Abstract
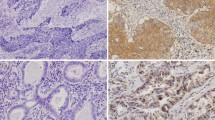
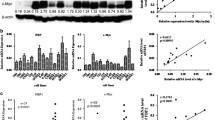
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), a malignant tumor at the top and side of the nasopharyngeal cavity, highly occurs in the southern region of China. Cancer cell metastasis is one of the leading causes of death in NPC patients. Osteopontin (OPN), is a phosphorylated extracellular matrix protein with a variety of functions, was found to be overexpressed in many cancers. However, the expression and role of OPN in patients with NPC in Guangxi, China are unclear. Here, we observed that NPC patients had upregulated OPN at mRNA protein and levels. Immunochemistry (IHC) analysis of OPN expression in 68 NPC clinical specimens indicated that high expression of OPN had positive correlation with NPC lymph node metastasis (P = 0.012), distant metastasis (P = 0.001) and TNM staging (P = 0.018). Moreover, compared with relatively low OPN, NPC patients with higher expression of OPN showed a poorer overall survival rate (P = 0.001, log rank test). Multivariate analysis showed that OPN expression in NPC was an independent prognostic marker. The proliferation, apoptosis and migration ability of CEN-2Z cancer cells in NPC were determined by MTT, flow cytometry and wound-healing assays, respectively. Upregulation of OPN in CEN-2Z cancer cells promoted cancer cell proliferation and migration, and suppressed apoptosis. In sum, our result suggests OPN could be used as a valuable oncoprotein and show that overexpression of OPN in NPC may serve as a potential prognostic marker.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman CH, Parvathaneni U, Yom SS (2017) Revisiting induction chemotherapy before radiotherapy for head and neck cancer, part II: nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Future Oncol 13:581–584
Wee JT, Ha TC, Loong SL, Qian CN. (2010) Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a “Cantonese cancer”?. Chin J Cancer 29: 517–26
Lin JH, Jiang CQ, Ho SY, Zhang WS, Mai ZM, Xu L, Lo CM, Lam TH (2015) Smoking and nasopharyngeal carcinoma mortality: a cohort study of 101,823 adults in Guangzhou, China. BMC Cancer 15:906
Wei Z, Zeng X, Xu J, Duan X, Yang J, Xie Y (2014) Prognostic value of the pretreatment serum level of cytokeratin fraction 21–1 in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a study of 332 cases. Head Neck 36:71–76
Bei JX, Li Y, Jia WH, Feng BJ, Zhou G, Chen LZ, Feng QS, Low HQ, Zhang H, He F, Tai ES, Kang T, Liu ET et al (2010) A genome-wide association study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma identifies three new susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42:599–603
Wei WI, Sham JS (2005) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 365:2041–2054
Young LS, Rickinson AB (2004) Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer 4:757–768
Zhang R, Pan X, Huang Z, Weber GF, Zhang G (2011) Osteopontin enhances the expression and activity of MMP-2 via the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One 6:e23831
Zhao XQ, Dong JH, Zhang WZ, Liu Z (2011) Prognosis of ampullary cancer based on immunohistochemical type and expression of osteopontin. Diagn Pathol 6:98
Yu TT, Han ZG, Shan L, Tao J, Zhang T, Yuan SF, Shen HL (2014) Expression of osteopontin in non-small cell lung cancer and correlative relation with microvascular density. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:29–32
Qiu Y, Hu Y, Zhang ZY, Ye L, Xu FH, Schneider ME, Ma XL, Du YX, Zuo XB, Zhou FS, Chen G, Xie XS, Zhang Y et al (2014) Genetic association of osteopontin (OPN) and its receptor CD44 genes with susceptibility to Chinese gastric cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140:2143–2156
Zhang H, Guo M, Chen JH, Wang Z, Du XF, Liu PX, Li WH (2014) Osteopontin knockdown inhibits alphav,beta3 integrin-induced cell migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis of breast cancer cells by inducing autophagy and inactivating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 33:991–1002
Wang HH, Wang XW, Tang CE (2011) Osteopontin expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: its relevance to the clinical stage of the disease. J Cancer Res Ther 7:138–142
Phillips RJ, Helbig KJ, Van der Hoek KH, Seth D, Beard MR (2012) Osteopontin increases hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in a CD44 dependant manner. World J Gastroenterol 18:3389–3399
Pang H, Lu H, Song H, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Liu N, Lan F, Liu Y, Yan S, Dong X, Cai L (2013) Prognostic values of osteopontin-c, E-cadherin and beta-catenin in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 37:985–992
Luo W, Fang W, Li S, Yao K (2012) Aberrant expression of nuclear vimentin and related epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 131:1863–1873
Li J, Guan HY, Gong LY, Song LB, Zhang N, Wu J, Yuan J, Zheng YJ, Huang ZS, Li M (2008) Clinical significance of sphingosine kinase-1 expression in human astrocytomas progression and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 14:6996–7003
Zhu F, Zhang Z, Wu G, Li Z, Zhang R, Ren J, Nong L (2011) Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil suppresses migration and invasion though down-regulating the expression of VEGF in lung cancer cell line A549. Med Oncol 28:565–571
Senger DR, Wirth DF, Hynes RO. (1979) Transformed mammalian cells secrete specific proteins and phosphoproteins. Cell. 16: 885–893
Anborgh PH, Mutrie JC, Tuck AB, Chambers AF (2010) Role of the metastasis-promoting protein osteopontin in the tumour microenvironment. J Cell Mol Med 14:2037–2044
Rao G, Du L, Chen Q (2013) Osteopontin, a possible modulator of cancer stem cells and their malignant niche. Oncoimmunology 2:e24169
Higashi A, Dohi Y, Uraoka N, Sentani K, Uga S, Kinoshita H, Sada Y, Kitagawa T, Hidaka T, Kurisu S, Yamamoto H, Yasui W, Kihara Y (2015) The potential role of inflammation associated with interaction between osteopontin and CD44 in a case of pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy caused by breast cancer. Intern Med 54:2877–2880
Wai PY, Kuo PC (2008) Osteopontin: regulation in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27:103–118
Xu K, Tian X, Oh SY, Movassaghi M, Naber SP, Kuperwasser C, Buchsbaum RJ (2016) The fibroblast Tiam1-osteopontin pathway modulates breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 18:14
Anborgh PH, Caria LB, Chambers AF, Tuck AB, Stitt LW, Brackstone M (2015) Role of plasma osteopontin as a biomarker in locally advanced breast cancer. Am J Transl Res 7:723–732
Gu X, Gao XS, Ma M, Qin S, Qi X, Li X, Sun S, Yu H, Wang W, Zhou D (2016) Prognostic significance of osteopontin expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 7:69666–69673
Hui EP, Sung FL, Yu BK, Wong CS, Ma BB, Lin X, Chan A, Wong WL, Chan AT (2008) Plasma osteopontin, hypoxia, and response to radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:7080–7087
Hou X, Wu X, Huang P, Zhan J, Zhou T, Ma Y, Qin T, Luo R, Feng Y, Xu Y, Chen L, Zhang L (2015) Osteopontin is a useful predictor of bone metastasis and survival in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 137:1672–1678
Chen J, Zhu C, He Z, Geng M, Li G, Tao X, Zhang F (2015) Association of OPN overexpression with tumor stage, differentiation, metastasis and tumor progression in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:7116–7124
Stemberger C, Matusan-Ilijas K, Avirovic M, Bulat-Kardum L, Ivancic A, Jonjic N, Lucin K (2014) Osteopontin is associated with decreased apoptosis and alphav integrin expression in lung adenocarcinoma. Acta Histochem 116:222–229
Ma R, Luo X, Feng S, Li J, Fan Y, Wen W, Li H (2014) Osteopontin promotes EZH2 expression and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 76:273–281
Jiang S, Chen X, Li C, Zhang X, Zhang T, Yue Y, Yang G (2012) Suramin inhibits the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the downregulation of osteopontin. Mol Med Rep 6:1351–1354
Yang G, Zhang Y, Wu J, Xiong J, Deng H, Wang J, Yang C, Zhu Z (2011) Osteopontin regulates growth and migration of human nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 4:1169–1173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2012GXNSFBA053121) and the Scientific Research Project of Guangxi Higher Educatio-n Institutions (No. KY2015ZD094).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Animal and human rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Haimei Qin and Rong Wang contributed equally to this work, and all should be considered first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Wang, R., Wei, G. et al. Overexpression of osteopontin promotes cell proliferation and migration in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is associated with poor prognosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 525–534 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4827-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4827-x