Abstract
Background
The identification of prognostic non-invasive biomarkers is a priority for cancer patients’ care. Circulating microRNA (miRNAs) have been described in numerous human malignancies as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic cancer biomarkers. The aim of our study was to analyze the expression profile of a set of miRNAs, involved in the modulation of the glycolytic pathway, as prognostic factors in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC).
Methods
Serum samples of 54 patients with untreated HNSCC were obtained at the time of diagnosis. The prognostic value of circulating miR-26b, miR-124, miR-155 and miR-375 was evaluated towards disease-free survival.
Results
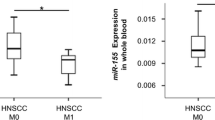
We found that there were optimal miRNAs cut-off values for lower risk of recurrence in HNSCC patients. Kaplan–Meier curves showed that higher levels of miR-26b and lower levels of miR-155 were associated with better disease-free survival rates. In the multivariate analysis, patients with serum miR-26b > 0.062 and miR-155 < 0.159 presented more than 2.9 times lower risk of poor outcome.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that two miRNAs that modulate the glycolytic pathway, miR-26b and miR-155, are independently associated with the risk of recurrence in patients with HNSCC. The overall results in this study supports the evidence that the glucose homeostasis may be a target to improve the outcomes for patients with HNSCC.
Level of evidence
Individual retrospective cohort study (2b).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quintana A, Avilés FX, Terra X et al (2013) Overexpression of the nuclear factor-kappa B (p65) in association with local failure in patients with head and neck carcinoma undergong radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. Head Neck. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.22979
Ho AS, Kraus DH, Ganly I et al (2014) Decision making in the management of recurrent head and neck cancer. Head Neck 36:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.23227
Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ, Hill AF (2014) Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J Extracell Vesicles 1:1–14
Fadaka AO, Pretorius A (2019) Biomarkers for stratification in colorectal cancer: microRNAs. Cancer Control 26:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073274819862784
Chen B, Li H, Zeng X et al (2012) Roles of microRNA on cancer cell metabolism. J Transl Med 10:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-228
Ortega AD, Sánchez-Aragó M, Giner-Sánchez D et al (2009) Glucose avidity of carcinomas. Cancer Lett 276:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.08.007
Yan J, Lin J, He X (2014) The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer. Int J Cancer 1018:1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28563
Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Nohata N et al (2012) The functional significance of microRNA-375 in human squamous cell carcinoma: aberrant expression and effects on cancer pathways. J Hum Genet 57:556–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.75
Zhao X, Lu C, Chu W et al (2017) MicroRNA-124 suppresses proliferation and glycolysis in non–small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AKT–GLUT1/HKII. Tumor Biol 39:101042831770621. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317706215
Zhang M, Piao L, Datta J et al (2015) miR-124 regulates the epithelial-restricted with serine box/epidermal growth factor receptor signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 14:2313–2320. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-1071
Arora A, Singh S, Bhatt AN et al (2015) Interplay between metabolism and oncogenic process: role of microRNAs. Transl Oncogenom 7:11–27. https://doi.org/10.4137/TOG.S29652
Xu G, Shi C, Ji C et al (2014) MiR-26b inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis induction via the downregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 driven glycolysis in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep 10:223–228. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3797
Avilés-Jurado FXFXFX, Flores JCJCJCJC, Gumà J et al (2017) Prognostic relevance of insulin resistance on disease-free survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: preliminary results. Head Neck 39:2501–2511. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24919
Chiesa F, Tradati N, Mauri S et al (1998) Prognostic factors in head and neck oncology: a critical appraisal for use in clinical practice. Anticancer Res 18:4769–4776
Wang J, Zhang K, Liu S, Sen S (2014) Tumor-associated circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers of cancer. Molecules 19:1912–1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19021912
Wang F, Zheng Z, Guo J, Ding X (2010) Correlation and quantitation of microRNA aberrant expression in tissues and sera from patients with breast tumor. Gynecol Oncol 119:586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.07.021
Levine AJ, Puzio-Kuter AM (2010) The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Science 330:1340–1344. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1193494
Sun Y, Zhao X, Luo M et al (2014) The pro-apoptotic role of the regulatory feedback loop between miR-124 and PKM1/HNF4α in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 15:4318–4332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034318
Li X, Fan Q, Li J et al (2017) MiR-124 down-regulation is critical for cancer associated fibroblasts-enhanced tumor growth of oral carcinoma. Exp Cell Res 351:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.01.001
Jin L, Miao J, Liu Y et al (2017) Icaritin induces mitochondrial apoptosis by up-regulating miR-124 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 85:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.023
Zhao Y, Ling Z, Hao Y et al (2017) MiR-124 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and its downstream signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:25005–25020. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15334
Kim S, Lee E, Jung J et al (2018) microRNA-155 positively regulates glucose metabolism via PIK3R1-FOXO3a-cMYC axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 37:2982–2991. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0124-4
La ShuS, Yang Y, Allen CL et al (2018) Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by melanoma exosome microRNA favours a pre-metastatic microenvironment. Sci Rep 8:12905. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31323-7
Xu Y, Han S, Lei K et al (2016) Anti-Warburg effect of rosmarinic acid via miR-155 in colorectal carcinoma cells. Eur J Cancer Prev 25:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000205
Lv X, Yao L, Zhang J et al (2016) Inhibition of microRNA-155 sensitizes lung cancer cells to irradiation via suppression of HK2-modulated glucose metabolism. Mol Med Rep 14:1332–1338. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5394
Wang JL, Wang X, Yang D, Shi WJ (2016) The expression of MicroRNA-155 in plasma and tissue is matched in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Yonsei Med J 57:298–305. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.298
Tian L, Zhang J, Ren X et al (2017) Overexpression of miR-26b decreases the cisplatin-resistance in laryngeal cancer by targeting ATF2. Oncotarget 8:79023–79033. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20784
Fukumoto I, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T et al (2015) MicroRNA expression signature of oral squamous cell carcinoma: functional role of microRNA-26a/b in the modulation of novel cancer pathways. Br J Cancer 112:891–900. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.19
Li J, Liang Y, Lv H et al (2017) miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-MYC pathway. Gene 625:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.05.001
Mathupala SP, Ko YH, Pedersen PL (2009) Hexokinase-2 bound to mitochondria: cancer’s stygian link to the “Warburg Effect” and a pivotal target for effective therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 19:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.11.006
Israël M, Schwartz L (2011) The metabolic advantage of tumor cells. Mol Cancer 10:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-10-70
Du J-Y, Wang L-F, Wang Q, Yu L-D (2015) miR-26b inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis induction via the downregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 driven glycolysis in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep 33:1890–1898. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3797
Linxweiler J, Junker K (2020) Extracellular vesicles in urological malignancies: an update. Nat Rev Urol 17:11–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-019-0261-8
Setti G, Pezzi ME, Viani MV et al (2020) Salivary MicroRNA for diagnosis of cancer and systemic diseases: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci 21:907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030907
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from Plan Estatal de I + D + I of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (FIS PI15/02047 and FIS PI18/0844 to FX A-J and IV, and FIS PI19/01661 to XL). Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER), A Way to Build Europe. XT is a Serra-Húnter fellow. Co-financed by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer by the Project LAB AECC 2018-LABAE18025AVIL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This work has the approval of the centre’s ethics committee (Ref. 15/02047).
Informed consent
All patients in this study have signed an informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avilés-Jurado, F.X., Muñoz, C., Meler, C. et al. Circulating microRNAs modulating glycolysis as non-invasive prognostic biomarkers of HNSCC. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 1585–1594 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06240-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06240-z