Abstract
Objectives
In this study, our aim was to identify the possible effects of montelukast sodium (ML) on the prevention of experimentally induced myringosclerosis.
Materials and methods
Twenty-eight female Wistar albino rats were used and they were divided into four groups randomly. Tympanic membranes (TM) of all animals were perforated and then group 1 received no treatment (control group), group 2 was treated with a topical saline solution, group 3 received topically ML and group 4 received orally ML. On the 15th day, all animals were euthanized. Tympanic membranes were evaluated otomicroscopically and histopathologically.
Results
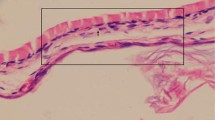
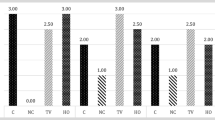
The histopathological findings, compared against a control and saline groups, showed the topically and orally ML groups had statistically significant differences of degree of myringosclerosis (p < 0.002) and median thickness of the TMs (p < 0.001). Suppression of inflammation was statistically significant only in the oral ML treatment group (p < 0.002).
Conclusion
Oral and topically administration of ML reduced myringosclerosis formation in myringotomies rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayata M, Kaptan Z, Uzunkulaoglu H, Akyıldız I, Tüzüner A, Ünverdi H, Karadas H (2015) Effect of enoxaparin sodium on experimentally-induced myringosclerosis in rats. J Int Adv Otol 11:192–195
Mattsson C, Magnuson K, Hellström S (1995) Myringosclerosis caused by increased oxygen concentration in traumatized tympanic membranes. Experimental study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104:625–632
Song JJ, Kwon SK, Cho CG, Park SW (2007) The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the prevention of experimentally induced myringosclerosis ester on the prevention of experimentally induced myringosclerosis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:1287–1291
Kazikdas KC, Uguz MZ, Erbil G, Tugyan K, Yilmaz O, Guneli E, Altun Z (2006) The anti-oxidant effect of alpha-tocopherol in the prevention of experimentally induced myringosclerosis. Otol Neurotol 27:882–886
Görür K, Ozcan C, Polat A, Unal M, Tamer L, Cinel I (2002) The anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic activities of selenium in the prevention of myringosclerosis in rats. J Laryngol Otol 116:426–429
Tos M, Stangerup SE, Larsen P (1987) Dynamics of eardrum changes following secretory otitis: a prospective study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:380–385
Möller P (1984) Tympanosclerosis of the ear drum. A scanning electron microscopic study. Acta Otolaryngol 91(Suppl 414):171–177
Parker AJ, Maw AR, Powell JE (1990) Intra-tympanic membrane bleeding after grommet insertion and tympanosclerosis. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 15:203–207
Zielnik-Jurkiewicz B, Olszewska-Sosińska O, Rakowska M (2006) Results of treatment with tympanostomy tubes in children with otitis media with effusion. Otolaryngol Pol 60:181–185
Slack RW, Maw AR, Capper JW, Kelly S (1984) Prospective study of tympanosclerosis developing after grommet insertion. J Laryngol Otol 98:771–774
Yaman H, Yilmaz S, Alkan N, Subasi B, Guclu E, Ozturk O (2010) Shepard grommet tympanostomy tube complications in children with chronic otitis media with effusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267:1221–1224
Kay DJ, Nelson M, Rosenfeld RM (2001) Meta-analysis of tympanostomy tube sequelae. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:374–380
Asiri S, Hahsam A, Anazy FA, Zakzouk S, Banjar A (1999) Tympanosclerosis: review of literature and incidence among patients with middle-ear infection. J Laryngol Otol 113:1076–1080
Mattsson C, Marklund SL, Hellström S (1997) Application of oxygen free radical scavengers to diminish the occurrence of myringosclerosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 106:513–518
Schiff M, Yoo TJ (1985) Immunologic aspects of otologic disease: an overview. Laryngoscope 95:259–269
Polat S, Ozturk O, Uneri C, Yuksel M, Haklar G, Bozkurt S, Küllü S (2004) Determination of reactive oxygen species in myringotomized tympanic membranes: effect of vitamin e treatment. Laryngoscope 114:720–725
Mattsson C, Stierna P, Hellström S (2000) Treatment with dexamethasone arrests the development of myringosclerosis after myringotomy. Am J Otol 21:804–808
Ozcan C, Gorur K, Cinel L, Talas DU, Unal M, Cinel I (2002) The inhibitory effect of topical N-acetylcysteine application on myringosclerosis in perforated rat tympanic membrane. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 63:179–184
Spratley JE, Hellstrom SO, Mattsson CK, Pais-Clemente M (2001) Topical ascorbic acid reduces myringosclerosis in perforated tympanic membranes a study in the rat. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:585–591
Anderson R, Theron AJ, Gravett CM, Steel HC, Tintinger GR, Feldman C (2009) Montelukast inhibits neutrophil pro-inflammatory activity by a cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 156:105–115
Beytur A, Ciftci O, Oguz F, Oguzturk H, Yilmaz H (2012) Montelukast attenuates side effects of cisplatin including testicular, spermatological, and hormonal damage in male rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:207–213
Ozkan E, Yardimci S, Dulundu E, Topaloğlu U, Sehirli O, Ercan F, Velioğlu-Oğünç A, Sener G (2010) Protective potential of montelukast against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res 159:588–594
Holma R, Salmenpera P, Virtanen I, Vapaatalo H, Korpela R (2007) Prophylactic potential of montelukast against mild colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 58:455–467
Kose E, Sapmaz HI, Sarihan E, Vardi N, Turkoz Y, Ekinci N (2012) Beneficial effects of montelukast against methotrexate-induced liver toxicity: a biochemical and histological study. Sci World J 2012:1–6
Hele DJ, Birrell MA, Webber SE, Foster ML, Belvisi MG (2001) Mediator involvement in antigen-induced bronchospasm and microvascular leakage in the airways of ovalbumin sensitized Brown Norway rats. Br J Pharmacol 132:481–488
İçer M, Zengin Y, Gunduz E, Dursun R, Durgun HM, Turkcu G, Yuksel H, Üstündağ M, Guloglu C (2016) Is montelukast as effective as N-acetylcysteine in hepatic injury due to acetaminophen intoxication in rats? Exp Toxicol Pathol 68:55–59
Akbaş Y, Pata YS, Görür K, Polat G, Polat A, Ozcan C, Unal M (2003) The effect of l-carnitine on the prevention of experimentally induced myringosclerosis in rats. Hear Res 184:107–112
Emir H, Kaptan ZK, Samim E, Sungu N, Ceylan K, Ustun H (2009) The preventive effect of ginkgo biloba extract in myringosclerosis: study in rats. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140:171–176
Capra V, Thompson MD, Sala A, Cole DE, Folco G, Rovati GE (2007) Cysteinyl-leukotrienes and their receptors in asthma and other inflammatory diseases: critical update and emerging trends. Med Res Rev 27:469–527
Henderson WR Jr (1994) Role of leukotrienes in asthma. Ann Allergy 72:272–278
Schoem SR, Willard A, Combs JT (2010) A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of montelukast’s effect on persistent middle ear effusion. Ear Nose Throat J 89:434–437
Aynali G, Yariktaş M, Yasan H, Karahan N, Başpinar S, Tüz M, Gümüş S (2011) The effects of methylprednisolone, montelukast and indomethacin in experimental otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:15–19
Kabasakal I, Sener G, Cetinel S, Contuk G, Gedik GN, Yegen BC (2005) Burn-induced oxidative injury of the gut is ameliorated by the leukotriene receptor blocker montelukast. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 72:431–440
Hemmati AA, Ghorbanzadeh B, Behmanesh MA (2013) Potentiation of indomethacin-induced anti-inflammatory response by montelukast in formalin-induced inflammation in rats. Acta Med Iran 51:675–680
Ozkan E, Akyuz C, Şehirli AO, Topaloğlu U, Ercan F, Sener G (2010) Montelukast, a selective cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 antagonist, reduces cerulein-induced pancreatic injury in rats. Pancreas 39:1041–1046
Peng J, Zhou H, Kuang G, Xie L, Tian T, Liu R (2017) The selective cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLT1R) antagonist montelukast regulates extracellular matrix remodeling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484:474–479
Santos PF, Leal MC, Peixoto C, Neto SC, Rosas ST (2005) Otomicroscopic and histologic findings of induced myringosclerosis in rats: a critical study of an experimental model. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 71:668–674
Sener G, Sakarcan A, Sehirli O, Ekşioğlu-Demiralp E, Sener E, Ercan F, Gedik N, Yeğen BC (2007) Chronic renal failure-induced multiple-organ injury in rats is alleviated by the selective CysLT1 receptor antagonist montelukast. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 83:257–267
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Gülin Gökçe Kesici (Yıldırım Beyazıt University, Atatürk Education and Research Hospital, Otolaryngology Clinic, Ankara, Turkey) for statistical analysis of data for her help during the experiment.
Funding
There is no financing in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Ethical approval
The experimental study complied with experimental ethical principles and animal protection laws according to the rules and regulations in Turkey, approved by the Local Ethics Committee in Ankara, Turkey (Prot. no: 01/03/2018-0045). This study was conducted in compliance with the guidelines for animal experimentation at the Department of Laboratory Animal Science of Medical School.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kargin Kaytez, S., Kavuzlu, A., Yumusak, N. et al. Is there any effect of montelukast on prevention of myringosclerosis after myringotomy in a rat model?. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 57–62 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5181-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5181-3