Abstract
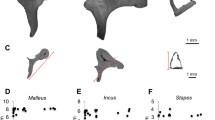
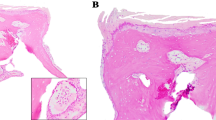
The aim of this study was to define the existence of surface changes on auditory ossicles caused by rheumatoid arthritis. The study comprised of nine pairs of auditory ossicles (mallei and incudes) from autopsy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and five pairs of ossicles from persons without RA, taken during autopsies. The specimens were studied with JEOL JSM 5300 type scanning electron microscope. Surface changes of auditory ossicles were defined, affected areas were calculated, and expressed in percentage of total surface. Changes in auditory ossicles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are significantly higher than in control ossicles, both on ossicular surface and articulations. Increased lysis of incudes, especially in the region of long propagation, corresponds to vascular damage. Articular degeneration is also present, indicating specific rheumatoid alteration. Both changes are statistically more intense in cases with longer duration of disease. In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis reduces vascularity of auditory ossicles and causes degeneration of articular surfaces.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murdin L, Patel S, Walmsley J et al (2008) Hearing difficulties are common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 27:637–640
Ozcan M, Karakuş MF, Gündüz OH et al (2002) Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 22:16–19
Colletti V, Fiorino FG, Bruni L et al (1997) Middle ear mechanics in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Audiology 3:136–146
Frade C, Martin C (1998) Diagnostic value of the multifrequency tympanometry in active rheumatoid arthritis. Auris Nasus Larynx 25:131–136
Huttenbrink KB (1987) Scanning electron microscopy changes in the malleus incus joint and reflections on the function of the middle ear muscles. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 4:180–185 (Stuttg)
Chen H, Okumura T, Emura S et al (2008) Scanning electron microscopic study of the human auditory ossicles. Ann Anat 190:53–58
Hotz MA, Speirs AD, Oxland T et al (1999) Radiologic and mechanical properties of inactivated ossicle homografts. Laryngoscope 109:65–69
Uno Y, Saito R (1995) Bone resorption in human cholesteatoma: morphological study with scanning electron microscopy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104:463–468
Halligan CS, Bauch CD, Brey RH et al (2006) Hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Laryngoscope 116:2044–2049
García Callejo FJ, Conill Tobías N, Muñoz Fernández N et al (2007) Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 58:232–238
Oztürk A, Yalçin S, Kaygusuz I et al (2004) High-frequency hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Otolaryngol 25:411–417
Raut VV, Cullen J, Cathers G (2001) Hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. J Otolaryngol 5:289–294
Takatsu M, Higaki M, Kinoshita H et al (2005) Ear involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Otol Neurotol 26:755–761
Reiter D, Konkle DF, Myers AR et al (1980) Middle ear immittance in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Otolaryngol 106:114–117
Ikiz AO, Unsal E, Kirkim G et al (2007) Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:1079–1085
Bayazit YA, Yilmaz M, Gunduz B et al (2007) Distortion product otoacoustic emission findings in Behçet’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 69:233–238
Biasi D, Fiorino F, Carletto A et al (1996) Middle ear function in rheumatoid arthritis: a multiple frequency tympanometric study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 14:243–247
Muszyński P, Składzień J, Reroń E et al (2007) Transient evoked otacoustic emission in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Otolaryngol Pol 61:972–978
Colletti V, Fiorino FG, Bruni L et al (1997) Middle ear mechanics in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Audiology 36:136–146
Siamanpoulou-Mavridou A, Asimakopoulos D, Mavridis A et al (1990) Middle ear function in patients with juvenile chronic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 49:620–623
Giannini P, Marciano E, Saulino C et al (1997) Middle ear involvement in children with chronic rheumatoid juvenile arthritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254:S30–S33
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milisavljevic, D., Stankovic, M., Zivic, M. et al. Changes in auditory ossicles in rheumatoid arthritis: scanning electron microscopic study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267, 363–366 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1072-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1072-y