Abstract
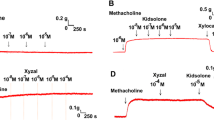
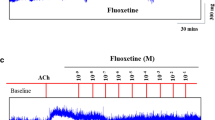
Cetirizine (Zytec) is often used as a histamine receptor-1 (H1) antagonist in rhinitis patients who are suffering from sneezing and rhinorrhea. This H1 antagonist is used as an oral tablet or nasal spray solution. The effect of H1 antagonist on nasal mucosa in vivo is well known; however, the effect of the drug on tracheal smooth muscle has been rarely explored. Therefore, during administration of the H1 antagonist for nasal symptoms, it might also affect the trachea via oral intake or inhalation. We used our preparation to test the effectiveness of Zytec on isolated rat’s tracheal smooth muscle. The following assessments of Zytec were performed: (1) effect on tracheal smooth muscle resting tension; (2) effect on contraction caused by 5 × 10−6 M methacholine as a parasympathetic mimetic; (3) effect of the drug on electrically induced tracheal smooth muscle contractions. Results indicated that addition of a parasympathetic mimetic to the incubation medium caused the trachea to contract in a dose-dependent manner. Addition of Zytec at doses of 10−5 M or above elicited a relaxation response to 5 × 10−6 M methacholine-induced contraction. Zytec could inhibit electrical field stimulation induced spike contraction, and basal tension was increased at the same time. However, it alone had a minimal effect on the basal tension of trachea as the concentration increased. This study indicated that high concentrations of Zytec might actually inhibit parasympathetic function of the trachea.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beny J, Pacicca C (1994) Bidirectional electrical communication between smooth muscle and endothelial cells in the pig coronary artery. Am J Physiol 266:H1465–H1472
Ichimura K, Jackson RT (1983) Calcium, calcium blockers, and nasal smooth muscle. Arch Otolaryngol 109:593–597
Bratton DL, Tanaka DT, Grunstein MM (1987) Effects of temperature on cholinergic contractility of rabbit airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol 63:1933–1941
Gonzalez O, Santacana GE (2001) Effect of low temperature on tracheal smooth muscle contractile and relaxing responses evoked by electrical field stimulation. P R Health Sci J 20:237–243
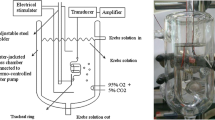
Wang H-W, Wang Y-T, Wu C-C (2007) A modified in vitro study of tracheal smooth muscle response to drugs. J Med Sci 27:203–206
Bousquet J, Godard P, Michel FB (1992) Antihistamines in the treatment of asthma. Eur Respir J 5:1137–1142
Holgate ST, Finnerty JP (1989) Antihistamines in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 83:537–547
Howarth PH (1990) Histamine and asthma: an appraisal based on specific H1-receptor antagonism. Clin Exp Allergy 20(suppl 2):31–41
Meltzer EO (1995) The use of anti-H1 drugs in mild asthma. Allergy 50:41–47
Grant JA, Nicodemus CF, Findlay SR et al (1995) Cetirzine in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis and concomitant asthma: prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 95:923–932
Simons FER, Simons KJ (1994) The pharmacology and use of H1-receptor-antagonist drugs. New Engl J Med 330:1663–1670
Yau KI, Ko FN, Chien CH (1999) Effects of prokinetic agents on contractile responses to electrical field stimulation of isolated guinea pig trachea. J Formos Med Assoc 98:567–572
Yau KI, Hwang TL (2002) The nonadrenergic noncholinergic system can modulate the effect of prokinetic agents on contractile response of isolated guinea pig trachea segments to electrical field stimulation. J Formos Med Assoc 101:695–699
Rimmer SJ, Church MK (1990) The pharmacology and mechanisms of action of histamine H1-antagonists. Clin Exp Allergy 20(Suppl 2):3–17
Wang H-W, Jackson RT (1988) Do cholinergic neurons directly innervate nasal blood vessels? Rhinology 26:139–146
White MV (1990) The role of histamine in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 86:599–605
Simons FER, Murray HE, Yi Z, Simons KJ (1994) Cetirizine and hydroxyzine concentrations in human skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol 93:222 abstract
Malick A, Grant JA (1997) Antihistamines in the treatment of asthma. Allergy 52:55–66
Rafferty P, Holgate ST (1989) Histamine and its antagonists in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 84:144–151
Rafferty P, Holgate ST (1987) Terfenadine (Seldane) is a potent and selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist in asthmatic airways. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:181–184
Town GI, Holgate ST (1990) Comparison of the effect of loratadine on the airway and skin responses to histamine, methacholine, and allergen in subjects with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 86:886–893
Brik A, Tashkin DP, Gong H Jr, Dauphinee B, Lee E (1987) Effect of cetirizine, a new histamine H1 antagonist, on airway dynamics and responsiveness to inhaled histamine in mild asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 80:51–56
Larsen JS (2001) Do antihistamines have a role in asthma therapy? Pharmacotherapy 21:28S–33S
Dijkman JH, Hekking PRM, Molkenboer JF et al (1990) Prophylactic treatment of grass pollen-induced asthma with cetirizine. Clin Exp Allergy 20:483–490
Rafferty P, Jackson L, Smith R, Holgate ST (1990) Terfenadine, a potent histamine H1-receptor antagonist in the treatment of grass pollen sensitive asthma. Br J Clin Pharmacol 30:229–235
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Tri-Service General Hospital (TSGH-C96-27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kao, CH., Chu, YH. & Wang, HW. Effects of cetirizine on isolated rat’s tracheal smooth muscle. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266, 753–757 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0838-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0838-y