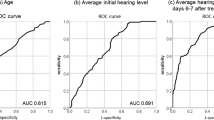
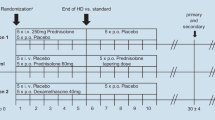
Abstract
A randomized placebo-controlled study has demonstrated no effect of prednisolone in customary dosage on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL). The aim of the present paper is to analyse a larger patient group by meta-analysis of data from the RCT together with a corresponding material drawn from the Swedish national database for ISSNHL. Data from 192 patients, 18–80 years with ISSNHL, were available. All had an acute hearing loss of at least 30 dB measured as PTA in the three most affected contiguous frequencies. All patients had been enrolled within one week after onset and evaluated by audiograms after 3 months. 45/99 (RCT) and 54/99 (the database) had been treated with prednisolone in tapering doses from 60 mg daily and 42/93 with placebo (RCT) or 51/93 with no treatment (the database). Primary outcome was the mean hearing improvement on day 90 for the different groups. A mean difference of >10 dB improvement was required to demonstrate a treatment effect for prednisolone compared to placebo/no treatment. No significant difference was seen between the prednisolone group and placebo/no treatment (p = 0.06). Total recovery was 38 % in prednisolone group, 40 % in the placebo and 14 % in the no treatment group. Vertigo at the onset of hearing loss and age at onset had an equal negative prognostic value in all groups and signs of inflammation had a positive effect. Prednisolone in customary dosage does not influence recovery after ISSNHL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei BPC, Stathopoulos D, O’Leary S (2013) Steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (7):CD003998. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003998.pub3
Siebenmann F (1894) Die Blutgejiisse im Lgbyrinthe des menschlichen Ohres. Wiesbaden
Naybena D (1923) A study in the comparative anatomy of the blood vascular system of the internal ear in mammalia and homo. Kioto Acta Scholae Med 6:1–13
Singleton GT (1971) Cervical sympathetic chain block in sudden deafness. Laryngoscope 81:734–736
Kellerhals B, Hippert F, Pfaltz CR (1971) Treatment of acute acoustic trauma with low molecular weight dextran. Pract Otorhinolaryngol (Basel) 33:260–264
Probst R, Tschopp K, Ludin E et al (1992) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of dextran/pentoxifylline medication in acute acoustic trauma and sudden hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 112:435–443
Nadol JB Jr (1975) Hearing loss of acquired syphilis: diagnosis confirmed by incudectomy. Laryngoscope 85:1888–1897
Wilson WR, Veltri RW, Laird N, Sprinkle PM (1983) Viral and epidemiologic studies of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91:653–658
Stokroos RJ, Albers FWJ, Tenvergert EM (1998) Antiviral treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Acta Otolaryngol 118:488–495
Westerlaken BO, Stokroos RJ, Wit HP et al (2003) Treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with antiviral therapy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 112:993–1000
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N (1980) The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol 106:772–776
Wei BPC, Mubiru S, O’Leary S (2009) Steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Lautermann J, Sudhoff H, Junker R (2005) Transtympanic corticoid therapy for acute profound hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262:587–591
Mattox DE, Simmons FB (1977) Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86:463–480
Byl FM Jr (1984) Sudden hearing loss: eight years’ experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope 94:647–661
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Arlinger S, Hultcrantz E (2007) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: results drawn from the Swedish national database. Acta Otolaryngol 127:1168–1175
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Hansson M, Hultcrantz E (2010) Assessment of diagnostic approaches to idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and their influence on treatment and outcome. Acta Otolaryngol 130:384–391
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Hultcrantz E (2012) Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled trial. Otol Neurotol 33:523–531
Conlin AE, Parnes LS (2007) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss II. A meta-analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:582–586
Arnold W, Brusis T, Canis M, Hesse G, Arolsen B, Klemm E, Löhler J et al (2014) Leitlinie der Dt. Ges. f. Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Heilkunde, Kopf- und Hals-Chirurgie. http://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/017-010l_S1_Hoersturz_2014-02.pdf
Seggas I, Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A et al (2011) Intratympanic steroid therapy for sudden hearing loss: a review of the literature. Otol Neurotol 32:29–35
Meltser I, Tahera Y, Canlon B (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase activity after restraint stress and acoustic trauma. J Neurotrauma 26:1835–1845
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hultcrantz, E., Nosrati-Zarenoe, R. Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: analysis of an RCT and material drawn from the Swedish national database. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3169–3175 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3360-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3360-4