Abstract
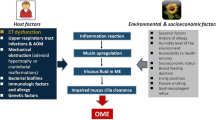
Chronic otitis media with effusion (OME) is associated with irreversible changes in the middle ear, sometimes leading to hearing loss and abnormal language development in children. While the pathogenesis of OME is not fully understood, inflammatory and allergic factors are thought to be involved. The study aimed to investigate the role of cytokines in the local development of chronic OME, and assess differences in the cytokine profiles between atopic and non-atopic children. 84 atopic and non-atopic children with chronic OME (mean age of 6 years 7 months) were studied. Age-matched children with hypertrophy of the adenoids and Eustachian tube dysfunction served as the control group. The number of past acute otitis media (AOM) episodes, their age, and the type of effusion were recorded for all children. Pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8) were determined and the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the patients’ effusions was examined. High concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 were found in the effusions in all children with chronic OME, with the highest levels observed in the non-atopic group. The atopic group showed persistently high IL-1β levels, while in the non-atopic children, IL-1β and TNF-α levels positively correlated with the patient’s age and the number of past AOM episodes. Pathogenic bacteria were more frequently isolated from effusions in non-atopic children. In both atopic and non-atopic children, pro-inflammatory cytokines are found at high concentrations. This argues in favor of instituting anti-inflammatory management for treating OME, regardless of atopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bluestone CD, Klein JO (1995) Clinical practice guideline on otitis media with effusion in young children: strengths and weaknesses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:507–511
Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, Ganiats TG, Hoberman A, Jackson MA, Joffe MD, Miller DT, Rosenfeld RM, Sevilla XD, Schwartz RH, Thomas PA, Tunkel DE (2013) The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Pediatrics 131:e964–e999
Qureishi A, Lee Y, Belfield K, Birchall JP, Daniel M (2014) Update on otitis media—prevention and treatment. Infect Drug Resist 7:15–24
Bluestone CD, Hebda PA, Alper CM, Sando I, Buchman CA, Stangerup SE, Felding JU, Swarts JD, Ghadiali SN, Takahashi H (2005) Recent advances in otitis media. 2. Eustachian tube, middle ear, and mastoid anatomy; physiology, pathophysiology, and pathogenesis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 194:16–30
Amin K, Hurst DS, Roomans GM, Venge P, Sevéus L (1999) Eosinophils and neutrophils in biopsies from the middle ear of atopic children with otitis media with effusion. Inflamm Res 48:626–631
Armstrong BW (1954) A new treatment for chronic secretory otitis media. AMA Arch Otolaryngol 59:653–654
Ball SS, Prazma J, Dais CG, Triana RJ, Pillsbury HC (1997) Role of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in endotoxin-induced middle ear effusions. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 106:633–639
Bernstein JM (1996) Role of allergy in eustachian tube blockage and otitis media with effusion: a review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114:562–568
Buchman CA, Doyle WJ, Skoner DP, Post JC, Alper CM, Seroky JT, Anderson K, Preston RA, Hayden FG, Fireman P et al (1995) Influenza A virus-induced acute otitis media. J Infect Dis 172:1348–1351
Sato K, Liebeler CL, Quartey MK, Le CT, Giebink GS (1999) Middle ear fluid cytokine and inflammatory cell kinetics in the chinchilla otitis media model. Infect Immun 67:1943–1946
Yariktas M, Doner F, Dogru H, Yasan H, Delibas N (2004) The role of free oxygen radicals on the development of otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68:889–894
Aydoğan B, Kiroğlu M, Altintas D, Yilmaz M, Yorgancilar E, Tuncer U (2004) The role of food allergy in otitis media with effusion. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:747–750
Döner F, Yariktas M, Demirci M (2004) The role of allergy in recurrent otitis media with effusion. J Invest Allergol Clin Immunol 14:154–158
Nsouli TM, Nsouli SM, Linde RE, O’Mara F, Scanlon RT, Bellanti JA (1994) Role of food allergy in serous otitis media. Ann Allergy 73:215–219
Pelikan Z (2009) Role of nasal allergy in chronic secretory otitis media. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 9:107–113
Hurst DS, Venge P (2002) The impact of atopy on neutrophil activity in middle ear effusion from children and adults with chronic otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:561–566
Luong A, Roland PS (2008) The link between allergic rhinitis and chronic otitis media with effusion in atopic patients. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 41:311–323
Lin J, Vambutas A, Haruta A, Paparella MM, Giebink GS, Kim Y (1999) Pneumococcus activation of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway and production of glycoproteins in the middle ear of rats. J Infect Dis 179:1145–1151
Dinarello CA (2000) Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 118:503–508
Barzilai A, Dekel B, Dagan R, Passwell JH, Leibovitz E (1999) Cytokine analysis of middle ear effusions during acute otitis media: significant reduction in tumor necrosis factor alpha concentrations correlates with bacterial eradication. Pediatr Infect Dis J 18:301–303
Himi T, Suzuki T, Kodama H, Takezawa H, Kataura A (1992) Immunologic characteristics of cytokines in otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 157:21–25
Lin J, Kim Y, Juhn SK (1998) Increase of mucous glycoprotein secretion by tumor necrosis factor alpha via a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism in cultured chinchilla middle ear epithelial cells. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:213–219
Nell MJ, Grote JJ (1999) Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in middle ear effusions in relation to upper airway infection. Laryngoscope 109:1815–1819
Ondrey FG, Juhn SK, Adams GL (1998) Early-response cytokine expression in adult middle ear effusions. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:342–345
Ophir D, Hahn T, Schattner A, Wallach D, Aviel A (1988) Tumor necrosis factor in middle ear effusions. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114:1256–1258
Smirnova MG, Kiselev SL, Gnuchev NV, Birchall JP, Pearson JP (2002) Role of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in the pathogenesis of the otitis media with effusion. Eur Cytokine Netw 13:161–172
Yellon RF, Doyle WJ, Whiteside TL, Diven WF, March AR, Fireman P (1995) Cytokines, immunoglobulins, and bacterial pathogens in middle ear effusions. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121:865–869
Yellon RF, Leonard G, Marucha PT, Craven R, Carpenter RJ, Lehmann WB, Burleson JA, Kreutzer DL (1991) Characterization of cytokines present in middle ear effusions. Laryngoscope 101:165–169
Jeon EJ, Park YS, Choi YC, Yeo SW, Jung TT (2001) Effect of inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on experimental otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:917–921
Hebda PA, Alper CM, Doyle WJ, Burckart GJ, Diven WF, Zeevi A (1998) Upregulation of messenger RNA for inflammatory cytokines in middle ear mucosa in a rat model of acute otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:501–507
Johnson MD, Fitzgerald JE, Leonard G, Burleson JA, Kreutzer DL (1994) Cytokines in experimental otitis media with effusion. Laryngoscope 104:191–196
Sato K, Kawana M, Nonomura N, Nakano Y (1999) Course of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha in the middle ear fluid of the guinea pig otitis media model induced by nonviable Haemophilus influenzae. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:559–563
Kawano H, Haruta A, Tsuboi Y, Kim Y, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Lin J (2002) Induction of mucous cell metaplasia by tumor necrosis factor alpha in rat middle ear: the pathological basis for mucin hyperproduction in mucoid otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111:415–422
Smirnova MG, Birchall JP, Pearson JP (2004) The immunoregulatory and allergy-associated cytokines in the aetiology of the otitis media with effusion. Mediators Inflamm 13:75–88
Lee HY, Chung JH, Lee SK, Byun JY, Kim YI, Yeo SG (2013) Toll-like receptors, cytokines and nitric oxide synthase in patients with otitis media with effusion. Indian J Med Res 138:523–530
Lee DH, Park YS, Jung TT, Yeo SW, Choi YC, Jeon E (2001) Effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on experimental otitis media with effusion. Laryngoscope 111:728–733
Lin J, Haruta A, Kawano H, Ho SB, Adams GL, Juhn SK, Kim Y (2000) Induction of mucin gene expression in middle ear of rats by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: potential cause for mucoid otitis media. J Infect Dis 182:882–887
Johnson MD, Contrino A, Contrino J, Maxwell K, Leonard G, Kreutzer D (1994) Murine model of otitis media with effusion: immunohistochemical demonstration of IL-1 alpha antigen expression. Laryngoscope 104:1143–1149
DeMaria TF, Briggs BR, Lim DJ, Okazaki N (1984) Experimental otitis media with effusion following middle ear inoculation of nonviable H. influenzae. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:52–56
Catanzaro A, Ryan A, Batcher S, Wasserman SI (1991) The response to human rIL-1, rIL-2, and rTNF in the middle ear of guinea pigs. Laryngoscope 101:271–275
Hunter SE, Singla AK, Prazma J, Jewett BS, Randell SH, Pillsbury HC 3rd (1999) Mucin production in the middle ear in response to lipopolysaccharides. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:884–888
Forseni M, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Hultcrantz M (2001) A study of inflammatory mediators in the human tympanosclerotic middle ear. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:559–564
Watanabe T, Hirano T, Suzuki M, Kurono Y, Mogi G (2001) Role of interleukin-1beta in a murine model of otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:574–580
Park MK, Lee BD (2013) Development of animal models of otitis media. Korean J Audiol 17:9–12
DeMaria TF, Murwin DM (1997) Tumor necrosis factor during experimental lipopolysaccharide-induced otitis media. Laryngoscope 107:369–372
DeMaria TF, Prior RB, Briggs BR, Lim DJ, Birck HG (1984) Endotoxin in middle-ear effusions from patients with chronic otitis media with effusion. J Clin Microbiol 20:15–17
Johnson M, Leonard G, Kreutzer DL (1997) Murine model of interleukin-8-induced otitis media. Laryngoscope 107:1405–1408
Willett DN, Rezaee RP, Billy JM, Tighe MB, DeMaria TF (1998) Relationship of endotoxin to tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta in children with otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:28–33
Barzilaia A, Dekel B, Dagan R, Leibovitz E (2000) Middle ear effusion IL-6 concentration in bacterial and non-bacterial acute otitis media. Acta Paediatr 89:1068–1071
Hebert CA, Baker JB (1993) Interleukin-8: a review. Cancer Invest 11:743–750
Kuna P, Lazarovich M, Kaplan AP (1996) Chemokines in seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 97:104–112
Tchorzewski H, Krasomski G, Biesiada L, Głowacka E, Banasik M, Lewkowicz P (2000) IL-12, IL-6 and IFN-gamma production by lymphocytes of pregnant women with rheumatoid arthritis remission during pregnancy. Mediators Inflamm 9:289–293
MacArthur CJ, Pillers DA, Pang J, Kempton JB, Trune DR (2011) Altered expression of middle and inner ear cytokines in mouse otitis media. Laryngoscope 121:365–371
Kubba H, Pearson JP, Birchall JP (2000) The aetiology of otitis media with effusion: a review. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 25:181–194
Kubba H (2000) An evidence-based patient information leaflet about otitis media with effusion. Clin Perform Qual Health Care 8:93–99
Ogra PL, Giebink GS, Barenkamp SJ, DeMaria TF, Juhn SK, Shurin PA, Andersson B, Bakaletz LO, Bernstein JM, Brinton CC et al (1989) Recent advances in otitis media. Microbiology, immunology, biochemistry, and vaccination. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 139:23–32
Fergie N, Bayston R, Pearson JP, Birchall JP (2004) Is otitis media with effusion a biofilm infection? Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:38–46
Giebink GS (1989) Progress in understanding the pathophysiology of otitis media. Pediatr Rev 11:133–137
Juhn SK, Giebink GS, Huff JS, Mills EL (1980) Biochemical and immunochemical characteristics of middle ear effusions in relation to bacteriological findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 89:161–167
Pereira MB, Pereira MR, Cantarelli V, Costa SS (2004) Prevalence of bacteria in children with otitis media with effusion. J Pediatr (Rio J) 80:41–48
Chung MH, Griffith SR, Park KH, Lim DJ, DeMaria TF (1993) Cytological and histological changes in the middle ear after inoculation of influenza A virus. Acta Otolaryngol 113:81–87
Yellon RF, Leonard G, Marucha P, Sidman J, Carpenter R, Burleson J, Carlson J, Kreutzer D (1992) Demonstration of interleukin 6 in middle ear effusions. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118:745–748
Juhn SK, Tolan CT, Garvis WJ, Cross DS, Giebink GS (1992) The levels of IL-1 beta in human middle ear effusions. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 493:37–42
Yetiser S, Satar B, Gumusgun A, Unal F, Ozkaptan Y (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta levels in recurrent and persistent otitis media with effusion. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:417–422
Ciprandi G, Buscaglia S, Pesce G, Pronzato C, Ricca V, Parmiani S, Bagnasco M, Canonica GW (1995) Minimal persistent inflammation is present at mucosal level in patients with asymptomatic rhinitis and mite allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 96:971–979
Skotnicka B, Hassmann E (2000) Cytokines in children with otitis media with effusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 257:323–326
Maxwell KS, Fitzgerald JE, Burleson JA, Leonard G, Carpenter R, Kreutzer DL (1994) Interleukin-8 expression in otitis media. Laryngoscope 104:989–995
Russo E, Smith CW, Friedman EM, Smith EO, Kaplan SL (2004) Cell adhesion molecules and cytokines in middle ear effusions in children with or without recent acute otitis media. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:242–248
Kerschner JE, Meyer TK, Yang C, Burrows A (2004) Middle ear epithelial mucin production in response to interleukin-6 exposure in vitro. Cytokine 26:30–36
Smirnova MG, Birchall JP, Pearson JP (2002) In vitro study of IL-8 and goblet cells: possible role of IL-8 in the aetiology of otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol 122:146–152
Bachert C, van Kempen M, Van Cauwenberge P (1999) Regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 118:375–379
Al-Amran FG, Hadi NR, Hashim AM (2013) Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast ameliorates acute lung injury following haemorrhagic shock in rats. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 43:421–427
Lee HY, Kim YI, Lee JW, Byun JY, Park MS, Yeo SG (2013) Decreased expression of TLR-9 and cytokines in the presence of bacteria in patients with otitis media with effusion. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 6:195–200
Matkovic SD, Vojvodić D, Baljosevic I (2007) Cytokine levels in groups of patients with different duration of chronic secretory otitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:1283–1287
Park YS, Auo HJ, Jeon EJ, Chang KH, Lee SK, Lee DH (2006) Effect of inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and oxatomide on immune mediated otitis media. Laryngoscope 116:1642–1646
Kim DH, Park YS, Jeon EJ, Yeo SW, Chang KH, Lee SK (2006) Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist, platelet activating factor antagonist, and nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on experimental otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 115:617–623
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The technical and language assistance was provided by Proper Medical Writing Sp. z o.o., Warsaw, Poland.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zielnik-Jurkiewicz, B., Stankiewicz-Szymczak, W. Pro-inflammatory interleukins in middle ear effusions from atopic and non-atopic children with chronic otitis media with effusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273, 1369–1378 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3683-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3683-9