Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the surgical experience and auditory functions and progress of speech development of cochlear implantation in malformed ears.
Materials and methods
Between November 1995 and July 2017, thirty-seven patients (26 females and 11 males; mean age: 138.275 ± 96.24 months) with diverse anomalies of the inner ear were retrospectively examined for surgical and audiological results. Speech Intelligibility Rating (SIR), Categories of Auditory Perception (CAP), Pure Tone Average (PTA), Speech Intelligibility Rating (SRT), and Word Discrimination Score (WDS) were the audiological tests used to evaluate the efficacy of CI in the malformed inner ears.
Results
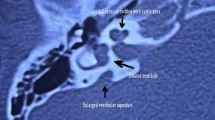
CSF gusher was experienced by six patients (three with LVA (large vestibular aqueduct), one with IP (incomplete partition) I, and two with both IP II Mondini malformations and LVA). Two patients had transient facial paresis after surgery. All patients fully recovered within 6 months. The postoperative PTA, SRT, and WDS test results showed significant differences between progressive and congenital sensorineural hearing loss (p values < 0.05 for all). On the other hand, the postoperative CAP and SIR test results revealed no significant differences between the two groups. According to etiology, the PTA and SRT values were significantly lower in common cavity patients than the LVA patients (p values < 0.01); no significant differences were found among the other etiological groups.
Conclusions
Cochlear implantation is safe in children with inner ear malformations. However, the success rate is low compared to patients with normal anatomy in terms of audiological results; the most successful group of patients with inner ear malformation is large vestibular aqueduct.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coudert Aurelie et al (2019) Analysis of inner ear malformations associated with a facial nerve anomaly in 653 children fitted with a cochlear implant. Clin Otolaryngol 44(1):96–101
Aldhafeeri Ahmad M, Alsanosi Abdulrahman A (2017) Management of surgical difficulties during cochlear implant with inner ear anomalies. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 92:45–49
Celik M, Karatas E, Kanlikama M (2018) Outcomes of cochlear implantation in children with and without inner ear malformations. Pak J Med Sci 34(2):380–384
Sennaroglu Levent, Saatci Isil (2002) A new classification for cochleovestibular malformations. Laryngoscope 112(12):2230–2241
Archbold S, Lutman ME, Marshall DH (1995) Categories of auditory performance. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 166:312–314
Allen MC, Nikolopoulos TP, O'Donoghue GM (1998) Speech intelligibility in children after cochlear implantation. Am J Otol 19:742–746
Häusler R (2002) Cochlear implantation without mastoidectomy: the pericanal electrode insertion technique. Acta Otolaryngol 122(7):715–719
Kiratzidis T (2000) Veria Operation´: cochlear implantation without a mastoidectomy and a posterior tympanotomy. Updates in cochlear implantation, vol. 57. Karger Publishers, Basel, 127–130
Kronenberg J, Migirov L, Dagan T (2001) Suprameatal approach: new surgical approach for cochlear implantation. J Laryngol Otol 115(4):283–285
Lavinsky L, Michelle L (2006) P139: combined approach technique to cochlear implantation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(2_suppl): P258–P259
Al Sanosi A (2012) Trans-aditus approach: an alternative technique for cochlear implantation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64:142–144
McElveen JT, Carrasco VN, Miyamoto RT et al (1997) Cochlear implantation in common cavity malformations using a transmastoid labyrinthotomy approach. Laryngoscope 107:1032Y6
Sun Chuan-Hung et al (2015) Residual hearing preservation after cochlear implantation via round window or cochleostomy approach. Laryngoscope 125(7):1715–1719
DL Tucci, SA Telian, S Zimmerman-Phillips, TA Zwolan, PR Kileny (1995) Cochlear implantation in patients with cochlear malformations. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:833e838
Ca Buchman, Copeland BJ, Yu KK, Brown CJ, Carrasco VN, Pillsbury HC (2004) Cochlear implantation in children with congenital inner ear malformations. Laryngoscope 114:309–316
Rachovitsas D, Psillas G, Chatzigiannakidou V, Triaridis S, Constantinidis J, Vital V (2012) Speech perception and production in children with inner ear malformations after cochlear implantation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:1370–1374
Farhood Z, Nguyen SA, Miller SC, Holcomb MA, Meyer TA, Rizk AHG (2017) Cochlear implantation in inner ear malformations: systematic review of speech perception outcomes and intraoperative findings. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 156(5):783–793
Clark G (2003) Cochlear implants, fundamentals and applications. In: Beyer RT (ed) AIP series in modern acoustics and signal processing. Springer, New York, Chapter 12.
Kirk KI (2000) Challenges in the clinical investigation of cochlear implant outcomes. Cochlear implants: Principles and practices 21:349–366
Luntz M, Balkany T, Hodges AV, Telischi FF (1997) Cochlear implants in children with congenital inner ear malformations. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123(9):974–997
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, B., Cesur, S., Sahin, A. et al. Outcomes of cochlear implantation in children with inner ear malformations. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2397–2403 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05475-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05475-9