Abstract
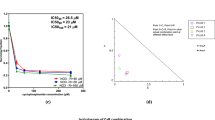
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of all-trans retinoid acid (ATRA) on two nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) cell lines and to evaluate the synergistic effect of ATRA used in combination with cisplatin, a standard chemotherapeutic agent for NPC. Two NPC cell lines (NPC-TW01 and NPC-TW04) were used, and the MTT assay was used to analyze cell growth inhibition under various concentrations of ATRA and cisplatin. Under low concentrations of ATRA, the growth of both cell lines was significantly inhibited. When ATRA was used in combination with cisplatin, the resulting synergistic effects were robust and significant. Only a low concentration of ATRA was required to produce a synergistic effect when combined with cisplatin, indicating the potential usefulness of a combination therapy regimen. Therefore, the combination of ATRA and cisplatin is a viable treatment option for NPC and should be further investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown WGS (2008) Scott-Brown’s otolaryngology, vol 2, 7th edn. Oxford University Press, USA
Horrison LB, Sessions RB, Hong WK (2008) Head and neck cancer: a multidisciplinary approach, vol 1, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadephia
Taiwan Cooperative Oncology Group (2000) Consensus for Nasopharyngeal cancer diagnosis and treatment. National Health Research Institutes. http://www.nhri.org.tw (in Chinese)
Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS (eds) (1994) The synthetic chemistry of retinoids. In: the retinoids: biology, chemistry, and medicine, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York
Adamson PC (1996) All-trans retinoic acid pharmacology and its impact on the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncologist 1(5):305–314
Miller WH Jr (1998) The emerging role of retinoids and retinoic acid metabolism blocking agents in the treatment of cancer. Cancer 83(8):1471–1482. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19981015)83:8<1471:AID-CNCR1>3.0.CO;2-6
Breitman TR, Selonick SE, Collins SJ (1980) Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77(5):2936–2940
Dimberg A, Oberg F (2003) Retinoic acid-induced cell cycle arrest of human myeloid cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma 44(10):1641–1650
Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, Chai JR, Lu JX, Zhoa L, Gu LJ, Wang ZY (1988) Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 72(2):567–572
Yang J, Han Z, Pei M, Xiao N (1999) Fatal side-effects of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 24(3):293–295
Dimberg A, Bahram F, Karlberg I, Larsson LG, Nilsson K, Oberg F (2002) Retinoic acid-induced cell cycle arrest of human myeloid cell lines is associated with sequential down-regulation of c-Myc and cyclin E and posttranscriptional up-regulation of p27(Kip1). Blood 99(6):2199–2206
Stordal B, Davey M (2007) Understanding cisplatin resistance using cellular models. IUBMB Life 59(11):696–699. doi:10.1080/15216540701636287
Trzaska S (2005) CISPLATIN. Chem Eng News 83(25):52. doi:10.1021/cen-v083n025.p052
Aebi S, Kroning R, Cenni B, Sharma A, Fink D, Los G, Weisman R, Howell SB, Christen RD (1997) All-trans retinoic acid enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian adenocarcinoma and in squamous head and neck cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 3(11):2033–2038
Masuda M, Toh S, Koike K, Kuratomi Y, Suzui M, Deguchi A, Komiyama S, Weinstein IB (2002) The roles of JNK1 and Stat3 in the response of head and neck cancer cell lines to combined treatment with all-trans retinoic acid and 5-fluorouracil. Jpn J Cancer Res 93(3):329–339
Satake K, Takagi E, Ishii A, Kato Y, Imagawa Y, Kimura Y, Tsukuda M (2003) Anti-tumor effect of vitamin A and D on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 30(4):403–412 [pii:S0385814603000919]
Scribner DR Jr, Benbrook DM (2002) Retinoids enhance cisplatin-based chemoradiation in cervical cancer cells in vitro. Gynecol Oncol 85(1):223–225. doi:10.1006/gyno.2002.6590
Shalinsky DR, Bischoff ED, Gregory ML, Lamph WW, Heyman RA, Hayes JS, Thomazy V, Davies PJ (1996) Enhanced antitumor efficacy of cisplatin in combination with ALRT1057 (9-cis retinoic acid) in human oral squamous carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 2(3):511–520
Shin DM, Glisson BS, Khuri FR, Clifford JL, Clayman G, Benner SE, Forastiere AA, Ginsberg L, Liu D, Lee JJ, Myers J, Goepfert H, Lotan R, Hong WK, Lippman SM (2002) Phase II and biologic study of interferon alfa, retinoic acid, and cisplatin in advanced squamous skin cancer. J Clin Oncol 20(2):364–370
Jiang N, Zhan F, Cao L, Yao K, Li G (2000) c-myc gene inactivation during induction of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with retinoic acid. Chin Med J (Engl) 113(9):823–826
Lin CT, Chan WY, Chen W, Huang HM, Wu HC, Hsu MM, Chuang SM, Wang CC (1993) Characterization of seven newly established nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest 68(6):716–727
Lin CT, Wong CI, Chan WY, Tzung KW, Ho JK, Hsu MM, Chuang SM (1990) Establishment and characterization of two nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Lab Invest 62(6):713–724
Saadeddin A, Torres-Molina F, Carcel-Trullols J, Araico A, Peris JE (2004) Pharmacokinetics of the time-dependent elimination of all-trans retinoic acid in rats. AAPS PharmSci 6(1):E1. doi:10.1208/ps060101
van Vliet T, Boelsma E, de Vries AJ, van den Berg H (2001) Retinoic acid metabolites in plasma are higher after intake of liver paste compared with a vitamin A supplement in women. J Nutr 131(12):3197–3203
Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE, Ensley JF (1998) Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: phase III randomized intergroup study 0099. J Clin Oncol 16(4):1310–1317
al-Sarraf M, Pajak TF, Cooper JS, Mohiuddin M, Herskovic A, Ager PJ (1990) Chemo-radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a radiation therapy oncology group study. J Clin Oncol 8(8):1342–1351
Belka C, Jendrossek V, Pruschy M, Vink S, Verheij M, Budach W (2004) Apoptosis-modulating agents in combination with radiotherapy-current status and outlook. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(2):542–554
Ma BB, Bristow RG, Kim J, Siu LL (2003) Combined-modality treatment of solid tumors using radiotherapy and molecular targeted agents. J Clin Oncol 21(14):2760–2776. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.10.044
Begg AC, Stewart FA, Vens C (2011) Strategies to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 11(4):239–253. doi:10.1038/nrc3007
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Cathay General Hospital Research Fund (CMRI-9605). No other financial disclosures are related to this study.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, SH., Lee, FP., Su, CH. et al. Effect of all-trans retinoic acid on the growth of two nasopharyngeal cancer cell lines and its treatment potential in combination with cisplatin. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 695–704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2068-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2068-6