Abstract
Objectives
To make otolaryngologists aware of the variant types of auricular sinus, we have performed a systematic review of patient diagnoses and presented our operative experiences.
Methods
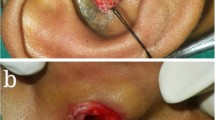
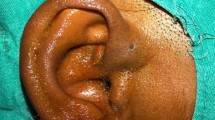
From 2009 to 2013 in Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, there was a total of 20 children with the variant type of auricular sinuses including the comprehensive group. Postauricular sinuses have pits located posterior to the imaginary vertical line that is tangent to the external auditory canal. Sinuses that penetrate the cartilage and cause postauricular swelling or skin defects characterize type 1 of the variant type, while sinuses that adhere to the cartilage and cause preauricular or auricular swelling or skin defects characterize type 2. Patients with pits both anterior to and posterior to the imaginary vertical line comprise the comprehensive group. The patients who had infected underwent auricular sinusectomy using a dual approach, with accurate fistula tracing and proper cartilage removal.
Results
Sixteen children who had infected sinus underwent surgery, while the other four were asymptomatic. Ten children (62.5%) of 16 patients were diagnosed as type 1 of the variant type, 2 (12.5%) as type 2. Four children (25%) were diagnosis as the comprehensive group. The asymptomatic could not be defined as the sinuses location were unknown. Sixteen children (100%) of 16 patients who underwent surgery had a history of misdiagnosis and treatment. These patients did not experience recurrence over a 5-year follow-up period.
Conclusion
The locations of pits and sinuses help to categorize the different types of auricular sinus. The effective method that we have described should be considered a viable way to reduce recurrence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SJ, Choung YH, Park K, Bae J, Park HY (2007) The variant type of preauricular sinus: postauricular sinus. Laryngoscope 117(10):1798–1802
Lam HC, Soo G, Wormald PJ, Van Hasselt CA (2001) Excision of the preauricular sinus: a comparison of two surgical techniques. Laryngoscope 111(2):317–319
Tsai FJ, Tsai CH (1993) Birthmarks and congenital skin lesions in Chinese newborns. J Formos Med Assoc 92(9):838–841
Chang PH, Wu CM (2005) An insidious preauricular sinus presenting as an infected postauricular cyst. Int J Clin Pract 59(3):370–372
Gan EC, Anicete R, Tan HK, Balakrishnan A (2013) Preauricular sinuses in the pediatric population: techniques and recurrence rates. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 77(3):372–378
Yeo SW et al (2006) The preauricular sinus: factors contributing to recurrence after surgery. Am J Otolaryngol 27(6):396–400
Kuczkowski J, Brzoznowski W, Kobierska-Gulida G, Czaczkowski J (2011) Diagnosis and treatment preauricular fistulas in children. Otolaryngol Pol 65(3):194–198
Wu CI, Chen CC, Chang SC (2010) Treatment of recurrent intractable periauricular fistula using temporoparietal fascia. J Craniofac Surg 21(4):1224–1225
Lee DH (2009) Re: Postoperative drainage with a vacutainer tube after excision of the preauricular sinus. Clin Otolaryngol 34(3):265–266
Prasad S, Grundfast K, Milmoe G (1990) Management of congenital preauricular pit and sinus tract in children. Laryngoscope 100(3):320–321
Currie AR, King WW, Vlantis AC, Li AK (1996) Pitfalls in the management of preauricular sinuses. Br J Surg 83(12):1722–1724
Coatesworth AP, Patmore H, Jose J (2003) Management of an infected preauricular sinus, using a lacrimal probe. J Laryngol Otol 117(12):983–984
Dunham B, Guttenberg M, Morrison W, Tom L (2009) The histologic relationship of preauricular sinuses to auricular cartilage. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(12):1262–1265
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong Science and Technology Program (A020212097) and the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M640863).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, J., Xiong, H., Liao, Q. et al. The diagnosis and treatment of a variant type of auricular sinus: postauricular sinus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 1961–1967 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05431-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05431-7