Abstract
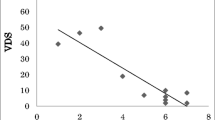
To determine the factors inducing aspiration following esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection (3FL) and the effect of the chin-down maneuver combined with supraglottic swallow (CDSS). Retrospective analysis of a consecutive case series. Videofluoroscopic (VF) evaluations of 25 patients who consulted with our out-patient clinic from 2006 to 2012 for swallowing dysfunction following esophagectomy with 3FL without tracheostomy were reviewed. The penetration aspiration scale (PAS) was used for evaluation. The assessment parameters of VF examination were set as follows: laryngeal elevation, peristaltic wave of the pharynx, upper esophageal sphincter opening, and bolus residue in the pyriform sinus and vallecula after swallowing. Associations of the degree of aspiration with these parameters and the effect of CDSS maneuver on PAS were statistically examined. Fourteen patients had swallowing dysfunction with PAS score (1–3). Disturbance of laryngeal elevation was significantly correlated with the degree of aspiration (p = 0.021). Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that reduced laryngeal elevation significantly enhanced aspiration (p = 0.0026). Sixteen patients had already acquired compensated chin-down swallowing at the time of VF (Group I). Among the remaining nine patients (Group II), the PAS score was significantly (p < 0.05) improved after training in chin-down swallowing. The mean PAS score of the Group I patients was not significantly different from that of the Group II patients after the training in CDSS. Laryngeal aspiration following esophagectomy with 3FL is significantly correlated with reduced laryngeal elevation and can be ameliorated after training in CDSS.
Level of evidence IV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H, Kajiyama Y (1994) Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 220:364–373
Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Yamana H et al (1994) Lymph node metastasis and recurrence in patients with a carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus who underwent three-field dissection. World J Surg 18:266–272
Altorki N, Kent M, Ferrara C, Port J (2002) Three-field lymph node dissection for squamous cell and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg 236:177–183
Heitmiller RF, Jones B (1991) Transient diminished airway protection after transhiatal esophagectomy. Am J Surg 162:442–446
Leder SB, Bayar S, Sasaki CT, Salem RR (2007) Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in assessing aspiration after transhiatal esophagectomy. J Am Coll Surg 205:581–585
Ellis FH, Gibb SP (1979) Esophagogastrectomy for carcinoma: current hospital mortality and morbidity rates. Ann Surg 190:699–705
Atkins BZ, Shah AS, Kelley A et al (2004) Reducing hospital morbidity and mortality following esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 78:1170–1176
Shanahan TK, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Kahrilas PJ (1993) Chin-down posture effect on aspiration in dysphagic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 74:736–739
Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Kahrilas PJ (1994) Effects of postural change on aspiration in head and neck surgical patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 110:222–227
Bülow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O (2001) Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia 16:190–195
Rosenbek JC, Robbins J, Roecker EV, Coyle JL, Woods JL (1991) A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11:93–98
Tanahashi T (1988) Scoring for the videofluoroscopic evaluation of pharyngeal swallowing dysfunction: Otorhinolaryngology 34:121–125 (Japanese article)
Yasuda T, Yano M, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Doki Y (2013) Evaluation of dysphagia and diminished airway protection after three-field esophagectomy and a remedy. World J Surg 37(2):416–423
Kinugasa S, Tachibana M, Yoshimura H et al (2004) Postoperative pulmonary complications are associated with worse short and long-term outcomes after extended esophagectomy. J Surg Oncol 88:71–77
Fang WT, Chen WH, Chen Y, Jiang Y (2007) Selective three-field lymphadenectomy for thoracic esophageal squamous carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 20:206–211
Dumont P, Wihlm JM, Hentz JG, Roeslin R, Lion G, Morand G (1995) Respiratory complications after surgical treatment of esophageal cancer. A study of 309 patients according to the type of resection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 9:539–543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This research involves human participants.
Informed consent
Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was obtained at Kumamoto University Hospital and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumai, Y., Samejima, Y., Watanabe, M. et al. Videofluoroscopic evaluation of pharyngeal swallowing dysfunction after esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 321–326 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4209-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4209-9