Abstract
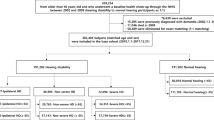
Age-related hearing loss (ARHL) is postulated to affect dementia. Our study aims to investigate the relationship between ARHL and the prevalence, and 10-year incidence of dementia in the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). We selected patients diagnosed with ARHL from the NHIRD. A comparison cohort comprising of patients without ARHL was frequency-matched by age, sex, and co-morbidities, and the occurrence of dementia was evaluated in both cohorts. The ARHL cohort consisted of 4108 patients with ARHL and the control cohort consisted of 4013 frequency-matched patients without ARHL. The incidence of dementia [hazard ratio (HR), 1.30; 95% confidence interval (CI 1.14–1.49); P = 0.002] was higher among ARHL patients. Cox models showed that being female (HR, 1.34; 95% CI 1.07–1.68), as well as having co-morbidities, including chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, stroke, head injury, chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, alcohol abuse/dependence, and tobacco abuse/dependence (HR, 1.27; 95% CI 1.11–1.45), were independent risk factors for dementia in ARHL patients. We found ARHL may be one of the early characteristics of dementia, and patients with hearing loss were at a higher risk of subsequent dementia. Clinicians should be more sensitive to dementia symptoms within the first 2 years following ARHL diagnosis. Further clinical studies of the relationship between dementia and ARHL may be necessary.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cappe C, Rouiller EM, Barone P (2009) Multisensory anatomical pathways. Hear Res 258:28–36
Roth TN (2015) Aging of the auditory system. Handb Clin Neurol 129:357–373
Reitz C, Mayeux R (2014) Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem Pharmacol 88:640–651
Gates GA, Gibbons LE, McCurry SM, Crane PK, Feeney MP, Larson EB (2010) Executive dysfunction and presbycusis in older persons with and without memory loss and dementia. Cogn Behav Neurol 23:218–223
Gates GA, Anderson ML, Feeney MP, McCurry SM, Larson EB (1996) Central auditory dysfunction, cognitive dysfunction, and dementia in older people. Arch Otolaryngol–Head Neck Surg 122:161–167
Kerbage C, Sadowsky CH, Jennings D, Cagle GD, Hartung PD (2013) Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by detecting exogenous fluorescent signal of ligand bound to Beta amyloid in the lens of human eye: an exploratory study. Front. Neurol 4:62
Dubno JR, Ahlstrom JB, Horwitz AR (2008) Binaural advantage for younger and older adults with normal hearing. J Speech Lang Hear Res 51:539–556
Kurniawan C, Westendorp RG, de Craen AJ, Gussekloo J, de Laat J, van Exel E. (2012) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E and age-related hearing loss. Neurobiol Aging 33:2230 e2237–2230 e2212.
Lin FR (2011) Hearing loss and cognition among older adults in the United States. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 66:1131–1136
Teipel S, Fritze T, Ovari A, Buhr A, Kilimann I, Witt G, Pau HW, Doblhammer G (2015) Regional pattern of dementia and prevalence of hearing impairment in Germany. J Am Geriatr Soc 63:1527–1533
Uhlmann RF, Larson EB, Rees TS, Koepsell TD, Duckert LG (1989) Relationship of hearing impairment to dementia and cognitive dysfunction in older adults. JAMA 261:1916–1919
Granick S, Kleban MH, Weiss AD (1976) Relationships between hearing loss and cognition in normally hearing aged persons. J Gerontol 31:434–440
Gurgel RK, Ward PD, Schwartz S, Norton MC, Foster NL, Tschanz JT. (2014) Relationship of hearing loss and dementia: a prospective, population-based study. Otol Neurotol 35:775–781.
Lin FR, Yaffe K, Xia J, Xue QL, Harris TB, Purchase-Helzner E, Satterfield S, Ayonayon HN, Ferrucci L, Simonsick EM; Health ABC Study Group (2013) Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults. JAMA Intern Med 173:293–299.
Peters CA, Potter JF, Scholer SG (1988) Hearing impairment as a predictor of cognitive decline in dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc 36:981–986
Gates GA, Beiser A, Rees TS, D’Agostino RB, Wolf PA (2002) Central auditory dysfunction may precede the onset of clinical dementia in people with probable Alzheimer’s disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 50:482–488
Gates GA, Anderson ML, McCurry SM, Feeney MP, Larson EB (2011) Central auditory dysfunction as a harbinger of Alzheimer dementia. Arch Otolaryngol–Head Neck Surg 137:390–395
Kaplan W, Wirtz, V.J., Mantel-Teeuwisse, A. (2013) A Public Health Approach to Innovation. Priority medicines for Europe and the World. 2013 Update: World Health Organization 2013.
Alzheimer’s A. (2014) Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Demen 10:e47–92.
Ott A, Stolk RP, van Harskamp F, Pols HA, Hofman A, Breteler MM (1999) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Neurology 53:1937–1942
Kivipelto M, Helkala EL, Laakso MP, Hänninen T, Hallikainen M, Alhainen K, Soininen H, Tuomilehto J, Nissinen A (2001) Midlife vascular risk factors and Alzheimer’s disease in later life: longitudinal, population based study. BMJ 322:1447–1451
Chang LY, Lowe J, Ardiles A, Lim J, Grey AC, Robertson K, Danesh-Meyer H, Palacios AG, Acosta ML (2014) Alzheimer’s disease in the human eye. Clinical tests that identify ocular and visual information processing deficit as biomarkers. Alzheimer’s Demen 10:251–261.
Mitchell P, Gopinath B, Wang JJ, McMahon CM, Schneider J, Rochtchina E, Leeder SR (2011) Five-year incidence and progression of hearing impairment in an older population. Ear Hear 32(2):251–257
Crews JE, Campbell VA (2004) Vision impairment and hearing loss among community-dwelling older Americans: implications for health and functioning. Am J Public Health 94:823–829
Cruickshanks KJ, Tweed TS, Wiley TL, Klein BE, Klein R, Chappell R, Nondahl DM, Dalton DS (2003) The 5-year incidence and progression of hearing loss: the epidemiology of hearing loss study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:1041–1046
Pearson JD, Morrell CH, Gordon-Salant S, Brant LJ, Metter EJ, Klein LL, Fozard JL (1995) Gender differences in a longitudinal study of age-associated hearing loss. J Acoust Soc Am 97:1196–1205
Cruickshanks KJ, Wiley TL, Tweed TS, Klein BE, Klein R, Mares-Perlman JA, Nondahl DM (1998) Prevalence of hearing loss in older adults in Beaver Dam, Wisconsin. The Epidemiology of Hearing Loss Study. Am J Epidemiol 148:879–886
Gates GA, Cobb JL, D’Agostino RB, Wolf PA (1993) The relation of hearing in the elderly to the presence of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk factors. Arch Otolaryngol–Head Neck Surg 119:156–161
Schuknecht HF. (1964) Further observations on the pathology of presbycusis. Arch Otolaryngol 80:369–382.
Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Pinto M et al (Dec 2012) Endothelial function and cardiovascular risk in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Atherosclerosis 225(2):511–516
Bao AM, Meynen G, Swaab DF (2008) The stress system in depression and neurodegeneration: focus on the human hypothalamus. Brain Res Rev 57(2):531–553
Leonard BE (2007) Inflammation, depression and dementia: are they connected? Neurochem Res 32:1749–1756
Zhang J (2015) Mapping neuroinflammation in frontotemporal dementia with molecular PET imaging. J Neuroinflammation 12:108
Holmgren S, Hjorth E, Schultzberg M, Lärksäter M, Frenkel D, Tysen-Bäckström AC, Aarsland D, Freund-Levi Y (2014) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia-a role for neuroinflammation? Brain Res Bull 108:88–93
Reale M, Brenner T, Greig NH, Inestrosa N, Paleacu D. (2010) Neuroinflammation, AD, and dementia. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2010: 974026.
Marques AH, Silverman MN, Sternberg EM (2009) Glucocorticoid dysregulations and their clinical correlates. From receptors to therapeutics. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1179:1–18
Silverman MN, Sternberg EM (2012) Glucocorticoid regulation of inflammation and its functional correlates: from HPA axis to glucocorticoid receptor dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1261:55–63
Simoens VL, Hebert S (2012) Cortisol suppression and hearing thresholds in tinnitus after low-dose dexamethasone challenge. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 12:4
Choung YH, Park K, Shin YR, Cho MJ (2006) Intratympanic dexamethasone injection for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 116:747–752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study is supported by grants of from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST103-2314-B-715-001-MY2, MOST104-2314-B-715 -003 -MY3), Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial and Research Center of Excellence (MOHW104-TDU-B-212-113002), China Medical University Hospital, Academia Sinica Taiwan Biobank Stroke Biosignature Project (BM104010092), NRPB Stroke Clinical Trial Consortium (MOST 103-2325-B-039 -006), Tseng-Lien Lin Foundation, Taichung, Taiwan, Taiwan Brain Disease Foundation, Taipei, Taiwan, and Katsuzo and Kiyo Aoshima Memorial Funds, Japan. Part of this article was prepared on the basis of our studies supported by intramural research grants from Mackay Medical College (MMC1012A10, MMC1012B13).
Conflict of interest
Every author declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The NHIRD contains only encrypted patient information; it provides anonymous identification numbers and corresponding claims information, including gender, date of birth, administered medical services, and prescriptions given. Patient consent is not required to access the data stored in NHIRD. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of China Medical University Hospital (CMUH104-REC2-115). The IRB waived the consent requirement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, P., Hsu, CC., Lin, HC. et al. Age-related hearing loss and dementia: a 10-year national population-based study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 2327–2334 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4471-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4471-5