Abstract
Introduction
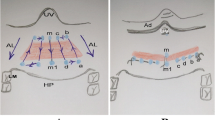
Persistent sleep apnea following tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children requires additional evaluation. One of the common areas of persistent upper airway obstruction in these children is the base of the tongue and lingual tonsils as well as epiglottic prolapse. Depending on the site of obstruction on sleep endoscopy or a cine MRI, surgical procedures include base of tongue reduction and lingual tonsillectomy with or without epiglottopexy.
Objective
To assess the swallowing outcomes in children undergoing epiglottopexy with lingual tonsillectomy.
Methods
A retrospective case series review of children undergoing epiglottopexy with or without lingual tonsillectomy. All patients underwent an epiglottopexy with lingual tonsillectomy using coblation. A detailed evaluation including a sleep study, sleep endoscopy, and thorough swallowing assessment preoperatively as well as postoperatively was performed.
Results
Five children underwent epiglottopexy with lingual tonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea. Epiglottopexy improved sleep apnea with Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) falling significantly from 4.6 to 0.5 (p < 0.05). All patients had a normal swallowing assessment postoperatively with functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) revealing no evidence of aspiration and penetration.
Conclusion
In our case series epiglottopexy with lingual tonsillectomy is a safe and effective technique, which improves sleep apnea in pediatric patients. It does not affect the swallowing mechanism, and the epiglottis still retains the laryngeal protective role.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcus CL, Moore RH, Rosen CL et al (2013) A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 368:2366–2376
Bhattacharjee R, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Spruyt K et al (2010) Adenotonsillectomy outcomes in treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in children: a multicenter retrospective study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:676–683
Friedman M, Wilson M, Lin HC, Chang HW (2009) Updated systematic review of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy for treatment of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140:800–808
Oomen K, Modi VK (2014) Epiglottopexy with and without lingual tonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 124:1019–1022
Berry R, Brooks R, Gamaldo C et al (2013) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. Version 2.0.2. Darien, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Bergeron M, de Alarcon A, Hart CK, Rutter MJ (2018) Factors associated with epiglottic petiole prolapse repositioning success. Laryngoscope
Werner JA, Lippert BM, Dünne AA et al (2002) Epiglottopexy for the treatment of severe laryngomalacia. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259:459–464
Whymark AD, Clement WA, Kubba H, Geddes NK (2006) Laser epiglottopexy for laryngomalacia: 10 years’ experience in the west of Scotland. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:978–982
Sandu K, Monnier P, Reinhard A, Gorostidi F (2015) Endoscopic epiglottopexy using Lichtenberger’s needle carrier to avoid breakdown of repair. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272:3385–3390
Yellon RF (2006) Epiglottic and base-of-tongue prolapse in children: grading and management. Laryngoscope 116:194–200
Ishman SL, Chang KW, Kennedy AA (2018) Techniques for evaluation and management of tongue-base obstruction in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 26:409–416
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Cheng J et al (1992) Closure mechanisms of laryngeal vestibule during swallow. Am J Physiol 262:338–344
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanotra, S.P., Givens, V.B. & Keith, B. Swallowing outcomes after pediatric epiglottopexy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 285–291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05664-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05664-6