Abstract
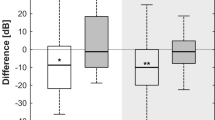
This retrospective follow-up study evaluates the efficacy and safety of bioactive glass (BAG) S53P4 when applied as filler material in mastoid obliteration surgery performed on non-cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media (NC-COM) patients with chronically discharging ears despite conservative therapy. 94 Patients (96 ears) were included. Patients underwent either intact canal wall (ICW) or canal wall down (CWD) mastoid surgery between 2005 and 2015. The intervention group comprised 23 patients (23 ears) who were treated with additional mastoid obliteration using BAG S53P4; the remaining 71 patients (73 ears) were considered controls. All patients underwent preoperative CT scanning of the mastoid. Primary functional outcome, as defined by control of suppuration, was assessed using Merchant’s scale. Hearing results as measured by air–bone gap and the incidence of adverse events were assessed as secondary outcomes. Thirty-two ears (44%) in the control group (n = 73) achieved complete control of infection at the most recent postoperative clinic visit vs 17 (74%) in the S53P4 obliteration group (n = 23). Comparing these outcomes yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 3.6 (p = 0.012, 95% CI 1.3–10.3). Complete failure to manage infection significantly differed (p = 0.048) between the control group (11 ears; 15%) and the S53P4 obliteration group (0 ears). No adverse events were observed in either group. Pre- and postoperative ABG results did not differ significantly between groups. Obliteration of the mastoid cavity using BAG S53P4 along with mastoidectomy in patients with chronically discharging NC-COM significantly improves the achievement of a dry and safe ear as compared to mastoidectomy alone. Importantly, no adverse events were observed with S53P4 BAG obliteration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mittal R, Lisi CV, Gerring R, Mittal J, Mathee K, Narasimhan G, Azad RK, Yao Q, Grati M, Yan D, Eshraghi AA, Angeli SI, Telischi FF, Liu XZ (2015) Current concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of chronic suppurative otitis media. J Med Microbiol 64(10):1103–1116. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.000155
Trinidade A, Page JC, Dornhoffer JL (2016) Therapeutic mastoidectomy in the management of noncholesteatomatous chronic otitis media: literature review and cost analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 155(6):914–922. doi:10.1177/0194599816662438
Mehta RP, Harris JP (2006) Mastoid obliteration. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 39(6):1129–1142. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2006.08.007
Nadol JB Jr (2006) Revision mastoidectomy. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 39(4):723–740. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2006.05.003 (vi–vii)
Alves RD, Cabral Junior F, Fonseca AC, Bento RF (2016) Mastoid obliteration with autologous bone in mastoidectomy canal wall down surgery: a literature overview. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 20(1):76–83. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1563382
van Gestel NA, Geurts J, Hulsen DJ, van Rietbergen B, Hofmann S, Arts JJ (2015) Clinical applications of S53P4 bioactive glass in bone healing and osteomyelitic treatment: a literature review. Biomed Res Int 2015:684826. doi:10.1155/2015/684826
Munukka E, Lepparanta O, Korkeamaki M, Vaahtio M, Peltola T, Zhang D, Hupa L, Ylanen H, Salonen JI, Viljanen MK, Eerola E (2008) Bactericidal effects of bioactive glasses on clinically important aerobic bacteria. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19(1):27–32. doi:10.1007/s10856-007-3143-1
Perez-Tanoira R, Kinnari TJ, Hyyrynen T, Soininen A, Pietola L, Tiainen VM, Konttinen YT, Aarnisalo AA (2015) Effects of S53P4 bioactive glass on osteoblastic cell and biomaterial surface interaction. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26(10):246. doi:10.1007/s10856-015-5568-2
Drago L, De Vecchi E, Bortolin M, Toscano M, Mattina R, Romano CL (2015) Antimicrobial activity and resistance selection of different bioglass S53P4 formulations against multidrug resistant strains. Future Microbiol 10(8):1293–1299. doi:10.2217/fmb.15.57
Sarin J, Grenman R, Aitasalo K, Pulkkinen J (2012) Bioactive glass S53P4 in mastoid obliteration surgery for chronic otitis media and cerebrospinal fluid leakage. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 121(9):563–569
Silvola JT (2012) Mastoidectomy cavity obliteration with bioactive glass: a pilot study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147(1):119–126. doi:10.1177/0194599812438168
Stoor P, Pulkkinen J, Grenman R (2010) Bioactive glass S53P4 in the filling of cavities in the mastoid cell area in surgery for chronic otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(6):377–382
Bernardeschi D, Pyatigorskaya N, Russo FY, De Seta D, Corallo G, Ferrary E, Nguyen Y, Sterkers O (2016) Anatomical, functional and quality-of-life results for mastoid and epitympanic obliteration with bioactive glass s53p4: a prospective clinical study. Clin Otolaryngol. doi:10.1111/coa.12748
de Veij Mestdagh PD, Colnot DR, Borggreven PA, Orelio CC, Quak JJ (2017) Mastoid obliteration with S53P4 bioactive glass in cholesteatoma surgery. Acta Otolaryngol. doi:10.1080/00016489.2017.1279346
Bernardeschi D, Nguyen Y, Russo FY, Mosnier I, Ferrary E, Sterkers O (2015) Cutaneous and labyrinthine tolerance of bioactive glass S53P4 in mastoid and epitympanic obliteration surgery: prospective clinical study. Biomed Res Int 2015:242319. doi:10.1155/2015/242319
Merchant SN, Wang P, Jang CH, Glynn RJ, Rauch SD, McKenna MJ, Nadol JB Jr (1997) Efficacy of tympanomastoid surgery for control of infection in active chronic otitis media. Laryngoscope 107(7):872–877
Csakanyi Z, Katona G, Konya D, Mohos F, Sziklai I (2014) Middle ear gas pressure regulation: the relevance of mastoid obliteration. Otol Neurotol 35(6):944–953. doi:10.1097/mao.0000000000000282
Yung M, Bennett A (2013) Use of mastoid obliteration techniques in cholesteatoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283646521
Linthicum FH Jr (2002) The fate of mastoid obliteration tissue: a histopathological study. Laryngoscope 112(10):1777–1781. doi:10.1097/00005537-200210000-00013
Kang MK, Ahn JK, Gu TW, Han CS (2009) Epitympanoplasty with mastoid obliteration technique: a long-term study of results. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(5):687–691. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2008.11.027
Eliades SJ, Limb CJ (2013) The role of mastoidectomy in outcomes following tympanic membrane repair: a review. Laryngoscope 123(7):1787–1802. doi:10.1002/lary.23752
Mokbel KM, Khafagy YW (2012) Single flap with three pedicles, bone pate and split-thickness skin graft for immediate mastoid obliteration after canal wall down mastoidectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(9):2037–2041. doi:10.1007/s00405-011-1853-y
Heo KW, Kang MK, Park JY (2014) Alternative to canal wall-down mastoidectomy for sclerotic mastoid cavities: epitympanoplasty with mastoid obliteration. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 123(1):47–52. doi:10.1177/0003489414521387
Kim CW, Oh JI, Choi KY, Park SM, Park MI (2012) A technique for concurrent procedure of mastoid obliteration and meatoplasty after canal wall down mastoidectomy. Auris Nasus Larynx 39(6):557–561. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2011.11.004
Schimanski G, Schimanski E (2015) Obliteration of mastoid cavities: 30 years of experience with recommendations for surgical strategy. HNO 63(8):538–545. doi:10.1007/s00106-015-0028-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JV wrote the manuscript. JV and PdVM analysed data. JQ, PB, DC designed research, performed research and surgery and drafted manuscript. CO provided scientific input and drafted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vos, J., de Vey Mestdagh, P., Colnot, D. et al. Bioactive glass obliteration of the mastoid significantly improves surgical outcome in non-cholesteatomatous chronic otitis media patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 4121–4126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4757-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4757-7