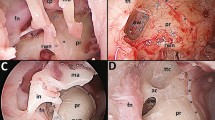
Abstract
Endoscopic surgery of the middle ear is progressively gaining the interest of otologists, as technological advances have overcome some of its main drawbacks. The long learning curve required to master this technique, urges the search for models to practice it. After the validation of sheep’s ear as a proper training model for microscopic stapedectomy, our objective is to demonstrate its adequacy for practicing stapes surgery but performed through a fully endoscopic approach. Endoscopic stapedectomy was performed by two surgeons in 40 sheep ears (20 specimens each). To analyze the effects of the learning curve on surgical success, complication rates and surgical time reduction, the sample was divided in two groups: group 1 being the first ten procedures of each surgeon, and group 2 the second set of stapedectomies. The impact of the operated side and the resection of the chordal spine were also studied. No statistically significant differences were found considering the operated side. A statistically significant improvement in some of the surgical steps was demonstrated comparing both groups and also after the resection of the chordal spine. Mean surgical time declined from 38 to 31.5 min (p < 0.05). Using this model for endoscopic stapedectomy, a learning curve was objectively demonstrated, along with other subjective appreciations such as improvement in depth perception and one-hand instrument handling. We believe that sheep ear is an optimal model for endoscopic middle ear surgery, as it allows for the acquisition of the skills required to master this technique.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nogueira Júnior JF, Martins MJ, Aguiar CV et al (2011) Fully endoscopic stapes surgery (stapedotomy): technique and preliminary results. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 77:721–727
Migirov L, Wolf M (2013) Endoscopic transcanal stapedotomy: how I do it. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:1547–1549
Sarkar S, Banerjee S, Chakravarty S et al (2013) Endoscopic stapes surgery: our experience in thirty two patients. Clin Otolaryngol 38:157–160
Poe DS (2000) Laser-assisted endoscopic stapedectomy: a prospective study. Laryngoscope 110:1–37
Cordero A, Medina MM, Alonso A et al (2011) Stapedectomy in sheep: an animal model for surgical training. Otol Neurotol 32:742–747
Yung MW, Oates J, Vowler SL (2006) The learning curve in stapes surgery and its implication to training. Laryngoscope 116:67–71
Gocer C, Eryilmaz A, Genc U et al (2007) An alternative model for stapedectomy training in residency program: sheep cadaver ear. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:1409–1412
Harris JP, Osborne E (1990) A survey of otologic training in US residency programs. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116:342–344
Backous DD, Coker NJ, Jenkins HA (1993) Prospective study of resident-performed stapedectomy. Am J Otol 14:451–454
Morris DP, Luff DA, Hargreaves SP et al (1998) Bones of contention. The supply of temporal bones for dissection: the legalities, problems and solutions. J Laryngol Otol 112:1138–1141
Nogueira JF, Mattioli F, Presutti L et al (2013) Endoscopic anatomy of the retrotympanum. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 46:179–188
Pothier DD (2013) Introducing endoscopic ear surgery into practice. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 46:245–255
Badr-El-Dine M, James AL, Panetti G et al (2013) Instrumentation and technologies in endoscopic ear surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 46:211–225
Kojima H, Komori M, Chikazawa S et al (2014) Comparison between endoscopic and microscopic stapes surgery. Laryngoscope 124:266–271
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Medtronic®, especially to Pilar Sobrino, for lending us the endoscope optics for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordero, A., Benítez, S., Reyes, P. et al. Ovine ear model for fully endoscopic stapedectomy training. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2167–2174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3114-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3114-3