Abstract
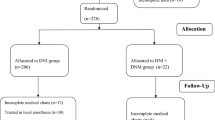
The goal of the study was to find out the risk factors for the development of mediastinitis in patients with deep neck infections (DNI) and describe the differences in symptoms and clinical image between uncomplicated DNI and infections with mediastinal spread. Our study represents the retrospective analysis of 634 patients with DNI. The file was divided into two groups. There were 619 patients (97.6 %) in the first group who had an uncomplicated course of DNI without spread of infection into mediastinum (DNI group). The second group included 15 patients (2.4 %) with descending mediastinitis as a complication of DNI (mediastinitis group). The most frequent comorbidities were cardiac and pulmonary diseases, which were more frequent in the mediastinitis group comparing to DNI group. Dental origin of the infection was more frequent in DNI group than in the mediastinitis group. On the other hand, tonsillar origin of the infection was more frequent in the mediastinitis group than in DNI group. In both mediastinitis and DNI groups, the typical presenting symptoms were pain, oedema and dysphagia. Furthermore, dysphagia, dyspnoea, dysphonia and restriction of neck movements were more significant in the mediastinitis group than in DNI group. The incidence of airway obstruction, sepsis, pneumonia and death was significantly higher in the mediastinitis group than in DNI group. Due to our results, the predisposing factors for mediastinal extension of DNI are cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases. Mediastinitis is associated with higher morbidity and mortality than DNI. The most common complications are airway obstruction, pneumonia and sepsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marioni G, Staffieri A, Parisi S, Marchese-Ragona R, Zuccon A, Staffieri C, Sari M, Speranzoni C, de Filippis C, Rinaldi R (2010) Rational diagnostic and therapeutic management of deep neck infections: analysis of 233 consecutive cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(3):181–187
Suehara AB, Goncalves AJ, Alcadipani FA, Kavabata NK, Menezes MB (2008) Deep neck infection: analysis of 80 cases. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 74(2):253–259
Bakir S, Tanriverdi MH, Gun R, Yorgancilar AE, Yildirim M, Tekbas G, Palanci Y, Meric K, Topcu I (2012) Deep neck space infections: a retrospective review of 173 cases. Am J Otolaryngol 33(1):56–63. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2011.01.003
Santos Gorjon P, Blanco Perez P, Morales Martin AC, Del Pozo de Dios JC, Estevez Alonso S, Calle de la Cabanillas MI (2012) Deep neck infection. Review of 286 cases. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 63 (1):31–41. doi:10.1016/j.otorri.2011.06.002
Hasegawa J, Hidaka H, Tateda M, Kudo T, Sagai S, Miyazaki M, Katagiri K, Nakanome A, Ishida E, Ozawa D, Kobayashi T (2011) An analysis of clinical risk factors of deep neck infection. Auris Nasus Larynx 38(1):101–107. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2010.06.001
Huang TT, Liu TC, Chen PR, Tseng FY, Yeh TH, Chen YS (2004) Deep neck infection: analysis of 185 cases. Head Neck 26(10):854–860. doi:10.1002/hed.20014
Eftekharian A, Roozbahany NA, Vaezeafshar R, Narimani N (2009) Deep neck infections: a retrospective review of 112 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(2):273–277. doi:10.1007/s00405-008-0734-5
Lee JK, Kim HD, Lim SC (2007) Predisposing factors of complicated deep neck infection: an analysis of 158 cases. Yonsei Med J 48(1):55–62
Parhiscar A, Har-El G (2001) Deep neck abscess: a retrospective review of 210 cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110(11):1051–1054
Kang SK, Lee S, Oh HK, Kang MW, Na MH, Yu JH, Koo BS, Lim SP (2012) Clinical features of deep neck infections and predisposing factors for mediastinal extension. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 45(3):171–176. doi:10.5090/kjtcs.2012.45.3.171
Bottin R, Marioni G, Rinaldi R, Boninsegna M, Salvadori L, Staffieri A (2003) Deep neck infection: a present-day complication. A retrospective review of 83 cases (1998-2001). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260(10):576–579. doi:10.1007/s00405-003-0634-7
Boyanova L, Kolarov R, Gergova G, Deliverska E, Madjarov J, Marinov M, Mitov I (2006) Anaerobic bacteria in 118 patients with deep-space head and neck infections from the University Hospital of Maxillofacial Surgery, Sofia Bulgaria. J Med Microbiol 55(Pt 9):1285–1289. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.46512-0
Acknowledgments
This article was supported by the project (Ministry of Health, Czech Republic) for conceptual development of research organization 00179906.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
Ethical approval was not considered necessary as the patients data were collected retrospectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celakovsky, P., Kalfert, D., Tucek, L. et al. Deep neck infections: risk factors for mediastinal extension. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 1679–1683 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2651-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2651-5