Abstract
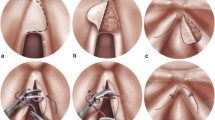
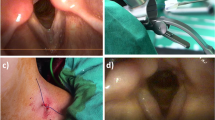
This work is a retrospective analysis to investigate the critical risk factor for the therapeutic effect of endoscopic keel placement on anterior glottic web. Altogether, 36 patients with anterior glottic web undergoing endoscopic lysis and silicone keel placement were enrolled. Their voice qualities were evaluated using the voice handicap index-10 (VHI-10) questionnaire, and improved significantly 3 months after surgery (21.53 ± 3.89 vs 9.81 ± 6.68, P < 0.0001). However, 10 (27.8%) cases had web recurrence during the at least 1-year follow-up. Therefore, patients were classified according to the Cohen classification or web thickness, and the recurrence rates were compared. The distribution of recurrence rates for Cohen type 1 ~ 4 were 28.6, 16.7, 33.3, and 40%, respectively. The difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.461). When classified by web thickness, only 2 of 27 (7.41%) thin type cases relapsed whereas 8 of 9 (88.9%) cases in the thick group reformed webs (P < 0.001). These results suggest that the therapeutic outcome of endoscopic keel placement mostly depends on the web thickness rather than the Cohen grades. Endoscopic lysis and keel placement is only effective for cases with thin glottic webs. Patients with thick webs should be treated by other means.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicollas R, Triglia JM (2008) The anterior laryngeal webs. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 41(5):877–888. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2008.04.008
Benmansour N, Remacle M, Matar N, Lawson G, Bachy V, Van der Vorst S (2012) Endoscopic treatment of anterior glottic webs according to Lichtenberger technique and results on 18 patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(9):2075–2080. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2001-z
Lahav Y, Shoffel-Havakuk H, Halperin D (2015) Acquired glottic stenosis-the ongoing challenge: a review of etiology, pathogenesis, and surgical management. J Voice. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.10.012
Cohen SR (1985) Congenital glottic webs in children. A retrospective review of 51 patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 121:2–16
Alkan U, Nachalon Y, Vaisbuch Y, Katz O, Hamzany Y, Stern Y (2016) Treating paediatric anterior glottic web: single-centre experience of 20 patients with comparison among techniques. Clin Otolaryngol. doi:10.1111/coa.12749
Amir M, Youssef T (2010) Congenital glottic web: management and anatomical observation. Clin Respir J 4(4):202–207. doi:10.1111/j.1752-699X.2009.00176.x
Xu W, Li H-Y, Hu R, Hu H-Y, Hou L-Z, Zhang L, Zhuang P-Y, Han D-M (2008) [Analysis of reliability and validity of the Chinese version of voice handicap index (VHI)]. Zhonghua er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi = Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 43(9):670–675
Rosen CA, Lee AS, Osborne J, Zullo T, Murry T (2004) Development and validation of the voice handicap index-10. Laryngoscope 114(9):1549–1556. doi:10.1097/00005537-200409000-00009
Miyamoto RC, Cotton RT, Rope AF, Hopkin RJ, Cohen AP, Shott SR, Rutter MJ (2004) Association of anterior glottic webs with velocardiofacial syndrome (chromosome 22q11.2 deletion). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130(4):415–417. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2003.12.014
Lichtenberger G, Toohill RJ (1991) The endo-extralaryngeal needle carrier. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 105(5):755–756
Lichtenberger G, Toohill RJ (1994) New keel fixing technique for endoscopic repair of anterior commissure webs. Laryngoscope 104(6 Pt 1):771–774. doi:10.1288/00005537-199406000-00023
Edwards J, Tanna N, Bielamowicz SA (2007) Endoscopic lysis of anterior glottic webs and silicone keel placement. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 116(3):211–216
Paniello RC, Desai SC, Allen CT, Khosla SM (2013) Endoscopic keel placement to treat and prevent anterior glottic webs. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 122(11):672–678
Montgomery WW, Gamble JE (1970) Anterior glottic stenosis: experimental and clinical management. Arch Otolaryngol 92(6):560–567
Izadi F, Delarestaghi MM, Memari F, Mohseni R, Pousti B, Mir P (2010) The butterfly procedure: a new technique and review of the literature for treating anterior laryngeal webs. J Voice 24(6):742–749. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2009.03.005
Garrel R, Amy de La Breteque B, Canitrot L, Frery A, Guerrier B (2012) One-step microsurgery for acquired anterior glottic web. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 129(1):61–63. doi:10.1016/j.anorl.2011.10.004
Xiao Y, Wang J, Han DM, Ma LJ, Ye JY, Xu W (2014) Vocal cord mucosal flap for the treatment of acquired anterior laryngeal web. Chin Med J 127(7):1294–1297. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.20132832
Kane-Smyth J, Barnett TP, O’Leary JM, Dixon PM (2016) Surgical treatment of iatrogenic ventral glottic stenosis using a mucosal flap technique. Vet Surg 45(4):436–442. doi:10.1111/vsu.12465
Bhongmakapat T, Kantapasuantara K, Praneevatakul P (2012) A small absorbable stent for treatment of anterior glottic web. J Voice 26(2):259–261. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2011.01.010
Adachi K, Umezaki T (2017) Effectiveness of fibrin coating in the management of web formation after laryngomicrosurgery. Am J Otolaryngol 38(1):1–6. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.09.010
Kwon SK, Ryu YJ, Kim DW, Chang H, Kim SY, Sung MW, Hah JH (2016) Prevention of anterior glottis web with hyaluronic acid derivatives in rabbit model. Laryngoscope 126(10):2320–2324. doi:10.1002/lary.26089
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China (No. 15401971600, 17411962000, and 16411960600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Jian Chen and Fang Shi share first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Shi, F., Chen, M. et al. Web thickness determines the therapeutic effect of endoscopic keel placement on anterior glottic web. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3697–3702 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4689-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4689-2