Abstract
Purpose
To review the current management of arytenoid subluxation/dislocation (AS/AD) focusing on diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic controversies.
Methods
The international literature of the last 20 years has been considered. After the application of inclusion criteria, 20 studies were selected (471 AS/AD cases in total).
Results
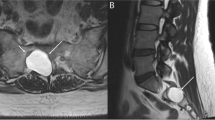
All the included investigations were retrospective case series. AS/AD was often iatrogenic occurring at least in 0.01% of patients undergone endo-tracheal intubation. The most common symptom was persistent hoarseness. The diagnosis was made by video-laryngoscopy and neck computed tomography in most reports, while some used also laryngeal electromyography. Laryngeal electromyography was fundamental to rule out unilateral vocal fold paralysis, the main differential diagnosis. The surgical relocation of AS/AD under general or local anesthesia was achieved in about 80% of patients.
Conclusion
AS/AD is a mechanical disorder of the larynx that can be successfully treated if promptly diagnosed. Clinical trials and multi-centric studies are necessary to set management guidelines.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Z, Liu Q (2002) A comparative study on the close reduction of arytenoid dislocation under indirect and direct laryngoscope. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 22(4):375–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02896791
Rubin AD, Hawkshaw MJ, Moyer CA, Dean CM, Sataloff RT (2005) Arytenoid cartilage dislocation: a 20-year experience. J Voice 19(4):687–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2004.11.002
Hiramatsu H, Tokashiki R, Kitamura M, Motohashi R, Tsukahara K, Suzuki M (2010) New approach to diagnose arytenoid dislocation and subluxation using three-dimensional computed tomography. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267(12):1893–1903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1300-5(Epub 2010 Jun 12)
Leelamanit V, Sinkijcharoenchai W (2012) A promising new technique for closed reduction of arytenoid dislocation. J Laryngol Otol 126(2):168–174. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002221511100226X(Epub 2011 Dec 15)
Lee DH, Yoon TM, Lee JK, Lim SC (2013) Treatment outcomes of closed reduction of arytenoid dislocation. Acta Otolaryngol 133(5):518–522. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2012.758387(Epub 2013 Jan 28)
Mallon AS, Portnoy JE, Landrum T, Sataloff RT (2014) Pediatric arytenoid dislocation: diagnosis and treatment. J Voice 28(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.08.016(Epub 2013 Oct 8)
Teng Y, Wang HE, Lin Z (2014) Arytenoid cartilage dislocation from external blunt laryngeal trauma: evaluation and therapy without laryngeal electromyography. Med Sci Monit 20:1496–1502. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.890530
Lee SW, Park KN, Welham NV (2014) Clinical features and surgical outcomes following closed reduction of arytenoid dislocation. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(11):1045–1050. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2014.2060
Shen L, Wang WT, Yu XR, Zhang XH, Huang YG (2014) Evaluation of risk factors for arytenoid dislocation after endotracheal intubation: a retrospective case-control study. Chin Med Sci J 29(4):221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-9294(14)60074-2
Lee DH, Yoon TM, Lee JK, Lim SC (2015) Clinical characteristics of arytenoid dislocation after endotracheal intubation. J Craniofac Surg 26(4):1358–1360. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001749
Tan PH, Hung KC, Hsieh SW, Chen TB, Liu PH, Chen WH (2016) Large-bore calibrating orogastric tube and arytenoid dislocation: a retrospective study. Br J Anaesth 116(2):296–298. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aev463
Cao L, Wu X, Mao W, Hayes C, Wei C (2016) Closed reduction for arytenoid dislocation under local anesthesia. Acta Otolaryngol 136(8):812–818. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2016.1157267(Epub 2016 Mar 22)
Lou Z, Lin Z (2017) The appropriate time for closed reduction using local anesthesia in arytenoid dislocation caused by intubation: a clinical research. Acta Otolaryngol 137(3):331–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2016.1230276(Epub 2016 Sep 22)
Tsuru S, Wakimoto M, Iritakenishi T, Ogawa M, Hayashi Y (2017) Cardiovascular operation: a significant risk factor of arytenoid cartilage dislocation/subluxation after anesthesia. Ann Card Anaesth 20(3):309–312. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_71_17
Lou Z, Yu X, Li Y, Duan H, Zhang P, Lin Z (2018) BMI may be the risk factor for arytenoid dislocation caused by endotracheal intubation: a retrospective case-control study. J Voice 32(2):221–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.05.010(Epub 2017 Jun 7)
Wu L, Shen L, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Huang Y (2018) Association between the use of a stylet in endotracheal intubation and postoperative arytenoid dislocation: a case–control study. BMC Anesthesiol 18(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-018-0521-9
Hung KC, Chen YT, Chen JY, Kuo CY, Wu SC, Chiang MH, Lan KM, Wang LK, Sun CK (2019) Clinical characteristics of arytenoid dislocation in patients undergoing bariatric/metabolic surgery: a STROBE-complaint retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(17):e15318. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015318
Xu X, Wang Y, Wang J, Reiss JF, Zhou L, Jiang JJ, Zhuang P (2019) Quantitative measurement of the three-dimensional structure of the vocal folds and its application in identifying the type of cricoarytenoid joint dislocation. J Voice 33(5):611–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2018.02.024(Epub 2018 Aug 23)
Wu X, Mao W, Zhang J, Wei C (2019) Treatment outcomes of arytenoid dislocation by closed reduction: a multidimensional evaluation. J Voice. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2019.10.010
Zheng T, Lou Z, Li X, Teng Y, Li Y, Lin X, Lin Z (2020) Regularity of voice recovery and arytenoid motion after closed reduction in patients with arytenoid dislocation: a self-controlled clinical study. Acta Otolaryngol 140(1):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2019.1691745(Epub 2019 Nov 25)
https://www.cebm.net/2016/05/ocebm-levels-of-evidence/. Accessed 21 Apr 2020
Nerurkar N, Chhapola S (2012) Arytenoid subluxation after a bout of coughing: a rare case. Am J Otolaryngol 33(2):275–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2011.07.001(Epub 2011 Aug 15)
Friedman AD, Kobler JB, Landau-Zemer T, Barbu AM, Burns JA (2012) High-force simulated intubation fails to dislocate cricoarytenoid joint in ex vivo human larynges. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 121(11):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941212101108
Gallet P, Nguyen DT, Toussaint B, Rumeau C (2019) Spontaneous arytenoid dislocation and crico-arytenoid instability. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 136(4):307–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anorl.2019.02.018(Epub 2019 Mar 23)
Chowdhury F, Siddiqui U, Tsui BC, El-Hakim H (2014) Postintubation arytenoid dislocation/subluxation in CHARGE infants. Paediatr Anaesth 24(2):225–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.12288
Yamanaka H, Hayashi Y, Watanabe Y, Uematu H, Mashimo T (2009) Prolonged hoarseness and arytenoid cartilage dislocation after tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth 103(3):452–455. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aep169(Epub 2009 Jun)
Inoue S, Abe R, Tanaka Y, Kawaguchi M (2015) Tracheal intubation by trainees does not alter the incidence or duration of postoperative sore throat and hoarseness: a teaching hospital-based propensity score analysis. Br J Anaesth 115(3):463–469. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aev234(Epub 2015 Aug 4)
Skoretz SA, Flowers HL, Martino R (2010) The incidence of dysphagia following endotracheal intubation: a systematic review. Chest 137(3):665–673. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-1823.Review
Ysunza-Rivera A, Landeros L, Pamplona MC, Silva-Rojas JA, Prado-Calleros HM, Fajardo-Dolci GE (2008) The role of electromyography in cases of vocal cord paralysis. Gac Med Mex 144(4):303–308
Sataloff RT, Praneetvatakul P, Heuer RJ, Hawkshaw MJ, Heman-Ackah YD, Schneider SM, Mandel S (2010) Laryngeal electromyography: clinical application. J Voice 24(2):228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2008.08.005(Epub 2008 Dec 25)
Lovato A, Barillari MR, Giacomelli L, Gamberini L, de Filippis C (2019) Predicting the outcome of unilateral vocal fold paralysis: a multivariate discriminating model including grade of dysphonia, jitter, shimmer, and voice handicap index-10. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 128(5):447–452
Norris BK, Schweinfurth JM (2011) Arytenoid dislocation: an analysis of the contemporary literature. Laryngoscope 121(1):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21276(Review)
Tan V, Seevanayagam S (2009) Arytenoid subluxation after a difficult intubation treated successfully with voice therapy. Anaesth Intensive Care 37(5):843–846
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, Vauthey JN, Dindo D, Schulick RD, de Santibañes E, Pekolj J, Slankamenac K, Bassi C, Graf R, Vonlanthen R, Padbury R, Cameron JL, Makuuchi M (2009) The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: 5-year experience. Ann Surg 250(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b13ca2
Quick CA, Merwin GE (1978) Arytenoid dislocation. Arch Otolaryngol 104(5):267–270. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1978.00790050033007
Lovato A, De Colle W, Giacomelli L, Piacente A, Righetto L, Marioni G, de Filippis C (2016) Multi-dimensional voice program (MDVP) vs praat for assessing euphonic subjects: a preliminary study on the gender-discriminating power of acoustic analysis software. J Voice 30(6):765.e1–765.e5
Lovato A, de Filippis C (2018) Comment on "Using innovative acoustic analysis to predict the postoperative outcomes of unilateral vocal fold paralysis". Biomed Res Int 2018:6269593
Lovato A, Bonora C, Genovese E, Amato C, Maiolino L, de Filippis C (2020) A panel of jitter/shimmer may identify functional dysphonia at risk of failure after speech therapy. Am J Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frosolini, A., Marioni, G., Maiolino, L. et al. Current management of arytenoid sub-luxation and dislocation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 2977–2986 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06042-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06042-3