Abstract
Introduction
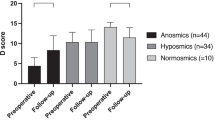
The primary aim of the current study was to examine the usefulness of our proposed olfactory scoring system in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients with olfactory disorders (n = 213) receiving endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS).
Materials and methods
Analyzed patients were divided into two groups: an eosinophilic CRS (ECRS) group (n = 153); and a non-ECRS group (n = 60). The T&T recognition threshold test was used to evaluate olfaction at baseline and at 3 and 12 months after ESS. Patients with mean recognition threshold < 2.0 at 3 or 12 months or with a decrease of ≥ 1.0 as compared with baseline were defined as showing clinical improvement. We scored mucosal conditions as normal (0 points), edema (1 point), and polyp (2 points) at the canopy of olfactory cleft (OC), middle and superior turbinates, superior nasal meatus, and sphenoethmoidal recess during ESS. The total score of OCs (SOCs) was calculated (range 0–20 points). We compared SOCs between ECRS and non-ECRS groups. Factors related to olfactory improvement were also investigated using uni- and multivariate analyses.
Results
SOCs in the ECRS and non-ECRS groups showed significant correlations with mean recognition thresholds at baseline and at 3 and 12 months. In the multivariate analysis for predicting improvement of mean recognition threshold, lower SOCs were significantly associated with olfactory improvement factors at 3 and 12 months postoperatively in the ECRS group.
Conclusion
SOCs appears promising for estimating olfactory prognosis after ESS in CRS patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRS:
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis
- ESS:
-
Endoscopic sinus surgery
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- ECRS:
-
Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis
- OC:
-
Olfactory cleft
- SOC:
-
Score of olfactory clefts
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
References
Kohli P, Naik AN, Harruff EE, Nguyen SA, Schlosser RJ, Soler ZM (2017) The prevalence of olfactory dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 127(2):309–320
Mattos JL, Schlosser RJ, Storck KA, Soler ZM (2017) Understanding the relationship between olfactory-specific quality of life, objective olfactory loss, and patient factors in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 7(7):734–740
Oka H, Tsuzuki K, Takebayashi H, Kojima Y, Daimon T, Sakagami M (2013) Olfactory changes after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 40(5):452–457
Kern RC (2000) Chronic sinusitis and anosmia: pathologic changes in the olfactory mucosa. Laryngoscope 110(7):1071–1077
Shimizu T, Suzaki H (2016) Past, present and future of macrolide therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Auris Nasus Larynx 43(2):131–136
Ishitoya J, Sakuma Y, Tsukuda M (2010) Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol Int 59(3):239–245
Bachert C, Pawankar R, Zhang L, Bunnag C, Fokkens WJ, Hamilos DL, Jirapongsananuruk O, Kern R, Meltzer EO, Mullol J, Naclerio R, Pilan R, Rhee CS, Suzaki H, Voegels R, Blaiss M (2014) ICON: chronic rhinosinusitis. World Allergy Organ J 7(1):25
Kohli P, Naik AN, Farhood Z, Ong AA, Nguyen SA, Soler ZM, Schlosser RJ (2016) Olfactory outcomes after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 155(6):936–948
Rudmik L (2017) Economics of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 17(4):20
Hull BP, Chandra RK (2017) Refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 50(1):61–81
Eloy JA, Marchiano E, Vázquez A (2017) Extended Endoscopic and Open Sinus Surgery for Refractory Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 50(1):165–182
Banglawala SM, Oyer SL, Lohia S, Psaltis AJ, Soler ZM, Schlosser RJ (2014) Olfactory outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis after medical treatments: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 4(12):986–994
Ichinose M, Sugiura H, Nagase H, Yamaguchi M, Inoue H, Sagara H, Tamaoki J, Tohda Y, Munakata M, Yamauchi K, Ohta K; Japanese Society of Allergology (2017) Allergol Int 66(2):163–189
Hong CJ, Tsang AC, Quinn JG, Bonaparte JP, Stevens A, Kilty SJ (2015) Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody therapy for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review. Syst Rev 4:166
Grgić MV, Ćupić H, Kalogjera L, Baudoin T (2015) Surgical treatment for nasal polyposis: predictors of outcome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(12):3735–3743
Morrison EE, Costanzo RM (1990) Morphology of the human olfactory epithelium. J Comp Neurol 297:1–13
Paik SI, Lehman MN, Seiden AM, Duncan HJ, Smith DV (1992) Human olfactory biopsy. The influence of age and receptor distribution. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:731–738
Leopold DA, Hummel T, Schwob JE, Hong SC, Knecht M, Kobal G (2000) Anterior distribution of human olfactory epithelium. Laryngoscope 110:417–421
Feron F, Perry C, McGrath JJ, Mackay-Sim A (1998) New techniques for biopsy and culture of human olfactory epithelial neurons. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:861–866
Mori E, Matsuwaki Y, Mitsuyama C, Okushi T, Nakajima T, Moriyama H (2013) Risk factors for olfactory dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 40(5):465–469
Masaki M, Tanaka Y (1998) Nasal polyps in the olfactory cleft. Laryngoscope 108(8 Pt 1):1243–1246
Sakuma Y, Ishitoya J, Komatsu M, Shiono O, Hirama M, Yamashita Y, Kaneko T, Morita S, Tsukuda M (2011) New clinical diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 38(5):583–588
Kohli P, Schlosser RJ, Storck K, Soler ZM (2016) Olfactory cleft computed tomography analysis and olfaction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 30(6):402–406
Chang H, Lee HJ, Mo JH, Lee CH, Kim JW (2009) Clinical implication of the olfactory cleft in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and olfactory loss. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:988–992
Pallanch JF, Yu L, Delone D, Robb R, Holmes DR 3rd, Camp J, Edwards P, McCollough CH, Ponikau J, Dearking AC, Lane J, Primak A, Shinkle A, Hagan J, Frigas E, Ocel JJ, Tombers N, Siwani R, Orme NM, Reed KB, Jerath N, Dhillon R, Kita H (2013) Three-dimensional volumetric computed tomographic scoring as an objective outcome measure for chronic rhinosinusitis: Clinical correlations and comparison to Lund-Mackay scoring. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 3:963–972
Soler ZM, Pallanch JF, Sansoni ER, Jones CS, Lawrence LA, Schlosser RJ, Mace JC, Smith TL (2015) Volumetric computed tomography analysis of the olfactory cleft in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5:846–854
Smith TL, Mendolia-Loffredo S, Loehrl TA, Sparapani R, Laud PW, Nattinger AB (2005) Predictive factors and outcomes in endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 115(11):2199–2205
Tokunaga T, Sakashita M, Haruna T, Asaka D, Takeno S, Ikeda H, Nakayama T, Seki N, Ito S, Murata J, Sakuma Y, Yoshida N, Terada T, Morikura I, Sakaida H, Kondo K, Teraguchi K, Okano M, Otori N, Yoshikawa M, Hirakawa K, Haruna S, Himi T, Ikeda K, Ishitoya J, Iino Y, Kawata R, Kawauchi H, Kobayashi M, Yamasoba T, Miwa T, Urashima M, Tamari M, Noguchi E, Ninomiya T, Imoto Y, Morikawa T, Tomita K, Takabayashi T, Fujieda S (2015) Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: the JESREC Study. Allergy 70:995–1003
Shiga H, Taki J, Okuda K, Watanabe N, Tonami H, Nakagawa H, Kinuya S, Miwa T (2017) Prognostic value of olfactory nerve damage measured with thallium-based olfactory imaging in patients with idiopathic olfactory dysfunction. Sci Rep 7(1):3581
Horikiri K, Kikuta S, Kanaya K, Shimizu Y, Nishijima H, Yamasoba T, Kondo K (2017) Intravenous olfactory test latency correlates with improvement in post-infectious olfactory dysfunction. Acta Otolaryngol 137(10):1083–1089
Lund VJ, Kennedy DW (1995) Quantification for staging sinusitis. The staging and therapy group. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 167:17–21
Wright ED, Agrawal S (2007) Impact of perioperative systemic steroids on surgical outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis: evaluation with the novel perioperative sinus endoscopy (POSE) scoring system. Laryngoscope 117:1–28
Tsuzuki K, Hinohira Y, Takebayashi H, Kojima Y, Yukitatsu Y, Daimon T, Sakagami M (2014) Novel endoscopic scoring system after sinus surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx 41:450–454
Soler ZM, Sauer DA, Mace J, Smith TL (2009) Relationship between clinical measures and histopathologic findings in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141:454–461
Durack DT, Ackerman SJ, Loegering DA, Gleich GJ (1981) Purification of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5165–5169
Fredens K, Dahl R, Venge P (1982) The Gordon phenomenon induced by the eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil protein X. J Allergy Clin Immunol 70:361–366
Cho SW, Kim DW, Kim JW, Lee CH, Rhee CS (2017) Classification of chronic rhinosinusitis according to a nasal polyp and tissue eosinophilia: limitation of current classification system for Asian population. Asia Pac Allergy 7(3):121–130
Bardaranfar MH, Ranjbar Z, Dadgarnia MH, Atighechi S, Mirvakili A, Behniafard N, Sadeghi M, Abbaslu F, Baradaranfar A (2014) The effect of an absorbable gelatin dressing impregnated with triamcinolone within the olfactory cleft on polypoid rhinosinusitis smell disorders. Am J Rhinol allergy 28:172–175
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the help of our technical assistants, Ms. Yumi Kida and Mrs. Midori Tanide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of the study: KT, KO, YM, and MS; acquisition of data: KO, KT, KH, HT, HO, YK, and YY; analysis and interpretation of data: KO, KT, KH, MS, and HN; drafting of the article: KO, KT, and HN.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, KAKENHI: numbers JP25462671 and JP16K11220) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Practical Research Project for Rare/Intractable Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The ethics committee meeting in our institution approved all study protocols (approval number 1512). Written informed consent from the participants was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
405_2017_4831_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary figure 1 SOCs in the improvement and unchanged groups at five assessment sites in the ECRS group at 3 months (A) and 12 months (B). Supplementary figure 2 SOCs in the improvement and unchanged groups at five assessment sites in the non-ECRS group at 3 months (A) and 12 months (B). (PPTX 14676 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, K., Tsuzuki, K., Hashimoto, K. et al. Usefulness of our proposed olfactory scoring system during endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 415–423 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4831-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4831-1