Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to perform a systematic literature review on the occurrence of gusher during stapes surgery, to understand its surgical management and outcomes.
Methods
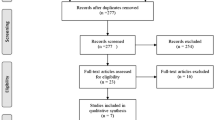
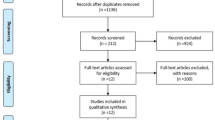
The PRISMA standard was applied to identify English, Italian or French-language studies, related to stapes surgery and mentioning gusher or perilymphatic leak. Full-texts lacking information on the management of gusher and/or the post-operative hearing outcome were excluded.
Results
Twenty-four articles were eventually included. Seventy-six patients were involved in the qualitative synthesis. The management of gusher mostly consisted in covering the oval window and/or filling the tympanic cavity, with absorbable and autologous graft materials. Packing of the external auditory canal was reported in 51 patients (67%). Gusher was related to complete/profound loss of hearing in 25% of the cases and to a worsening of hearing function in 31% of patients. In 19% of patients an improvement in hearing tests was reported; in 28% the hearing function was unchanged. Post-operative vestibular symptoms were reported in 7 patients, and were mainly mild and transient. The absence of vestibular symptoms was underlined in 9 cases, while in 79% of the patients the authors did not provide information.
Conclusion
The unexpected occurrence of gusher during stapes surgery represents a relevant issue for the otologic surgeon. Its management most commonly consists in plugging the oval window and the tympanic cavity. In most of the cases, a stapes prosthesis could be positioned. The results on hearing and vestibular functions are widely variable.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Causse J, Causse JB (1980) Eighteen-year report on stapedectomy I Problems of stapedial fixation. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 5(1):49–59
Schuknecht HF, Reisser C (1988) The morphologic basis for perilymphatic gushers and oozers. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 39:1–12
Glasscock ME 3rd (1973) The stapes gusher. Arch Otolaryngol 98(2):82–91
Quesada JL, Cammaroto G, Bonanno L, Galletti F, Quesada P (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid leak during stapes surgery: gushing leaks and oozing leaks, two different phenomena. Ear Nose Throat J 96(8):302–310
Farrior JB, Endicott JN (1971) Congenital mixed deafness: cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea. Ablation of the aqueduct of the cochlea. Laryngoscope 81(5):684–699
Causse JB, Causse JR, Wiet RJ, Yoo TJ (1983) Complications of stapedectomies. Am J Otol 4(4):275–280
Wiet RJ, Harvey SA, Bauer GP (1993) Complications in stapes surgery. Options for prevention and management. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 26(3):471–490
Shea JJ Jr (1963) Complications of the stapedectomy operation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 72:1108–1123
Allen GW (1987) Fluid flow in the cochlear aqueduct and cochlea-hydrodynamic considerations in perilymph fistula, stapes gusher, and secondary endolymphatic hydrops. Am J Otol 8(4):319–322
Skolnik EM, Ferrer JL (1959) Cerebrospinal otorrhea. AMA. Arch Otolaryngol 70:795–799
Kaufman B, Jordan VM, Pratt LL (1969) Positive contrast demonstration of a cerebrospinal fluid fistula through the fundus of the internal auditory meatus. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 9:83–90
Gundersen T, Haye R (1970) Cerebrospinal otorrhea. Arch Otolaryngol 91(1):19–23
Jackler RK, Hwang PH (1993) Enlargement of the cochlear aqueduct: fact or fiction? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 109(1):14–25
Cremers CW, Hombergen GC, Scaf JJ, Huygen PL, Volkers WS, Pinckers AJ (1985) X-linked progressive mixed deafness with perilymphatic gusher during stapes surgery. Arch Otolaryngol 111(4):249–254
Olson NR, Lehman RH (1968) Cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea and the congenitally fixed stapes. Laryngoscope 78(3):352–360
Nance WE, Setleff R, McLeod A, Sweeney A, Cooper C, McConnel F (1971) X-linked mixed deafness with congenital fixation of the stapedial footplate and perilymphatic gusher. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 7(4):64–69
Cremers CW, Huygen PL (1983) Clinical features of female heterozygotes in the X-linked mixed deafness syndrome (with perilymphatic gusher during stapes surgery). Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 6(2):179–185
Papadaki E, Prassopoulos P, Bizakis J, Karampekios S, Papadakis H, Gourtsoyiannis N (1998) X-linked deafness with stapes gusher in females. Eur J Radiol 29(1):71–75
Cassano P, Decandia N, Cassano M, Fiorella ML, Ettorre G (2003) Perilymphatic gusher in stapedectomy: demonstration of a fistula of internal auditory canal. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 23(2):116–119
Varadarajan VV, DeJesus RO, Antonelli PJ (2018) Novel computed tomography findings suggestive of perilymph gusher. Otol Neurotol 39(8):1066–1069
Krouchi L, Callonnec F, Bouchetemblé P, Tollard E, Dehesdin D, Marie JP (2013) Preoperative computed tomography scan may fail to predict perilymphatic gusher. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 122(6):374–377
Nguyen DQ, Morel N, Dumas G, Boubagra K, Schmerber S (2006) Dehiscence of the anterior semicircular canal and otosclerosis: a case report. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 127(3):151–155
Rebol J (2004) The unilateral stapes gusher. Wien Klin Wochenschr 116(Suppl 2):90–92
Couvreur P, Baltazart B, Lacher G, Filippini JF, Vincey P (2003) Perilymphatyc effusion as a complication of otosclerosis. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 124(1):31–37
Shirazi A, Fenton JE, Fagan PA (1994) Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome and stapes fixation. J Laryngol Otol 108(11):989–990
Talbot JM, Wilson DF (1994) Computed tomographic diagnosis of X-linked congenital mixed deafness, fixation of the stapedial footplate, and perilymphatic gusher. Am J Otol 15(2):177–182
Carlson DL, Reeh HL (1993) X-linked mixed hearing loss with stapes fixation: case reports. J Am Acad Audiol 4(6):420–425
Flood LM, Kemink JL, Kartush JM (1985) Pneumocephalus following treatment of a stapes gusher. Am J Otol 6(6):508–511
Cremers CW, Hombergen GC, Wentges RT (1983) Perilymphatic gusher and stapes surgery. A predictable complication? Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 8(4):235–240
Daniilidis J, Maganaris T, Dimitriadis A, Iliades T, Manolidis L (1978) Stapes gusher and Klippel-Feil syndrome. Laryngoscope 88:1178–1183
Wolferman A (1964) Cerebrospinal otorrhea, complications of stapes surgery. Laryngoscope 74:1368–1380
McFadden MD, Wilmoth JG, Mancuso AA, Antonelli PJ (2005) Preoperative computed tomography may fail to detect patients at risk for perilymph gusher. Ear Nose Throat J 84(12):770–774
Jensen J, Terkildsen K, Thomsen KA (1977) Inner ear malformations with oto-liquorrhea. Tomographic findings in three cases with a mixed hearing impairment. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 214(3):271–282
Hipskind MM, Lindsay JR, Jones TD, Valvassori GE (1976) Recurrent meningitis and labyrinthine gusher, related to congenital defects of the labyrinthine capsule and stapes footplate. Laryngoscope 86(5):682–689
Ward PH (1961) Cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea. A complication in stapes surgery. Arch Otolaryngol 74:399–404
Pech A, Goubert JL, Zanaret M, Collignon G (1983) Otoliquorrhea in footplate surgery. J Fr Otorhinolaryngol Audiophonol Chir Maxillofac 32(7):439–446
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Research does not involve human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alicandri-Ciufelli, M., Molinari, G., Rosa, M. et al. Gusher in stapes surgery: a systematic review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2363–2376 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05538-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05538-x