Abstract
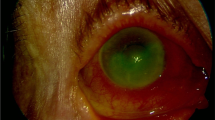
We present two case reports of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (triad of fever, stomatitis and conjunctivitis) due to klavox (amoxicillin + clavulanic acid) which has been reported in few publications as etiology but it is not commonly seen. We conclude that klavox can precipitate development of SJS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stevens AM, Johnson FC (1922) A new eruptive fever associated with stomatitis and ophthalmia. Am J Dis Child 24:526–533
Safai B, Good RA, Day NK (1977) Erythema multiforme: report of 2 cases and speculation on immune mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 7:379–385
Huff JC, Weston WL, Tonnesan MG (1983) Erythema multiforme: a critical review of characteristics, diagnostics criteria and causes. J Am Acad Dermatol 8:763–775
French LE (2006) Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens–Johnson syndrome: our current understanding. Allergol Int 55(1):9–16
Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC (1993) Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrosis, Stevens–Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol 129:92–96
Yativ JZ, Bianchine JR, Owen JA (1980) Etiologic factors of the Stevens–Johnson syndrome. South Med J 73:599–602
Gaultier F, Ejeil A, Igondjo-Tchen S, Dohan D, Dridi SM, Maman L, Wierzba CB, Stania D, Pellat B, Lafont A, Godeau G, Gogly B (2004) Possible involvement of gelatinase A (MMP2) and gelatinase B (MMP9) in toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Arch Dermatol Res 296:220–225
Mockenhaupt M, Messenheimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J (2005) Risk of Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics. Neurology 64(7):1134–1138
Parrillo SJ (2007) Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 7(4):243–247
Chen K-T, Twu S-J, Chang H-J, Lin R-S (2003) Outbreak of Stevens–Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with mebendazole and metronidazole use among Filipino laborers in Taiwan. Am J Public Health 93:489–492
Clayton NA, Kennedy PJ (2007) Management of dysphagia in toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS). Dysphagia 22:187–192
Zipitis CS, Thalange N (2007) Intravenous immunoglobulins for the management of Stevens–Johnson syndrome with minimal skin manifestations. Eur J Pediatr 166:585–588
Kakourou T, Klontza D, Soteropoulou F, Kattamis C (1997) Corticosteroid treatment of erythema multiforme major (Stevens–Johnson syndrome) in children. Eur J Pediatr 156:90–93
Limauro DL, Chan-Tompkins NH, Carter RW, Brodmerkel GJ, Agrawal RM (1999) Amoxicillin/clavulanate-associated hepatic failure with progression to Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Ann Pharmacother 33:560–564
Salvo F, Polimeni G, Moretti U, Conforti A, Leone R, Leoni O, Motola D, Dusi G, Caputi AP (2007) Adverse drug reactions related to amoxicillin alone and in association with clavulanic acid: data from spontaneous reporting in Italy. J Antimicrob Chemother 60:121–126
Conflict of interest statement
The author states no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou-Elhamd, KE.A. Two cases of Stevens–Johnson syndrome following intake of klavox with review of literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266, 1327–1330 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0785-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0785-7