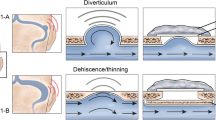
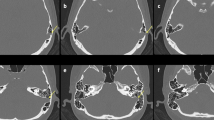
Abstract
Purpose
The present analysis aims to describe a surgical approach wherein pulsatile tinnitus (PT) arising due to sigmoid sinus wall anomalies (SSWA) can be treated via combination internal and external sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction. We further evaluated the utility of temporal bone 3D-CT imaging during both the pre- and post-operative assessments of all treated patients.
Methods
Data pertaining to 11 patients that had undergone sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction were retrospectively analyzed. All of these patients underwent preoperative 3D-CT imaging assessment. These patients were additionally subjected to sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction via a combined internal and external layer approach. Postoperatively, all patients underwent a radiological assessment of auricular cartilage and autologous bone powered displacement. Patients were additionally asked about any subjective changes in PT or associated symptoms at follow-up time points.
Results
SSWA in the 3D-CT imaging from these patients were all distinct. In 10/11 patients, PT fully resolved following reconstruction of the sinus wall. The remaining patients exhibited significant improvements in symptoms postoperatively, with PT fully resolving within a 1-month follow-up period. No patients suffered any major complications.
Conclusions
Temporal bone 3D-CT imaging allow for effective visualization of SSWA, enabling effective pre- and post-operative assessments of treated patients. A combined internal and external layer approach to sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction can be implemented safely and effectively, yielding high rates of satisfactory outcomes and achieving rigid reconstruction of this surface. As such, there is clear value in the consideration of this approach when treating individuals suffering from PT as a result of SSWA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liyanage SH, Singh A, Savundra P, Kalan A (2006) Pulsatile tinnitus. J Laryngol Otol 120(2):93–97. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215105001714
Mattox DE, Hudgins P (2008) Algorithm for evaluation of pulsatile tinnitus. Acta Otolaryngol 128(4):427–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480701840106
Miller TR, Serulle Y, Gandhi D (2016) Arterial abnormalities leading to tinnitus. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 26(2):227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2015.12.00
Ahsan SF, Seidman M, Yaremchuk K (2015) What is the best imaging modality in evaluating patients with unilateral pulsatile tinnitus? Laryngoscope 125(2):284–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24822 Epub 2014 Jul 9
Hofmann E, Behr R, Neumann-Haefelin T, Schwager K (2013) Pulsatile tinnitus: imaging and differential diagnosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int 110(26):451–458. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2013.0451
Liu Z, Dong C, Wang X, Han X, Zhao P, Lv H, Li Q, Wang Z (2015) Association between idiopathic intracranial hypertension and sigmoid sinus dehiscence/diverticulum with pulsatile tinnitus: a retrospective imaging study. Neuroradiology 57(7):747–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1517-5
Shin RK, Balcer LJ (2001) New developments in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 1(5):463–470
Harvey RS, Hertzano R, Kelman SE, Eisenman DJ (2014) Pulse-synchronous tinnitus and sigmoid sinus wall anomalies: descriptive epidemiology and the idiopathic intracranial hypertension patient population. Otol Neurotol 35(1):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182a4756c
Eisenman DJ, Raghavan P, Hertzano R, Morales R (2018) Evaluation and treatment of pulsatile tinnitus associated with sigmoid sinus wall anomalies. Laryngoscope 128(2):S1–S13. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27218
Navsa N, Kramer B (1998) A quantitative assessment of the jugular foramen. Ann Anat 180:269–273
Wang AC, Nelson AN, Pino C, Svider PF, Hong RS, Chan E (2017) Management of sigmoid sinus associated pulsatile tinnitus: a systematic review of the literature. Otol Neurotol 38(10):1390–1396. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000001612
Paramasivam S, Furtado S, Shigamatsu T, Smouha E (2016) Endovascular management of sigmoid sinus diverticulum. Interv Neurol 5(1–2):76–80. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444507
Li B, Lv X, Wu Z, Cao X, Wang J, Ge A, Liu X, Li S (2016) Stent-assisted coil embolization of a transverse-sigmoid sinus diverticulum presenting with pulsatile tinnitus. Turk Neurosurg 26(4):632–634. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149
Eisenman DJ (2011) Sinus wall reconstruction for sigmoid sinus diverticulum and dehiscence: a standardized surgical procedure for a range of radiographic findings. Otology and neurotology: official publication of the American Otological Society. Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol 32(7):1116–1119. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e31822a1c7d
Song JJ, Kim YJ, Kim SY, An YS, Kim K, Lee SY, Koo JW (2015) Sinus wall resurfacing for patients with temporal bone venous sinus diverticulum and ipsilateral pulsatile tinnitus. Neurosurgery 77(5):709–717. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000902
Zeng R, Wang GP, Liu ZH, Liang XH, Zhao PF, Wang ZC, Gong SS (2016) Sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction for pulsatile tinnitus caused by sigmoid sinus wall dehiscence: a single-center experience. PLoS ONE 11(10):e0164728. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164728
Zhang C, Li Q, Li S (2019) Physical and psychological outcomes of simple sigmoid sinus bony wall repair for pulsatile tinnitus due to sigmoid sinus wall anomalies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(5):1327–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05380-1
Sun J, Sun J (2019) Sandwich technique for sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction for treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by sigmoid sinus diverticulum/dehiscence. Acta Otolaryngol 139(12):1063–1066. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2019.1668960
Yeo WX, Xu SH, Tan TY, Low YM, Yuen HW (2018) Surgical management of pulsatile tinnitus secondary to jugular bulb or sigmoid sinus diverticulum with review of literature. Am J Otolaryngol 39(2):247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.12.019
Kim CS, Kim SY, Choi H, Koo JW, Yoo SY, An GS, Lee K, Choi I, Song JJ (2016) Transmastoid reshaping of the sigmoid sinus: preliminary study of a novel surgical method to quiet pulsatile tinnitus of an unrecognized vascular origin. J Neurosurg 125(2):441–449. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.6.JNS15961
Mundada P, Singh A, Lingam RK (2015) CT arteriography and venography in the evaluation of Pulsatile tinnitus with normal otoscopic examination. Laryngoscope 125(4):979–984. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25010
Ding H, Zhao P, Lv H, Liu X, Zeng R, Wang G, Gong S, Wang Z (2019) Temporal bone contrast-enhanced high-resolution CT evaluation of pulsatile tinnitus after sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction. Acta Radiol 60(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185118773509
Dong C, Zhao P, Liu Z, Xu W, Lv H, Pang S, Wang Z (2016) Association between the extent of sigmoid sinus dehiscence and an occurrence of pulsatile tinnitus: a retrospective imaging study. Clin Radiol 71(9):883–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2016.06.106
Liu Z, Chen C, Wang Z, Gong S, Xian J, Wang Y, Liang X, Ma X, Li Y (2013) Sigmoid sinus diverticulum and pulsatile tinnitus: analysis of CT scans from 15 cases. Acta Radiol 54:812–816. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185113481698
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by DW, YZ and BT. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University approved this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Availability of data and material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Zhao, Y. & Tong, B. Treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by anomalies of the sigmoid sinus wall via combined internal and external sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction with 3D temporal bone CT guidance. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 2439–2445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-05989-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-05989-7