Abstract
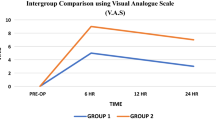
The aim of this prospective single-blinded and controlled study is to evaluate the efficacy of levobupivacaine infiltration on post-tonsillectomy pain relief in adults. The study was conducted with 40 adult patients who underwent tonsillectomy. These patients were randomized in either study group (SG) who received levobupivacaine infiltration to peritonsillary fossae prior to surgery or control group (CG) with no medication. After surgery, all the patients were queried for pain scores by visual analog scale. In addition, the volume of intraoperative bleeding, the duration of operation, the severity of postoperative complications, and the amount of analgesic requirement were the other outcome measures of this study. There were significant differences between groups regarding pain scores for the first 24 h in favor of SG. The analgesic requirement was also significantly lower in SG (p = 0.009). Although there was a sustained decrement at pain score during first 24 h for SG, however, the change from baseline score (immediate score) for each time interval revealed no significance compared to CG. In addition, the duration of operation and the volume of intraoperative bleeding were similar (p = 0.64 and p = 0.165). In conclusion, preincisional infiltration of levobupivacaine is a safe and reliable method for post-tonsillectomy pain reduction in adults. However, more in-depth, double-blinded and placebo controlled studies are required to elucidate its long term benefits.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grainger J, Saravanappa N (2008) Local anaesthetic for post-tonsillectomy pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol 33:411–419
Sylvester DC, Rafferty A, Bew S, Knight LC (2011) The use of ice-lollies for pain relief post-paediatric tonsillectomy. A single-blinded, randomised, controlled trial. Clin Otolaryngol 36:566–570
Cocelli LP, Ugur BK, Durucu C, Kul S, Arik H, Mumbuc S (2012) Comparison of pre-emptive tonsillar lodge infiltration with ropivacaine versus intravenous tramadol in pediatric tonsillectomies: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:653–657
Sampaio AL, Pinheiro TG, Furtado PL, Araújo MF, Olivieira CA (2007) Evaluation of early postoperative morbidity in pediatric tonsillectomy with the use of sucralfate. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:645–651
Kasapoglu F, Kaya FN, Tuzemen G, Ozmen OA, Kaya A, Onart S (2011) Comparison of peritonsillar levobupivacaine and bupivacaine infiltration for post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: placebo-controlled clinical study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:322–326
Yilmaz S, Demiraran Y, Akkan N, Yaman H, Iskender A, Güçlü E, Oztürk O (2009) The effects of topical levobupivacaine on morbidity in pediatric tonsillectomy patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1208–1210
Vasan NR, Stevenson S, Ward M (2002) Preincisional bupivacaine in posttonsillectomy pain relief: a randomized prospective study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:145–149
Egeli E, Harputluoglu U, Oghan F, Demiraran Y, Guclu E, Ozturk O (2005) Does topical lidocaine with adrenaline have an effect on morbidity in pediatric tonsillectomy? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 69:811–815
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I (1991) The effect of pre-incisional infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. Pain 47:305–308
Kaygusuz I, Susaman N (2003) The effects of dexamethasone, bupivacaine and topical lidocaine spray on pain after tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 67:737–742
Karaaslan K, Yilmaz F, Gulcu N, Sarpkaya A, Colak C, Kocoglu H (2008) The effects of levobupivacaine versus levobupivacaine plus magnesium infiltration on postoperative analgesia and laryngospasm in pediatric tonsillectomy patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72:675–681
Kemal O (2012) Harmonic scalpel versus bipolar tonsillectomy: a double-blind clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:1533–1536
Diakos EA, Gallos ID, El-Shunnar S, Clarke M, Kazi R, Mehanna H (2011) Dexamethasone reduces pain, vomiting and overall complications following tonsillectomy in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin Otolaryngol 36:531–542
El-Hakim H, Nunez DA, Saleh HA, Macleod DM, Gardiner Q (2000) A randomised controlled trial of the effect of regional nerve blocks on immediate post-tonsillectomy pain in adult patients. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 25:413–417
Ginström R, Silvola J, Saarnivaara L (2005) Local bupivacaine-epinephrine infiltration combined with general anesthesia for adult tonsillectomy. Acta Otolaryngol 125:972–975
McLeod GA, Burke D (2001) Levobupivacaine. Anaesthesia 56:331–341 (Review)
Tas E, Hanci V, Ugur MB, Turan IO, Yigit VB, Cinar F (2010) Does preincisional injection of levobupivacaine with epinephrine have any benefits for children undergoing tonsillectomy? An intraindividual evaluation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:1171–1175
Woolf CJ, Chong MS (1993) Preemptive analgesia—treating postoperative pain by preventing the establishment of central sensitization. Anesth Analg 77:362–379
Mazoit JX, Dalens BJ (2004) Pharmacokinetics of local anesthetics in infants and children. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:17–32
Mowafi HA, Telmessani L, Ismail SA, Naguib MB (2011) Preoperative lornoxicam for pain prevention after tonsillectomy in adults. J Clin Anesth 23:97–101
Rasgon BM, Cruz RM, Hilsinger RL Jr, Korol HW, Callan E, Wolgat RA, Selby JV (1991) Infiltration of epinephrine in tonsillectomy: a randomized, prospective, double-blind study. Laryngoscope 101:114–118
Arikan OK, Ozcan S, Kazkayasi M, Akpinar S, Koc C (2006) Preincisional infiltration of tonsils with ropivacaine in post-tonsillectomy pain relief: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled intraindividual study. J Otolaryngol 35:167–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasapoglu, F., Demir, U.L., Kaya, F.N. et al. The effects of levobupivacaine infiltration on post-tonsillectomy pain relief in adults: a single-blinded, randomized, and controlled clinical study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 761–766 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2194-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2194-1