Abstract
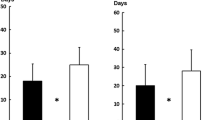
The objectives of this study are to elucidate the oncologic validity of the supracricoid laryngectomy (SCL) for locally advanced endolaryngeal cancers and as a salvage procedure, and to determine its safety in maintaining laryngeal physiology. The medical records of 114 patients that underwent SCL were reviewed. We examined whether the extended procedures, salvage procedure, adjuvant treatment, and type of reconstruction were associated with patient survival and the mean time of decannulation and nasogastric tube removal. Postoperative complications were investigated. There was no significant difference in survival according to the extent of the resection of the primary tumors and the presence or absence of previous treatment. However, the survival of patients that received radiation or concurrent chemoradiation after SCL was significantly lower than that of patients without any adjuvant treatment. Decannulation and nasogastric tube removal was possible for all except for two patients, and the mean time required was 18.4 and 26.1 days, respectively. The interval to starting oral feeding was significantly increased in cases that underwent cricohyoidopexy, an extended procedure, and salvage surgery compared to their counterparts. Pulmonary complications, particularly aspiration pneumonia, were the most common postoperative complications. The results of this study suggest that SCL was feasible for locally advanced laryngeal cancers and as a salvage procedure. Active and effective postoperative swallowing rehabilitation, particularly in cases that underwent cricohyoidopexy, an extended procedure, and salvage surgery, is needed to prevent aspiration pneumonia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G, Menard M, Brasnu D (1990) Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy: a partial laryngeal procedure for glottic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 99(6 pt 1):421–426
Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G, Menard M, Brasnu D (1990) Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidopexy: a partial laryngeal procedure for selected supraglottic and transglottic carcinomas. Laryngoscope 100(7):735–741
Deganello A, Gallo O, De Cesare JM et al (2008) Supracricoid partial laryngectomy as salvage surgery for radiation therapy failure. Head Neck 30(8):1064–1071
Soudry E, Marmor Y, Hazan A, Marx S, Sadov R, Feinmesser R (2008) Supracricoid partial laryngectomy: an alternative to total laryngectomy for locally advanced laryngeal cancers. J Laryng Otol 122(11):1219–1223
Rizzotto G, Succo G, Lucioni M, Pazzaia T (2006) Subtotal laryngectomy with tracheohyoidopexy: a possible alternative to total laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 116(10):1907–1917
Rifai M (2007) Extended supracricoid laryngectomy with excision of both arytenoids: the modified reconstructive laryngectomy. Acta Otolaryngol 127(6):642–650
Holsinger FC, Weinstein GS, Laccourreye O (2005) Supracricoid partial laryngectomy: an organ-preservation surgery for laryngeal malignancy. Curr Probl Cancer 29(4):190–200
Lewin JS, Hutcheson KA, Barringer DA et al (2008) Functional analysis of swallowing outcomes after supracricoid partial laryngectomy. Head Neck 30(5):559–566
Lima RA, Freitas EQ, Dias FL et al (2006) Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy for advanced glottic cancer. Head Neck 28(6):481–486
Nakayama M, Okamoto M, Miyamoto S et al (2008) Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglotto-pexy or cricohyoido-pexy: experience on 32 patients. Auris Nasus Larynx 35(1):77–82
Sparano A, Chernock R, Feldman M, Laccourreye O, Brasnu D, Weinstein G (2005) Extending the inferior limits of supracricoid partial laryngectomy: a clinicopathological correlation. Laryngoscope 115(2):297–300
Ganly I, Patel SG, Matsuo J et al (2006) Results of surgical salvage after failure of definitive radiation therapy for early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the glottic larynx. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132(1):59–66
Suoglu Y, Guven M, Kiyak E, Enoz M (2008) Significance of pre-epiglottic space invasion in supracricoid partial laryngectomy with cricohyoidopexy. J Laryngol Otol 122(6):623–627
Hinerman RW, Morris CG, Amdur RJ et al (2006) Surgery and postoperative radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and pharynx. Am J Clin Oncol 29(6):613–621
Marioni G, Marchese-Ragona R, Ottaviano G, Staffieri A (2004) Supracricoid laryngectomy: is it time to define guidelines to evaluate functional results? a review. Am J Otolaryngol 25(2):98–104
Gallo O, Deganello A, Gitti G et al (2009) Prognostic role of pneumonia in supracricoid and supraglottic laryngectomies. Oral Oncol 45(1):30–38
Woisard V, Puech M, Yardeni E, Serrano E, Pessey JJ (1996) Deglutition after supracricoid laryngectomy: compensatory mechanisms and sequelae. Dysphagia 11(4):265–269
Naudo P, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G, Jouffre V, Laccourreye H, Brasnu D (1998) Complications and functional outcome after supracricoid partial laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118(1):124–129
Laccourreye O, Ross J, Brasnu D, Chabardes E, Kelly JH, Laccourreye H (1994) Extended supracricoid partial laryngectomy with tracheocricohyoidoepiglottopexy. Acta Otolaryngol 114(6):669–674
Ganly I, Patel SG, Matsuo J et al (2009) Analysis of postoperative complications of open partial laryngectomy. Head Neck 31(3):338–345
Logemann JA (1997) Role of the modified barium swallow in management of patients with dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116(3):335–338
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, K.J., Joo, Y.H., Sun, D.I. et al. Supracricoid laryngectomy: oncologic validity and functional safety. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267, 1919–1925 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1279-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1279-y