Abstract
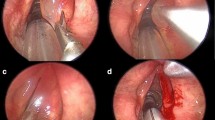
The purpose of this study was to present our experience with combined use of CO2 laser and cold instrumentation for Reinke’s edema surgery and to evaluate 1-year follow-up results of the technique in a series of professional voice users. Fifteen patients with Reinke’s edema who underwent microlaryngoscopic surgery were included. Videolaryngostroboscopy, perceptual and acoustic voice analyses were performed before and after surgery. During the 1-year follow-up, no recurrence of Reinke’s edema was encountered. Significant postoperative improvement was obtained in the quality of voice, in terms of GRBAS scores, Fo, jitter, shimmer and NHR. No evidence of laryngeal cancer was found on the histological examinations. Combined use of CO2 laser and cold instrumentation provides a reliable and safe method for Reinke’s edema surgery, and cessation of smoking, voice rest and control of the laryngopharyngeal reflux contribute to the success of surgery. We consider that the removal of redundant mucosa of the vocal fold reduces the risk of the recurrence of Reinke’s edema and provides better quality of voice. However, it does not imply that our method is superior to others’, but this procedure constitutes an effective treatment of choice for Reinke’s edema patients, including professional voice users.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett S, Bishop SG, Lumpkin S (1989) Phonatory characteristics following surgical treatment of severe polypoid degeneration. Laryngoscope 99:525–532
Hirano M (1981) Clinical examination of voice. Springer, Vienna
Hirano M (1975) Phonosurgery: basic and clinical investigations. Otologia (Fukuoka) 21:239–442
Hirano M, Shin T, Morio M et al (1976) An improvement in surgical treatment for polypoid vocal cord- sucking technique. Otologia (Fukuoka) 22:583–589
Hojslet PE, Moesgard-Nielsen V, Karlmose M (1990) Smoking cessation in chronic reinke’s oedema. J Laryngol Otol 104:626–628
Lumpkin SMM, Bennett S, Bishop SG (1990) Postsurgical follow-up study of patients with severe polypoid degeneration. Laryngoscope 100:399–402
Moesgaard Nielsen V, Hojslet PE, Karlmose M (1986) Surgical treatment of Reinke’s oedema. J Laryngol Otol 100:187–190
Moesgaard-Nielsen V, Hojslet PE, Palvio D (1986) Reinke’s oedema: a premalignant condition. J Laryngol Otol 100:1159–1162
Moesgard Nielsen V, Hojslet PE (1987) Topical treatment of Reinke’s oedema with beclomethasone dipropionate (BDP) inhalation aerosol. J Laryngol Otol 101:921–924
Remacle M, Lawson G, Watelet JB (1999) Carbon dioxide laser microsurgery of benign vocal fold lesions: indications, techniques, and results in 251 patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:156–64
Sant’Anna G, Mauri M (2000) Use of microdebrider for Reinke’s edema surgery. Laryngoscope 110:2114–2116
Sato K, Hirano M, Nakashima T (1999) Electron microscopic and immunohistochemical investigation of Reinke’s edema. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:1068–1072
Thibeault SL (2005) Advances in our understanding of the Reinke space. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:148–151
Zeitels SM, Hillman RE, Bunting GW et al (1997) Reinke’s edema: phonatory mechanisms and management strategies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 106:533–543
Zeitels SM (1995) Premalignant epithelium and microinvasive cancer of the vocal fold: the evolution of phonomicrosurgical management. Laryngoscope 105:1–51
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kenan Kose, PhD, for his assistance in the statistical assessment of acoustic results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dursun, G., Ozgursoy, O.B., Kemal, O. et al. One-year follow-up results of combined use of CO2 laser and cold instrumentation for Reinke’s edema surgery in professional voice users. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264, 1027–1032 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0309-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0309-x