Abstract
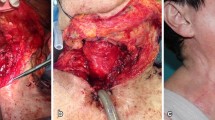
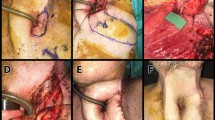
This paper presents our surgical technique and the results of using bipedicled superior chest flaps for head and neck reconstructions. The study design consisted of a case series of surgical technique. The study was conducted at tertiary referral centers with otorhinolaryngology-head and neck surgery departments. In seven patients, we used bipedicled superior chest flaps for reconstruction of anterior cutaneous neck defects due to surgery for the recurrence of laryngopharyngeal carcinoma. The largest flap size was 45 × 14 cm. All donor sites were closed primarily with advancement in the lateral part and split thickness skin grafts in the superior midline of chest. The highest point of reconstruction was in the hypopharynx internally and hyoid externally. All flaps survived without major complications. A bipedicled upper chest flap can reliably cover the skin defects that create following salvage total laryngectomies in patients with advanced stage tumors with skin involvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummings. Otolaryngology, head and neck surgery, 5th edn. Mosby Elsevier, pp 1482–1512
Patel UA, Keni SP (2009) Pectoralis myofascial flap during salvage laryngectomy prevents pharyngocutaneous fistula. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141(2):190–195
Ganly I, Patel S, Matsuo J et al (2005) Postoperative complications of salvage total laryngectomy. Cancer 103:2073–2081
Grau C, Johansen LV, Hansen HS et al (2003) Salvage laryngectomy and pharyngocutaneous fistulae after primary radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: a national survey from DAHANCA. Head Neck 25:711–716
Withrow KP, Rosenthal EL, Gourin CG et al (2007) Free tissue transfer to manage salvage laryngectomy defects after organ preservation failure. Laryngoscope 117:781–784
Cavalot AL, Gervasio CF, Nazionale G et al (2000) Pharyngocutaneous fistula as a complication of total laryngectomy: review of the literature and analysis of case records. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:587–592
Saki N, Nikakhlagh S, Kazemi M (2008) Pharyngocutaneous fistula after laryngectomy: incidence, predisposing factors, and outcome. Arch Iran Med 11(3):314–317
Antohi N, Tibirna G, Suharski I (1993) Microvascular free tissue reconstruction after total laryngectomy. Eur J Plast Surg 16(4–5):198–203
Ugurlu K, Karsidag T, Akcal A, Karsidag S, Yazar M, Seven H (2011) Bare serratus anterior free flap in the reconstruction of the partial pharyngoesophageal defect. J Craniofac Surg 22:1010–1012
Bogdasarian JR, Healy GB, Di Troia J, Shapshay SM, Strong MS (1981) A sliding chest wall flap for the management of advanced laryngeal carcinoma with anterior cervical skin invasion. Laryngoscope 91(4):644–648
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghibzadeh, M., Bakhshaee, M., Irani, S. et al. Bipedicles chest flap: a novel technique for the reconstruction of anterior neck defect. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 1427–1431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2135-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2135-z