Abstract
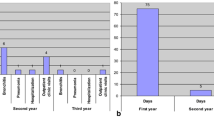
CS gas (o-chlorobenzylidenemalononitrile) is one of the most commonly used riot agents. It can create excessive tearing, conjunctivitis, uncontrolled blinking (blepharospasm) and a sensation of burning and pain at initial exposure. Pulmonary edema (ARDS) and/or diffuse airway lesions on human would be lethal after CS inhalation. We report a case with acute laryngeal and bronchial obstruction due to vocal cord edema and extensive crusting at glottic level, trachea and bronchi. The CS gas was sprayed in a 6 × 6 m2 closed room, and she was exposed to increased concentration of the gas for 10 s. Surprisingly, her initial symptoms were raised 21 days after CS spray exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salem H, Olajos EJ, Katz SA (2001) Riot-control agents. In: Somani SM, Romano JA Jr (eds) Chemical warfare agents: toxicity at low levels. CRC Press LLC, Danvers, pp 321–372
Hill AR, Silverberg NB, Mayorga D et al (2000) Medical hazards of the tear gas CS: a case persistent, multisystem, hypersensitivity reaction and review of the literature. Medicine 79:234–240
Anderson PJ, Lau GSN, Taylor WRJ et al (1996) Acute effects of the potent lacrimator o-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile (CS) tear gas. Hum Exp Toxicol 15:461–465
National Poisons Information Service (London), March 1996 [News Sheet]
Karagama YG, Newton JR, Newbegin CJR (2003) Short-term and long-term physical effects of exposure to CS spray. J R Soc Med 96:172–174
Bothe M, Ronzitti N, Rosas A (eds) (1998) The new chemical weapons convention—implementation and prospects. Kluwer Law International, The Hague, p 17
Cotes JE, Dabbs JM, Evans MR et al (1972) Effect of CS aerosol upon lung gas transfer and alveolar volume in healthy men. Q J Exp Physiol 57:199–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karaman, E., Erturan, S., Duman, C. et al. Acute laryngeal and bronchial obstruction after CS (o-chlorobenzylidenemalononitrile) gas inhalation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266, 301–304 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0653-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0653-5