Abstract
Objectives
To investigate whether disclosed symptoms (coughing, choking and throat clearing) can be used as early predictors of swallowing disorders in non-hospitalized elderly population. In addition, to determine the presence of early findings of swallowing disorders through fiber optic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES).
Materials and methods
One hundred subjects older than 60 years were recruited from local community social meetings for seniors, they fulfilled inclusion criteria, and were given an oral interview and underwent FEES, with findings classified as: (1) saliva stasis; (2) pharyngeal residue; (3) penetration; (4) aspiration; (5) laryngeal sensitivity.
Results
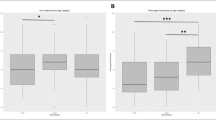
Twenty-one percent of subjects declared previous choking, 10% coughing, and 7% throat clearing, 39% had pharyngeal residue; 6% saliva stasis; 9% penetration; 2% aspiration; and 92% laryngeal sensitivity present. Thirty-three percent showed pharyngeal residue without saliva stasis, while only 6% showed positivity for both (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
Our data suggest that health care professionals should be aware that among an apparently healthy population, some subjects may have swallowing disorders without clinical complaints and that a nasolaryngoscopy exam may not be enough to predict dysphagia. We suggest that FEES should be performed to look for surrogate of dysphagia such as pharyngeal residue, laryngeal penetration, and aspiration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wirth R, Dziewas R, Beck AM, Clavé P, Hamdy S, Heppner HJ, Langmore S, Leischker AH, Martino R, Pluschinski P, Rösler A, Shaker R, Warnecke T, Sieber CC, Volkert D (2016) Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons—from pathophysiology to adequate intervention: a review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin Interv Aging 11:189–208. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S97481.eCollection2016
Ciucci M, Jones CA, Malandraki GA, Hutcheson KA (2016) Dysphagia practice in 2035: beyond fluorography, thickener, and electrical stimulation. Semin Speech Lang 37:201–218. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1584155
Eibling DE, Coyle JL (2017) Dysphagia in the elderly. In: Carrau RL, Murry T, Howell RJ (eds) Comprehensive management of swallowing disorders, 2nd edn. Plural Publishing, San Diego, pp 489–497
Puisieux F, D’Andrea C, Baconnier P, Bui-Dinh D, Castaings-Pelet S, Crestani B, Desrues B, Ferron C, Franco A, Gaillat J, Guenard H, Housset B, Jeandel C, Jebrak G, Leymarie-Saddles A, Orvoen-Frija E, Piette F, Pinganaud G, Salle JY, Strubel D, Vernejoux JM, de Wazières B, Weil-Engerer S (2011) Swallowing disorders, pneumonia and respiratory tract infectious disease in the elderly. Rev Mal Respir 28:76–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmr.2011.09.007
Ney D, Weiss J, Kind A, Robbins J (2009) Senescent swallowing: impact, strategies and interventions. Nutr Clin Pract 24:395–413. https://doi.org/10.1177/0884533609332005
Humbert IA, Robbins J (2008) Dysphagia in the elderly. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 19:853–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2008.06.002
Crary MA, Groher ME (2003) Introduction to adult swallowing disorders. Butterworth Heinemann, Philadelphia
Sutton JP (2013) Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease is responsive to levodopa. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:282–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.11.007
Baijens LWJ, Clavé P, Cras P, Ekberg O, Forster A, Kolb GF, Leners JC, Masiero S, Mateos-Nozal J, Ortega O, Smithard DG, Speyer R, Walshe M (2016) European Society for Swallowing Disorders—European Union Geriatric Medicine Society white paper: oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin Interv Aging 11:1403–1428. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S107750
Flacker JM (2003) What is a geriatric syndrome anyway? J Am Geriatr Soc 51(4):574–576. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51174.x
Butler SG, Maslan J, Stuart A, Leng X, Wilhelm E, Lintzenich CR, Williamson J, Kritchevsky SB (2011) Factors influencing bolus dwell times in healthy older adults assessed endoscopically. Laryngoscope 121:2526–2534. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.22372
Carrau RL, Howell RJ (2017) The otolaryngologist’s perspective. In: Carrau RL, Murry T, Howell RJ (eds) Comprehensive management of swallowing disorders, 2nd edn. Plural Publishing, San Diego, pp 37–42
Belafsky PC, Mouadeb DA, Rees CJ, Pryor JC, Postma GN, Allen J, Leonard RJ (2008) Validity and realiability of eating assessment tool (EAT-10). Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 117:919–924. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940811701210.
Wallace KL, Middleton S, Cook IJ (2000) Development and validation of a self-report symptom inventory to assess the severity of oral–pharyngeal dysphagia Gastroenterology 118:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1053/gg.2000.5949
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N (1988) Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia 2:216–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414429
Langmore SE, Terpenning MS, Schork A, Chen Y, Murray JT, Lopatin D, Loesche WJ (1998) Predictors of aspiration pneumonia: how important is dysphagia? Dysphagia 13:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009559
Langmore SE (2006) Endoscopic evaluation of oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. GI Motility online https://doi.org/10.1038/gimo28Published. Accessed 16 June 2017
Leder SB, Sasaki CT, Burrell MI (1998) Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of dysphagia to identify silent aspiration. Dysphagia 13:19–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009544
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olson N (1991) Endoscopic and videofluoroscopic evaluations of swallowing and aspiration. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 100:678–681. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949110000815
Murray J, Langmore SE, Ginsberg S, Dostie A (1996) The significance of accumulated oropharyngeal secretions and swallowing frequency in predicting aspiration. Dysphagia 11:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417898
Steele CM, Cichero JAY (2014) Physiological factors related to aspiration risk: a systematic review. Dysphagia 29:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9516-y
Santoro P, Furia C, Forte A, Lemos E, Garcia R, Tavares R, Imamura R (2011) Otolaryngology and speech therapy evaluation in the assessment of oropharyngeal dysphagia: a combined protocol proposal. Braz J Otolaryngol 77(2):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1808-86942011000200010
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL (1996) A penetration–aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417897
Langmore SE (2017) History of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing for evaluation and management of pharyngeal dysphagia: changes over the years. Dysphagia 32:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9775-x
Smith Hammond CA, Goldstein LB (2006) Cough and aspiration of food and liquids due to oral–pharyngeal dysphagia: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 129:154S–168S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.129.1Suppl.154S
Daggett A, Logemann J, Rademaker A, Pauloski B (2006) Laryngeal penetration during deglutition in normal subjects of various ages. Dysphagia 21(4):270–274
Butler SG, Stuart A, Markley L, Rees C (2009) Penetration and aspiration in healthy older adults as assessed during endoscopie evaluation of swallowing. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118:190–198. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940911800306
Marik PE, Kaplan D (2003) Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest 24:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.124.1.328
Robbins J, Coyle J, Rosenbek J, Roecker E, Wood J (1999) Differentiation of normal and abnormal airway protection during swallowing using the penetration–aspiration scale. Dysphagia 14:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009610
Aviv JE, Murry T (2005) Flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST). Plural Publishing, San Diego, pp 2–4
Almirall J, Cabre M, Clave P (2007) Aspiration pneumonia. Med Clin (Barc) 129:424–432
Pendergast DR, Fisher NM, Calkins E (1993) Cardiovascular, neuromuscular, and metabolic alterations with age leading to frailty. J Gerontol 48:61–67
Todd JT, Stuart A, Lintzenich CR, Wallin J, Grace-Martin K, Butler SG (2013) Stability of aspiration status in health adults. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 122(5):289–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941312200501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors received no financial support for this study.
Conflict of interest
All author and co-authors declare that they do not have conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional, CAAE 08674612.2.0000.5505 and it was approved (152.28) by UNIFESP-EPM.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lima Alvarenga, E.H., Dall’Oglio, G.P., Murano, E.Z. et al. Continuum theory: presbyphagia to dysphagia? Functional assessment of swallowing in the elderly. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 443–449 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4801-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4801-7