Abstract
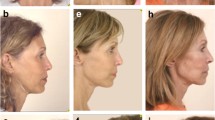
The aim of this study is to show differences between a modified facelift incision (MFI) for partial parotidectomy versus a bayonet-shaped incision (BSI). 24 patients presenting with a parotid tumor were surgically treated with a partial parotidectomy using a MFI. We generated a “matched pair control group” regarding age, tumor size and gender, who received a BSI. A questionnaire was sent to all patients and relevant data reviewed. The cosmetic satisfaction on a VAS with a MFI was 9.74 (±0.47) compared to BSI with 7.63 (±2.44, p = 0.004). The scoring in the two subgroups “visible scar” and “people noticed my surgery” was significantly better in the MFI group The postoperative skin numbness, skin depression, facial nerve function postoperatively showed no statistical differences. The MFI for parotid tumors has a better outcome than the BSI regarding cosmetic satisfaction and visible scarring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann I et al (2009) Development and validation of the Parotidectomy Outcome Inventory 8 (POI-8). Measurement of quality of life after parotidectomy in benign diseases. HNO 57(9):884–888
Jost G, Legent F, Baudelot S (1968) Filling of residual depressions after parotidectomy by a sterno-cleido-mastoid flap. Ann Chir Plast 13(3):187–191
Jost G, Guenon P, Gentil S (1999) Parotidectomy: a plastic approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 23(1):1–4
Appiani E, Delfino MC (1984) Plastic incisions for facial and neck tumors. Ann Plast Surg 13(4):335–352
Meningaud JP, Bertolus C, Bertrand JC (2006) Parotidectomy: assessment of a surgical technique including facelift incision and SMAS advancement. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 34(1):34–37
Terris DJ, Tuffo KM, Fee WE Jr (1994) Modified facelift incision for parotidectomy. J Laryngol Otol 108(7):574–578
Grover N, D’Souza A (2013) Facelift approach for parotidectomy: an evolving aesthetic technique. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148(4):548–556
Bianchi B et al (2011) Improving esthetic results in benign parotid surgery: statistical evaluation of facelift approach, sternocleidomastoid flap, and superficial musculoaponeurotic system flap application. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69(4):1235–1241
Honig JF (2004) Facelift approach with a hybrid SMAS rotation advancement flap in parotidectomy for prevention of scars and contour deficiency affecting the neck and sweat secretion of the cheek. J Craniofac Surg 15(5):797–803
Lohuis PJ et al (2009) Superficial parotidectomy via facelift incision. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118(4):276–280
Amin A et al (2011) Parotidectomy for benign parotid tumors: an aesthetic approach. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 23(2):67–72
Lin TC et al (2011) Intra-auricular modification of facelift incision with sternocleidomastoid flap–a cosmetic approach for parotidectomy: how we do it. Clin Otolaryngol 36(4):375–379
To EW, Pang PC, Chu GM (2000) The use of modified rhytidectomy for parotidectomy. Br J Plast Surg 53(1):80
Lee SY et al (2011) The extended indication of parotidectomy using the modified facelift incision in benign lesions: retrospective analysis of a single institution. World J Surg 35(10):2228–2237
Wasson J et al (2010) Cervicomastoidfacial versus modified facelift incision for parotid surgery: a patient feedback comparison. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 92(1):40–43
Zhi K et al (2011) Face-lift incision combined with sternomastoid muscular flap in parotidectomy. Aesthet Plast Surg 35(4):558–562
Iro H et al (2013) Follow-up of parotid pleomorphic adenomas treated by extracapsular dissection. Head Neck 35(6):788–793
Mantsopoulos K et al (2015) Evolution and changing trends in surgery for benign parotid tumors. Laryngoscope 125(1):122–127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no other funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulut, O.C., Plinkert, P. & Federspil, P.A. Modified facelift incision for partial parotidectomy versus bayonet-shaped incision: a comparison using visual analog scale. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273, 3269–3275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3878-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3878-0