would be beneficial to evaluate these patients using a multidisciplinary approach and inform them before surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagler R, Laufer D (1997) Tumors of the major and minor salivary glands: review of 25 years of experience. Anticancer Res 17(1B):701–707
Pinkston JA, Cole P (1999) Incidence rates of salivary gland tumors: results from a population-based study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120(6):834–840
Ciuman RR, Oels W, Jaussi R, Dost P (2012) Outcome, general, and symptom-specific quality of life after various types of parotid resection. Laryngoscope 122(6):1254–1261
Guru K, Manoor UK, Supe SS (2012) A comprehensive review of head and neck cancer rehabilitation: physical therapy perspectives. Indian J Palliat Care 18(2):87
Koch M, Zenk J, Iro H (2010) Long-term results of morbidity after parotid gland surgery in benign disease. Laryngoscope 120(4):724–730
Ruohoalho J, Mäkitie AA, Aro K, Atula T, Haapaniemi A, Keski-Säntti H, Takala A, Bäck LJ (2017) Complications after surgery for benign parotid gland neoplasms: a prospective cohort study. Head Neck 39(1):170–176
Cardoso LR, Rizzo CC, De Oliveira CZ, Dos Santos CR, Carvalho AL (2015) Myofascial pain syndrome after head and neck cancer treatment: prevalence, risk factors, and influence on quality of life. Head Neck 37(12):1733–1737
Unal-Cevik I, Sarioglu-Ay S, Evcik D (2010) A comparison of the DN4 and LANSS questionnaires in the assessment of neuropathic pain: validity and reliability of the Turkish version of DN4. J Pain 11(11):1129–1135
Bouhassira D, Attal N, Alchaar H, Boureau F, Brochet B, Bruxelle J, Cunin G, Fermanian J, Ginies P, Grun-Overdyking A (2005) Comparison of pain syndromes associated with nervous or somatic lesions and development of a new neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire (DN4). Pain 114(1–2):29–36
Aslan E, Karaduman A, Yakut Y, Aras B, Simsek IE, Yaglý N (2008) The cultural adaptation, reliability and validity of neck disability index in patients with neck pain: a Turkish version study. Spine 33(11):E362–E365
Pool JJ, Ostelo RW, Hoving JL, Bouter LM, De Vet HC (2007) Minimal clinically important change of the Neck Disability Index and the Numerical Rating Scale for patients with neck pain. Spine 32(26):3047–3051
Hisli N (1989) Beck depresyon envanterinin universite ogrencileri icin gecerliligi, guvenilirligi. (A reliability and validity study of Beck Depression Inventory in a university student sample). J Psychol 7:3–13
House W (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 93:184–193
Vanswearingen JM, Brach JS (1996) The Facial Disability Index: reliability and validity of a disability assessment instrument for disorders of the facial neuromuscular system. Phys Ther 76(12):1288–1298
Ucuncu Kefeli A, Sanal-Toprak C, Asedov R, Ozen Z, Akyuz G, Dane F, Atasoy BM (2020) Long-term neuromusculoskeletal side effects and quality of life in nasopharyngeal cancer patients receiving radiochemotherapy. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 77(8):2325–2333
Van Wilgen CP, Dijkstra PU, van der Laan BF, Plukker JT, Roodenburg JL (2004) Morbidity of the neck after head and neck cancer therapy. Head Neck J Sci Spec Head Neck 26(9):785–791
Cramer JD, Johnson JT, Nilsen ML (2018) Pain in head and neck cancer survivors: prevalence, predictors, and quality-of-life impact. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 159(5):853–858
Ghei A, Khot S (2010) Pain management in patients with head and neck carcinoma. Otorhinolaryngol Clin 2:69–75
Foghsgaard S, Foghsgaard J, Homøe P (2007) Early post-operative morbidity after superficial parotidectomy: a prospective study concerning pain and resumption of normal activity. Clin Otolaryngol 32(1):54–57
Buchakjian MR, Davis AB, Sciegienka SJ, Pagedar NA, Sperry SM (2017) Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in head and neck cancer surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 126(9):646–653
Marchese-Ragona R, De Filippis C, Marioni G, Staffieri A (2005) Treatment of complications of parotid gland surgery. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 25(3):174
Moretti A, Citraro L, Petrucci AG, Di Giovanni P, Di Mauro R, Giacomini PG (2015) Great auricular nerve preservation in parotid surgery: rationale and long-term results insights. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(11):3515–3520
Zheng C, Cao R, Gao M, Huang Z, Sheng M, Hu Y (2019) Comparison of surgical techniques for benign parotid tumours: a multicentre retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48(2):187–192
Kato MG, Erkul E, Nguyen SA, Day TA, Hornig JD, Lentsch EJ, Gillespie MB (2017) Extracapsular dissection vs superficial parotidectomy of benign parotid lesions: surgical outcomes and cost-effectiveness analysis. JAMA Otolaryng Head Neck Surg 143(11):1092–1097
Prats-Golczer V, Gonzalez-Cardero E, Exposito-Tirado J, Montes-Latorre E, Gonzalez-Perez L, Infante-Cossio P (2017) Impact of dysfunction of the facial nerve after superficial parotidectomy: a prospective study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55(8):798–802
Erkan A, Yavuz H, Ozer C, Ozer F, Ozluoglu L (2008) Quality of life after surgery for benign disease of the parotid gland. J Laryngol Otol 122(4):397–402
Nitzan D, Kronenberg J, Horowitz Z, Wolf M, Bedrin L, Chaushu G, Talmi YP (2004) Quality of life following parotidectomy for malignant and benign disease. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(5):1060–1067
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
There has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tugba Ozsoy-Unubol: design, collection, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and final approval. Suphi Bulgurcu: design, collection, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and final approval. Bulent Evren Erkul: design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by local Hamidiye ethics committee of University of Health Sciences (approval number: 11.10.2019-2019/6-19/122). The manuscript has three authors and each author is responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozsoy-Unubol, T., Bulgurcu, S. & Erkul, B.E. Longitudinal perioperative pain, neuromusculoskeletal complications and quality-of-life assessment in partial parotidectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 239–245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06241-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06241-y