Abstract
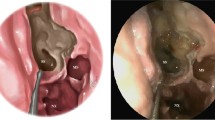
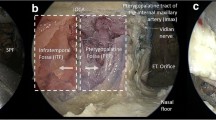
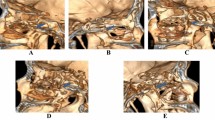
The objective of this study was to evaluate different methods and measurements for localization of the sphenopalatine foramen (SPF) during endoscopic transnasal exposure. The study design consisted of descriptive anatomical study and the setting was in Microsurgical Cadaver Dissection Lab. Sixteen lateral nasal walls were dissected endoscopically to identify and localize the SPF. Multiple measurements were obtained from nasal sill (NS) to SPF, ethmoid crest (EC), and other related landmarks. The results showed that EC was identified in all sides with different degrees of projection. SPF extended below the inferior edge of EC, i.e., lying both in the superior and middle meatus, in 12 sides (75 %), while it was laying only in the superior meatus in 4 sides (25 %). An accessory foramen was identified in 3 sides (18.7 %), all of which were located in middle meatus. The distance from NS to SPF ranged widely from 55 to 76 mm (mean ± SD 64.4 ± 6 mm). The average angle of elevation formed between SPF to NS and nasal floor was 11.4° (range 11–12°). Although many previous studies have reported measurements to SPF, we do not believe these measurements are of practical help due to the wide range of measurements and the lack of standard reference points. The main constant landmark for SPF remains the EC. Since SPF frequently extends below EC, the mucoperiosteal flap should be extended below the inferior edge of this crest to avoid missing the middle meatal part of SPF or any accessory foramina.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budrovich R, Saetti R (1992) Microscopic and endoscopic ligature of the sphenopalatine artery. Laryngoscope 102:1390–1394
Kumar S, Shetty A, Rockey J et al (2003) Contemporary surgical treatment of epistaxis. What is the evidence for sphenopalatine artery ligation. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 28(4):360–363
Feusi B, Holzmann D, Steurer J (2005) Posterior epistaxis: systematic review on the effectiveness of surgical therapies. Rhinology 43(4):300–304
Abdelkader M, Leong SC, White PS (2007) Endoscopic control of the sphenopalatine artery for epistaxis: long-term results. J Laryngol Otol 121(8):759–762
Nouraei SA, Maani T, Hajioff D et al (2007) Outcome of endoscopic sphenopalatine artery occlusion for intractable epistaxis: a 10-year experience. Laryngoscope 117(8):1452–1456
Asanau A, Timoshenko AP, Vercherin P et al (2009) Sphenopalatine and anterior ethmoidal artery ligation for severe epistaxis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118(9):639–644
Padua FGM, Voegels RL (2008) Severe posterior epistaxis. Endoscopic surgical anatomy. Laryngoscope. 118:156–161
Wareing MJ, Pagdam ND (1998) Osteologic classification of the sphenopalatine foramen. Laryngoscope 108:125–127
Bolger WE, Borgie RC, Melder P (1999) The role of the crista ethmoidalis in endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation. Am J Rhinol 13:81–86
Lee HY, Kim HU, Kim SS et al (2002) Surgical anatomy of the sphenopalatine artery in lateral nasal wall. Laryngoscope 112:1813–1818
Prades JM, Asanau A, Timoshenko AP et al (2008) Surgical anatomy of the sphenopalatine foramen and its arterial content. Surg Radiol Anat 30(7):583–587
Antunes-Scanavine AB, Caldas-Navarro A, Molinari de Carvalho SR, Anselmo-Lima WT (2009) Anatomical study of the sphenopalatine foramen. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75:37–41
Tolosanaa SH, Liesaa RF, Castellónb JE et al (2011) Sphenopalatinum foramen: an anatomical study. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 62(4):274–278
Trinidad G, Rejas E, Gónzalez A, Pantoja CG et al (2006) Aspectospracticossobre el tratamientoendoscópico de la epistaxis. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 57:394–400
Simmen DB, Briner HR et al (2006) The anatomy of the Sphenopalatine artery for the endoscopic sinus surgeon. Am J Rhinol 20:502–505
Cai WW, Zhang GH, Yang QT et al (2010) Endoscopic endonasal anatomy of pterygopalatine fossa and infratemporal fossa: comparison of endoscopic and radiological landmarks. Chin J OHNS 45(10):843–848
Gui P, Zhou S, Liang W, Ji R, Fu M, Xie G (2004) The study of microdissection of endoscopic transnasal surgery in the sphenopalatine foramen. Chin J OHNS 18(10):606–608
Hadoura L, Douglas C, McGarry GW et al (2009) Mapping surgical coordinates of the sphenopalatine foramen: surgical navigation study. J Laryngol Otol 123(7):742–745
Scanavine AB, Navarro JA, Megale SR, Anselmo-Lima WT (2009) Anatomical study of the sphenopalatine foramen. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75(1):37–41
Shires CB, Boughter JD, Sebelik ME (2011) Sphenopalatine artery ligation: a cadaver anatomic study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145(3):494–497
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the technical staff of the Departments of Otolaryngology and Human Anatomy for their great efforts and help with the study arrangements and preparation.
Financial disclosure
This research was supported by a research grant from the Institute of Scientific Research and Revival of Islamic Heritage, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alherabi, A., Marglani, O., Herzallah, I.R. et al. Endoscopic localization of the sphenopalatine foramen: do measurements matter?. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 2455–2460 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2881-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2881-1